算法学习(八)递归和回溯法
这样的算法思想通常都应用在树形问题上
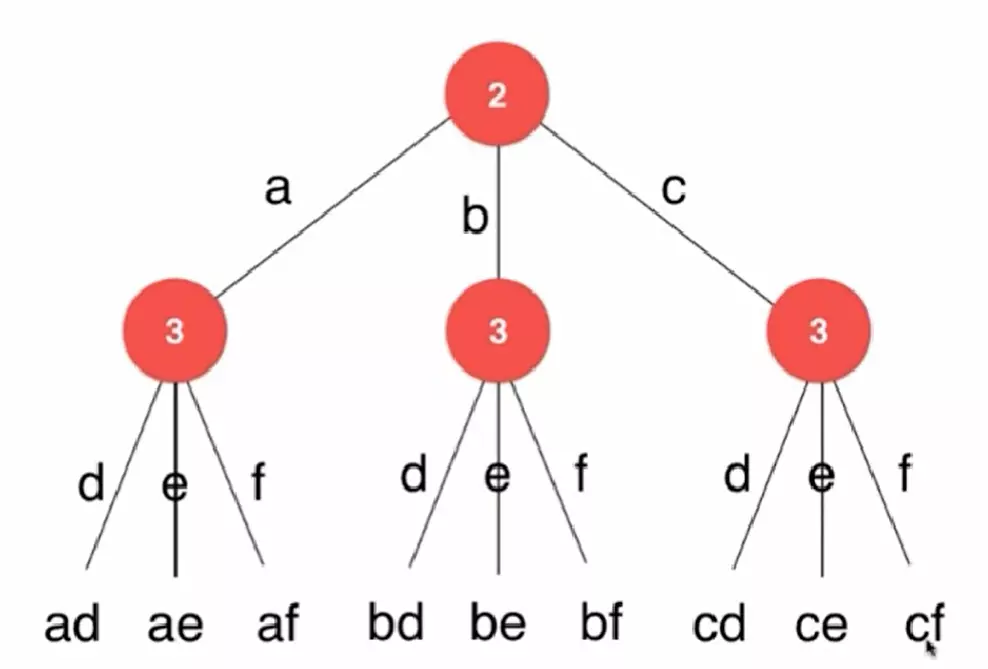
leetcode17. 电话号码的字母组合
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
输入:"23"
输出:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
转换为树
回溯算法,复杂度O(2^n)
class Solution {
private String letterMap[] = {
" ", //0
"", //1
"abc", //2
"def", //3
"ghi", //4
"jkl", //5
"mno", //6
"pqrs", //7
"tuv", //8
"wxyz" //9
};
private ArrayList res = new ArrayList<>();
public List letterCombinations(String digits) {
res.clear();
if (digits.isEmpty()) {
return res;
}
findCombination(digits, 0, "");
return res;
}
//s中保存了此时从digits[0...index-1]翻译得到的一个字母字符串
//寻找gidits[index]匹配的字母,获得digits[0...index]翻译得到的解
private void findCombination(String digits, int index, String s) {
if(index == digits.length()){
res.add(s);
return;
}
Character c = digits.charAt(index);
String letters = letterMap[c - '0'];
for(int i = 0 ; i < letters.length() ; i ++){
findCombination(digits, index+1, s + letters.charAt(i));
}
return;
}
}
相关问题,93,131
2、回溯算法的应用
排列问题
leetcode46. 全排列
给定一个没有重复数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
输入: [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
image.png
Perms(nums[0...n-1])={取出一个数字}+Perms(nums{0...n-1}-这个数字]}
class Solution {
private List> res = new ArrayList<>();
private boolean[] used;
public List> permute(int[] nums) {
res.clear();
if (nums.length == 0) {
return res;
}
used = new boolean[nums.length];
LinkedList p = new LinkedList<>();
generatePermutation(0, nums, p);
return res;
}
//p中保存了一个有index个元素的排列
//向这个排列的末尾添加低index+1,获得一个有index+1个元素的排列
private void generatePermutation(int index, int[] nums, LinkedList p) {
if (index == nums.length) {
res.add((List)p.clone());
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (!used[i]) {
p.addLast(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
generatePermutation(index + 1, nums, p);
p.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
return;
}
}
相关问题,47
组合问题
leetcode77. 组合
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 ... n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
输入: n = 4, k = 2
输出:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
class Solution {
LinkedList> res = new LinkedList();
public List> combine(int n, int k) {
res.clear();
if (n <= 0 || k <= 0 || k > n) {
return res;
}
LinkedList c = new LinkedList<>();
findCombination(n, k, 1, c);
return res;
}
//求解C(n,k),当前已经找到的组合存储在c中,需要从start开始搜索新元素
private void findCombination(int n, int k, int start, LinkedList c) {
if (c.size() == k) {
res.addLast((List) c.clone());
return;
}
//还有k-c.size()个空位,所以,[i...n]中至少要有k-c.size()个元素
//i最多为n-(k-c.size())+1
for (int i = start; i <= n-(k-c.size())+1; i++) {
c.addLast(i);
findCombination(n, k, i + 1, c);
c.removeLast();
}
return;
}
}
相关问题39,40,216,78,90,401
3、二维平面上使用回溯法
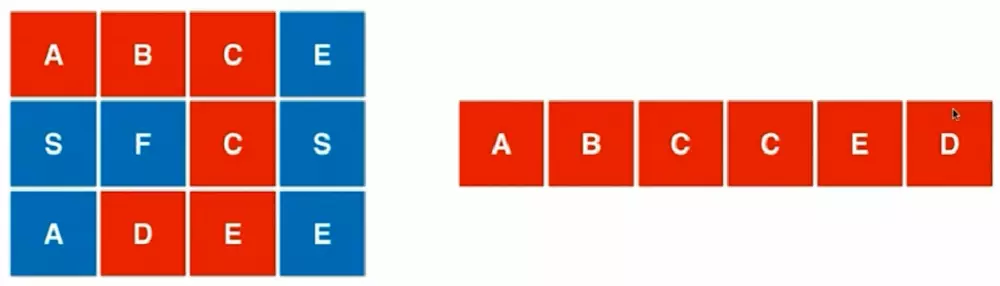
leetcode79. 单词搜索
给定一个二维网格和一个单词,找出该单词是否存在于网格中。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
board =
[
['A','B','C','E'],
['S','F','C','S'],
['A','D','E','E']
]
