tensorflow中的seq2seq的代码详解
seq2seq模型详解中我们给出了seq2seq模型的介绍,这篇文章介绍tensorflow中seq
2seq的代码,方便日后工作中的调用。本文介绍的代码是版本1.2.1的代码,在1.0版本后,tensorflow要重新给出一套seq2seq的接口,把0.x的seq2seq搬到了legacy_seq2seq下,今天读的就是legacy_seq2seq的代码。目前很多代码还是使用了老的seq2seq接口,因此仍有熟悉的必要。整个seq2seq.py的代码结构如下图所示:
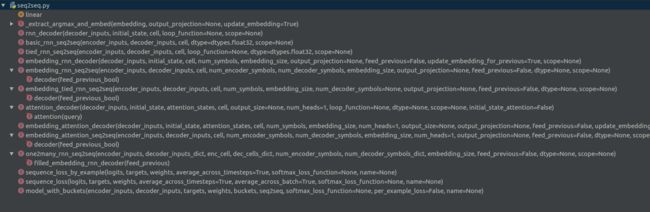
接下来,将按照seq2seq的调用顺序依次介绍model_with_buckets、embedding_rnn_seq2seq、embedding_rnn_decoder、_extract_argmax_and_embed、sequence_loss、sequence_loss_by_example等函数。其他函数如basic_rnn_seq2seq、tied_rnn_seq2seq、embedding_attention_seq2seq的流程和embedding_rnn_seq2seq类似,将在最后做简要分析。
model_with_buckets
def model_with_buckets(encoder_inputs,
decoder_inputs,
targets,
weights,
buckets,
seq2seq,
softmax_loss_function=None,
per_example_loss=False,
name=None):
if len(encoder_inputs) < buckets[-1][0]:
raise ValueError("Length of encoder_inputs (%d) must be at least that of la"
"st bucket (%d)." % (len(encoder_inputs), buckets[-1][0]))
if len(targets) < buckets[-1][1]:
raise ValueError("Length of targets (%d) must be at least that of last"
"bucket (%d)." % (len(targets), buckets[-1][1]))
if len(weights) < buckets[-1][1]:
raise ValueError("Length of weights (%d) must be at least that of last"
"bucket (%d)." % (len(weights), buckets[-1][1]))
all_inputs = encoder_inputs + decoder_inputs + targets + weights
losses = []
outputs = []
with ops.name_scope(name, "model_with_buckets", all_inputs):
for j, bucket in enumerate(buckets):
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
variable_scope.get_variable_scope(), reuse=True if j > 0 else None):
bucket_outputs, _ = seq2seq(encoder_inputs[:bucket[0]],
decoder_inputs[:bucket[1]])
outputs.append(bucket_outputs)
if per_example_loss:
losses.append(
sequence_loss_by_example(
outputs[-1],
targets[:bucket[1]],
weights[:bucket[1]],
softmax_loss_function=softmax_loss_function))
else:
losses.append(
sequence_loss(
outputs[-1],
targets[:bucket[1]],
weights[:bucket[1]],
softmax_loss_function=softmax_loss_function))
return outputs, losses输入参数:
encoder_inputs:这里的inputs是ids的形式还是传入input_size的形式,要根据后面seq2seq定义的那个函数决定,一般就只传入两个参数x, y分别对应encoder_inputs和decoder_inputs(另外特定seq2seq需要的参数需要在自定义的这个seq2seq函数内部传入)。这个时候,如果我们使用的是embedding_seq2seq,那么实际的inputs就应该是ids的样子;否则,就是input_size的样子。
targets:a list因为每一时刻都会有target,并且每一时刻输入的是batch_size个,因此每一时刻的target是[batch_size,]的形式,最终导致targets是a list of [batch_size, ]
buckets:a list of (input_size, output_size)
per_example_loss:默认是False,表示losses是[batch_size, ]。接下来会讲到的sequence_loss_by_example的结果是[batch_size,],而sequence_loss的结果是一个scalar。
实现:
根据中间for循环可以看到,对每一个bucket都实现了一个seq2seq的model。如果设置了3个buckets=[(5, 10), (10, 15), (15, 20)],第1个bucket是(5,10),那么数据集中encoder_input < 5并且 decoder_input < 10的数据会被padding,并且进行seq2seq,得到输出是a list of [batch_size, output_size],然后将这个输出加入到outputs中。
最终得到的outputs就是一个bucket_size长度(这里为3)的列表,列表中每个元素是长度不等的list(之所以长度不等是因为每个bucket所定义的max_decoder_length不等,依次增大)。这里定义了可以使用bucket的seq2seq,接下来我们看seq2seq是如何实现的。
embedding_rnn_seq2seq
def embedding_rnn_seq2seq(encoder_inputs,
decoder_inputs,
cell,
num_encoder_symbols,
num_decoder_symbols,
embedding_size,
output_projection=None,
feed_previous=False,
dtype=None,
scope=None):
with variable_scope.variable_scope(scope or "embedding_rnn_seq2seq") as scope:
if dtype is not None:
scope.set_dtype(dtype)
else:
