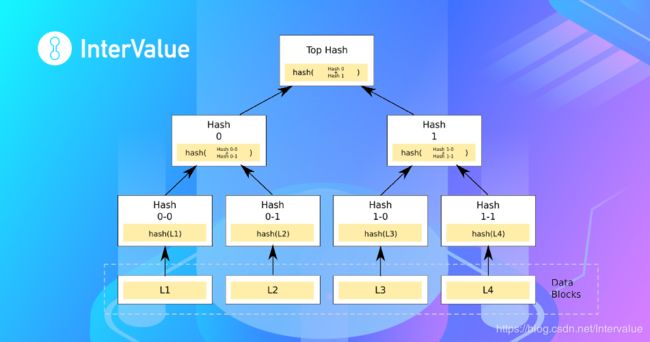
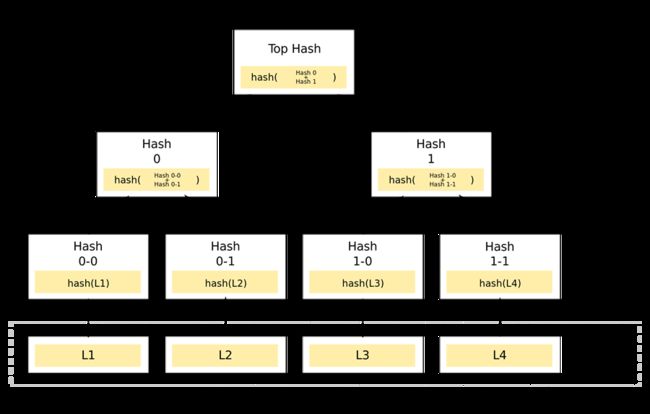
InterValue使用Merkle tree来验证区块是否被篡改
通常来讲,首先我们对数据块进行hash化(例如:使用sha256就会使不同大小的块变为256定长),而后对相邻的两个hash结果进行拼接,再进行hash,这样操作直到只有一个顶层hash。当然,有一种特殊情况:如果数据块数量为奇数(如果图上还有L5的话),就可以增加一个L5来进行计算(图上就变为L1,L2,L3,L4,L5,L5进行配对)。
Merkle Tree现有的理论比较成熟,机制原理也较容易理解。问题在于它的应用场景的细节没有相关说明。另外由Java语言实现的,成熟的商业开源方案还处于凤毛麟角的状况。
2.业务需求
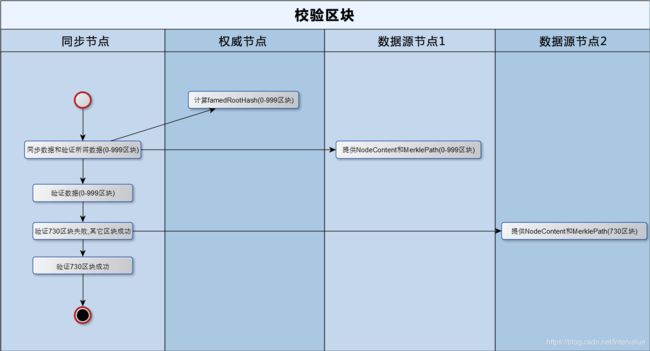
最近,InterValue研发团队在开发一个快速同步功能(fast sync),需要把共识节点的海量区块快速同步到新加入的节点,这里面有一个关键的任务是:需要同步区块的节点能主动发现其中有问题的区块,发现后只需要重新下载有问题的区块(例如,如果有100个区块共同下载到同步节点,其中2个块有问题,只需要重新下载有问题的2个块,不需要全部重新下载,提高下载效率),并且下载的区块验证数据大小不能呈指数级上升。
3.InterValue用Java语言实现标准的Merkle Tree
源代码已经发布在:
https://github.com/intervalue/intervalue-2.0.0-mainnet-rtm/tree/master/localfullnode2/src/main/java/one/inve/localfullnode2/utilities/merkle
4.Merkle Tree怎样应用到InterValue节点校验数据区块中
有几个关键概念需要提前知晓:
**NodeContent:**区块或者文件块被视为NodeContent,它提供两个关键功能:产生hash和比较功能。
**FamedRootHash:**由权威节点计算自己的merkle tree的hash根。
**MerklePath:**它由hash数组和index数组(它指定同位置hash里值是左值“l”还是右值“r”)组成。上图为例,L1的hash数组为{“hash0-1”,“hash1”},L1的index数组为{“r”,“r”}。
**CalculatedRootHash:**根据NodeContent和MerklePath计算出来的hash根,它会被用于与famedRootHash做比较。
public void validateSyncBlock() {
INodeContent[] blocks = buildBlocks();
INodeContent[] tamperedBlocks = buildTamperedBlocks();
MerkleTree mt = MerkleTree.create(blocks);
Node root = mt.getRoot();
byte[] famedRootHash = root.getHash();// which is provided by 3rd famed host
MerklePath mp = mt.getMerklePath(blocks[2]);
INodeContent tamperedBlock = tamperedBlocks[2];
INodeContent integralBlock = blocks[2];
// ignore these processes:
// .......serialize (famedRootHash,mp,tamperedBlock,integralBlock)
// ..........................................network transmission
// .....deserialize (famedRootHash,mp,tamperedBlock,integralBlock)
if (!mp.validate(tamperedBlock, famedRootHash)) {
System.out.println("bad news 1: tampered item");// this would be displayed.
}
if (!mp.validate(integralBlock, famedRootHash)) {
System.out.println("bad news 2: tampered item");// this wouldn't be displayed.
}
}
protected INodeContent[] buildBlocks() {
INodeContent[] blocks = new INodeContent[3];
blocks[0] = new Block("hello", 1);
blocks[1] = new Block("blockchain", 2);
blocks[2] = new Block("world", 3);
return blocks;
}
protected INodeContent[] buildTamperedBlocks() {
INodeContent[] blocks = new INodeContent[3];
blocks[0] = new Block("hello", 1);
blocks[1] = new Block("blockchain", 2);
blocks[2] = new Block("worlds", 3);// tampered item
return blocks;
}
6.作者简介
Francis.Deng([email protected]),InterValue区块链架构师和项目源码的主要贡献者之一。