给定 word = "ABCCED", 返回 true.
给定 word = "SEE", 返回 true.
给定 word = "ABCB", 返回 false.
class Solution {
// x-1,y
// x,y-1 x,y x,y+1
// x+1,y
private int[][] d = { { -1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// 盘面上有多少行
private int m;
// 盘面上有多少列
private int n;
private boolean[][] visited;//被访问过
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
m = board.length;
if (m == 0) {
return false;
}
n = board[0].length;
visited=new boolean[m][n];
char[] wordChar=word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[i].length; j++) {
if (searchWord(board, wordChar, 0, i, j)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//从board的[startx][starty]开始,寻找word[index...word.length]
private boolean searchWord(char[][] board, char[] word, int index, int startx, int starty) {
if (index == word.length - 1) {
return board[startx][starty] == word[index];
}
if (board[startx][starty] == word[index]) {
visited[startx][starty] = true;
//从startx,starty出发,向四个方向寻找
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newx = startx + d[i][0];
int newy = starty + d[i][1];
if (inArea(newx, newy) && !visited[newx][newy]) {
if (searchWord(board, word, index + 1, newx, newy)) {
return true;
}
}
}
visited[startx][starty] = false;//回溯
}
return false;
}
private boolean inArea(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
}
floodfill算法,一类经典问题
这个算法的本质是深度优先遍历
leetcode200. 岛屿数量
给定一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,计算岛屿的数量。一个岛被水包围,并且它是通过水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成的。你可以假设网格的四个边均被水包围。
输入:
11110
11010
11000
00000
输出: 1
class Solution {
private int[][] d = { { -1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
int m, n;
private boolean[][] visited;//被访问过
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
m = grid.length;
if (m == 0) {
return 0;
}
n = grid[0].length;
visited = new boolean[m][n];
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
//没有被标记过的陆地
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j]) {
res++;
visited[i][j] = true;//将陆地标记
dfs(grid, i, j);//从这个陆地开始找,和他相连的陆地都标记上
}
}
}
return res;
}
//从gird[x][y]的位置开始,进行floodfill
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int x, int y) {
visited[x][y]=true;//将陆地标记
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newx = x + d[i][0];
int newy = y + d[i][1];
//保证(x,y)合法,且grid[x][y]是没有被访问过的陆地,这个也是递归终止条件
if (inArea(newx, newy) && !visited[newx][newy] && grid[newx][newy] == '1') {
dfs(grid, newx, newy);
}
}
return;
}
private boolean inArea(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
}
相关问题,130,417
4、回溯法是经典人工智能的基础
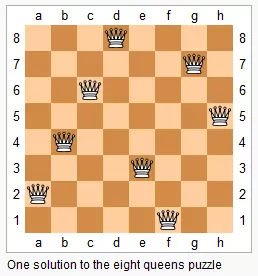
leetcode51. N皇后
n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。(即任意两个皇后都不能处于同一行、同一列或同一斜线上)
给定一个整数 n,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个明确的 n 皇后问题的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位
输入: 4
输出: [
[".Q..", // 解法 1
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."],
["..Q.", // 解法 2
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."]