dtype = scope.dtype
# Encoder.
encoder_cell = copy.deepcopy(cell)
encoder_cell = core_rnn_cell.EmbeddingWrapper(
encoder_cell,
embedding_classes=num_encoder_symbols,
embedding_size=embedding_size)
_, encoder_state = rnn.static_rnn(encoder_cell, encoder_inputs, dtype=dtype)
# Decoder.
if output_projection is None:
cell = core_rnn_cell.OutputProjectionWrapper(cell, num_decoder_symbols)
if isinstance(feed_previous, bool):
return embedding_rnn_decoder(
decoder_inputs,
encoder_state,
cell,
num_decoder_symbols,
embedding_size,
output_projection=output_projection,
feed_previous=feed_previous)
# If feed_previous is a Tensor, we construct 2 graphs and use cond.
def decoder(feed_previous_bool):
reuse = None if feed_previous_bool else True
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
variable_scope.get_variable_scope(), reuse=reuse):
outputs, state = embedding_rnn_decoder(
decoder_inputs,
encoder_state,
cell,
num_decoder_symbols,
embedding_size,
output_projection=output_projection,
feed_previous=feed_previous_bool,
update_embedding_for_previous=False)
state_list = [state]
if nest.is_sequence(state):
state_list = nest.flatten(state)
return outputs + state_list
outputs_and_state = control_flow_ops.cond(feed_previous,
lambda: decoder(True),
lambda: decoder(False))
outputs_len = len(decoder_inputs) # Outputs length same as decoder inputs.
state_list = outputs_and_state[outputs_len:]
state = state_list[0]
if nest.is_sequence(encoder_state):
state = nest.pack_sequence_as(
structure=encoder_state, flat_sequence=state_list)
return outputs_and_state[:outputs_len], state参数:
inputs:既然embedding是内部帮我们完成,则inputs shape= a list of [batch_size],每个时间步长都是batch_size个token id。内部使用一个core_rnn_cell.Embedding_wrapper()函数,lookup向量表(vocab_size*embedding_size),生成a list of [batch_size, embedding_size]的tensor。
num_encoder_symbols:通俗的说其实就是encoder端的vocab_size。enc和dec两端词汇量不同主要在于不同语言的translate task中,如果单纯是中文到中文的生成,不存在两端词汇量的不同。
num_decoder_symbols:同上。
embedding_size:每个vocab需要用多少维的vector表示。
output_projection=None:这是一个非常重要的变量。如果output_projection为默认的None,此时为训练模式,这是的cell加了一层OutputProjectionWrapper,即将输出的[batch_size, output_size]转化为[batch_size,symbol]。而如果output_projection不为空,此时的cell的输出还是[batch_size, output_size]。两个cell是不同的,这就直接影响到后续的embedding_rnn_decoder的解码过程和loop_function的定义操作。
feed_previous=False:如果feed_previous只是简单的一个True or False,则直接返回embedding_rnn_decoder的结果。重点是feed_previous还能传入一个boolean tensor,暂时无此需求。
实现:
可以看出,将token的id转化为向量以后,使用static_rnn函数得到encoder的编码向量,即encoder的最后一个时间步长的隐含状态ht。其中static_rnn是实现比较早的rnn代码,时间步长是固定的;而dynamic_rnn可以实现动态的时间步长,使用更加方便。有关dynamic_rnn可以移步我的博客我的博客。
得到ht以后,直接调用embedding_rnn_decoder函数,所以接下来我们分析这个函数。
embedding_rnn_decoder
def embedding_rnn_decoder(decoder_inputs,
initial_state,
cell,
num_symbols,
embedding_size,
output_projection=None,
feed_previous=False,
update_embedding_for_previous=True,
scope=None):
with variable_scope.variable_scope(scope or "embedding_rnn_decoder") as scope:
if output_projection is not None:
dtype = scope.dtype
proj_weights = ops.convert_to_tensor(output_projection[0], dtype=dtype)
proj_weights.get_shape().assert_is_compatible_with([None, num_symbols])