]
解释: 4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
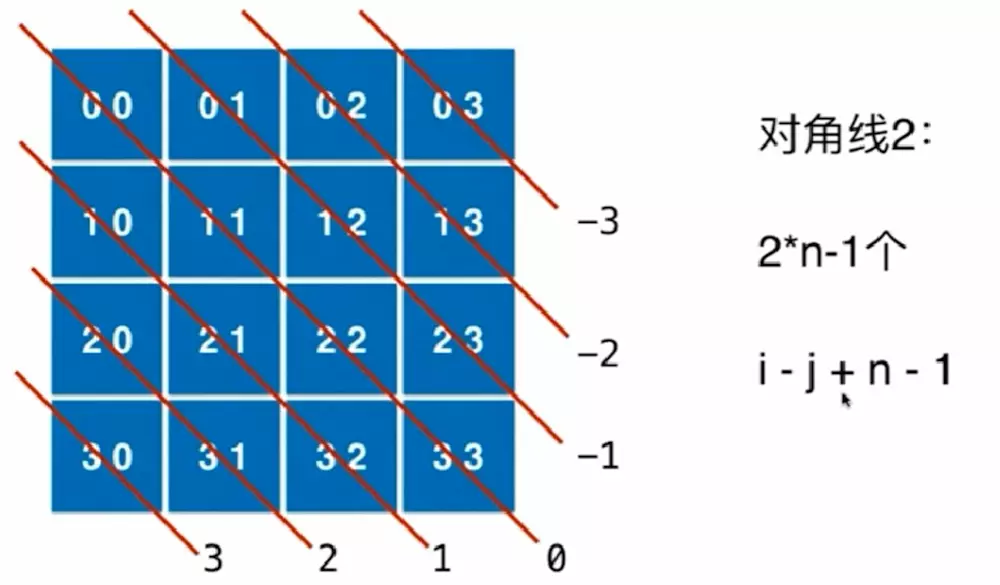
快速判断不合法的情况
竖向:col[i]表示第i列被占用
对角线1:dia1[i]表示在对角线1中,第i个元素被占用
对角线2:dia2[i]表示在对角线2中,第i个元素被占用
可以用横纵坐标相加的值表示对角线1
可以用横纵坐标相减的值表示对角线2,为了方便用数组表示还要+n-1
class Solution {
private List> res = new ArrayList();
private boolean[] colUsed;// 纵方向
private boolean[] dia1, dia2;// 2个斜对角线
public List> solveNQueens(int n) {
res.clear();
colUsed = new boolean[n];
dia1 = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
dia2 = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
List row = new ArrayList();
putQueen(n, 0, row);
return res;
}
// 尝试在一个n皇后问题中,摆放第index行的皇后位置,结果存在row
private void putQueen(int n, int index, List row) {
if (index == n) {
res.add(generateBoard(n, row));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 尝试将第index行的皇后摆放在第i列
if (!colUsed[i] && !dia1[index + i] && !dia2[index - i + n - 1]) {
row.add(i);
colUsed[i] = true;
dia1[index + i] = true;
dia2[index - i + n - 1] = true;
putQueen(n, index + 1, row);
colUsed[i] = false;
dia1[index + i] = false;
dia2[index - i + n - 1] = false;
row.remove(row.size() - 1);
}
}
return;
}
private List generateBoard(int n, List row) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String s = "";
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (j == row.get(i)) {
s += "Q";
} else {
s += ".";
}
}
list.add(s);
}
return list;
}
}
相关问题,52,37