proj_biases = ops.convert_to_tensor(output_projection[1], dtype=dtype)
proj_biases.get_shape().assert_is_compatible_with([num_symbols])
embedding = variable_scope.get_variable("embedding",
[num_symbols, embedding_size])
loop_function = _extract_argmax_and_embed(
embedding, output_projection,
update_embedding_for_previous) if feed_previous else None
emb_inp = (embedding_ops.embedding_lookup(embedding, i)
for i in decoder_inputs)
return rnn_decoder(
emb_inp, initial_state, cell, loop_function=loop_function)输入参数:
decoder_inputs:这里input是token id,shape为a list of [batch_size, ]也就是说,输入不需要自己做embedding,直接输入tokens在vocab中对应的idx(即ids)即可,内部会自动帮我们进行id到embedding的转化。
num_symbols:就是vocab_size
embedding_size:每个token需要embedding成的维数。
output_projection:如果output_projection为默认的None,此时为训练模式,这时的cell加了一层OutputProjectionWrapper,即将输出的[batch_size, output_size]转化为[batch_size,nums_symbol]。而如果output_projection不为空,此时的cell的输出还是[batch_size, output_size]。
update_embedding_for_previous:如果前一时刻的output不作为当前的input的话(feed_previous=False),这个参数没影响();否则,该参数默认是True,但如果设置成false,则表示不对前一个embedding进行更新,那么bp的时候只会更新”GO”的embedding,其他token(decoder生成的)embedding不变。
输出:
outputs:如果output_projection=None的话,也就是不进行映射(此时的cell直接输出的是num_symbols的个数),那么a list of [batch_size, num_symbols];如果不为None(此时的cell直接输出的是[batch_size, output_size]的大小),说明outputs要进行映射,则outputs是a list of [batch_size, output_size]。
state同上。
rnn_decoder
def rnn_decoder(decoder_inputs,
initial_state,
cell,
loop_function=None,
scope=None):
with variable_scope.variable_scope(scope or "rnn_decoder"):
state = initial_state
outputs = []
prev = None
for i, inp in enumerate(decoder_inputs):
if loop_function is not None and prev is not None:
with variable_scope.variable_scope("loop_function", reuse=True):
inp = loop_function(prev, i)
if i > 0:
variable_scope.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
output, state = cell(inp, state)
outputs.append(output)
if loop_function is not None:
prev = output
return outputs, state参数:
decoder_inputs:是a list,其中的每一个元素表示的是t_i时刻的输入,每一时刻的输入又会有batch_size个,每一个输入(通差是表示一个word或token)又是input_size维度的。
initial_state:初始状态,通常是encoder的ht。
cell:如果output_projection为默认的None,此时为训练模式,这时的cell加了一层OutputProjectionWrapper,即将输出的[batch_size, output_size]转化为[batch_size,symbol]。而如果output_projection不为空,此时的cell的输出还是[batch_size, output_size]。
loop_function: 如果loop_function有设置的话,decoder input中第一个”GO”会输入,但之后时刻的input就会被忽略,取代的是input_ti+1 = loop_function(output_ti)。这里定义的loop_function,有2个参数,(prev,i),输出为next
实现:
这个函数就是seq2seq的核心代码。
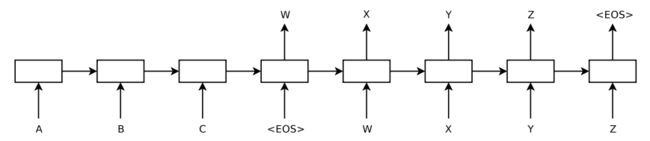
训练时,loop_function为none,output_projection为none,此时的dec_input按照时间步长对齐,输入到decoder,得到的每个cell的输出,shape为[batch_size,symbol_nums]。如下图:
预测时,loop_function不为none,output_projection不为none。此时,仅读取decoder的第一个时间步长的。其他时间步长的输入都采用上一个时间步长的输出。在介绍embedding_rnn_decoder时候说道,当output_projection不为none时,cell的输出为[batch_size, output_size],因此loop_function的作用就是将[batch_size, output_size]变为[batch_size, symbol_nums],然后取出概率最大的符号,并进行embedding,作为下一个时间步长的输入。如下图所示:
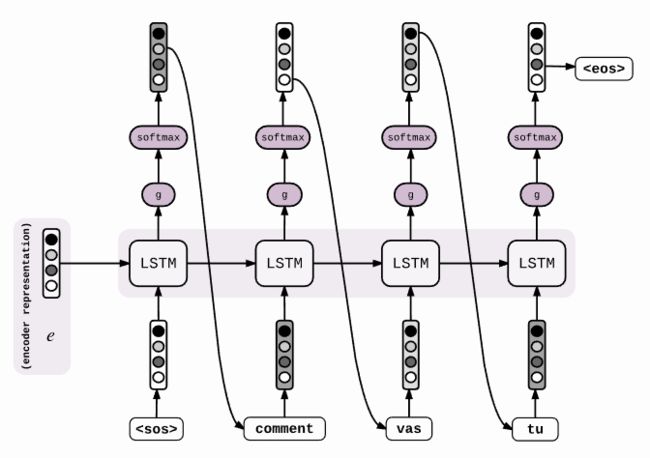
def loop_function(prev, _):
if output_projection is not None:
prev = nn_ops.xw_plus_b(prev, output_projection[0], output_projection[1])
prev_symbol = math_ops.argmax(prev, 1)
# Note that gradients will not propagate through the second parameter of
# embedding_lookup.
emb_prev = embedding_ops.embedding_lookup(embedding, prev_symbol)
if not update_embedding:
emb_prev = array_ops.stop_gradient(emb_prev)
return emb_prev输出:
outputs:如果output_projection为默认的None,此时为训练模式,这时的cell加了一层OutputProjectionWrapper,即将输出的[batch_size, output_size]转化为[batch_size,symbol_nums]。而如果output_projection不为空,此时的cell的输出还是[batch_size, output_size]。
state:最后一个时刻t的cell state,shape=[batch_size, cell.state_size]
sequence_loss
def sequence_loss(logits,
targets,
weights,
average_across_timesteps=True,
average_across_batch=True,
softmax_loss_function=None,
name=None):
with ops.name_scope(name, "sequence_loss", logits + targets + weights):
cost = math_ops.reduce_sum(
sequence_loss_by_example(
logits,
targets,
weights,
average_across_timesteps=average_across_timesteps,
softmax_loss_function=softmax_loss_function))
if average_across_batch:
batch_size = array_ops.shape(targets[0])[0]
return cost / math_ops.cast(batch_size, cost.dtype)
else:
return cost输入参数:
logits:a list of [batch_size*symbol_nums] 2维
targets:a list of batch_size 1维
weights:每个时间步长的权重,和targets的shape一样。
返回:
一个float的标量,句子的平均log困惑度。
实现:
整个seq2seq通过以上几个函数就可以实现完了,然后需要计算seq2seq的loss。调用sequence_loss_by_example实现计算loss的功能。
sequence_loss_by_example
def sequence_loss_by_example(logits,
targets,
weights,
average_across_timesteps=True,
softmax_loss_function=None,
name=None):
if len(targets) != len(logits) or len(weights) != len(logits):
raise ValueError("Lengths of logits, weights, and targets must be the same "
"%d, %d, %d." % (len(logits), len(weights), len(targets)))
with ops.name_scope(name, "sequence_loss_by_example",
logits + targets + weights):
log_perp_list = []
for logit, target, weight in zip(logits, targets, weights):
if softmax_loss_function is None:
# TODO(irving,ebrevdo): This reshape is needed because
# sequence_loss_by_example is called with scalars sometimes, which
# violates our general scalar strictness policy.
target = array_ops.reshape(target, [-1])
crossent = nn_ops.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=target, logits=logit)
else:
crossent = softmax_loss_function(labels=target, logits=logit)
log_perp_list.append(crossent * weight)
log_perps = math_ops.add_n(log_perp_list)
if average_across_timesteps:
total_size = math_ops.add_n(weights)
total_size += 1e-12 # Just to avoid division by 0 for all-0 weights.
log_perps /= total_size
return log_perps输入:
logits:同上sequence_loss。
targets:同上sequence_loss。
weights:同上sequence_loss。注:可能句子中有的词会是padding得到的,所以可以通过weights减小padding的影响。
返回值:
1D batch-sized float Tensor:为每一个序列(一个batch中有batch_size个sequence)计算其log perplexity,也是名称中by_example的含义
实现:
首先我们看这么一段代码:
import tensorflow as tf
A = tf.random_normal([5,4], dtype=tf.float32)
B = tf.constant([1,2,1,3,3], dtype=tf.int32)
w = tf.ones([5], dtype=tf.float32)
D = tf.nn.seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example([A], [B], [w])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(D))
输出:
[ 1.39524221 0.54694229 0.88238466 1.51492059 0.95956933]就可以直观看到sequence_loss_by_example的含义,logits是一个二维的张量,比如是a*b,那么targets就是一个一维的张量长度为a,并且targets中元素的值是不能超过b的整形,32位的整数。也即是如果b等于4,那么targets中的元素的值都要小于4。weights就是一个一维的张量长度为a,并且是一个tf.float32的数。这是权重的意思。
logits、targets、weights都是列表,那么zip以后变成了一个包含tuple的列表,list[0]代表第一个cell的logit、target、weight。那么for循环之后的大小就是a list of [batch_size,]。但是此时请注意for循环后还有一个log_perps = math_ops.add_n(log_perp_list)的操作。会将list中的[batch_size,]的标量相加,得到一个batch_size大小的float tensor。
然后将batch_size大小的float tensor传回sequence_loss,除以batch_size得到一个标量。
attention_decoder
def attention_decoder(decoder_inputs,
initial_state,
attention_states,
cell,
output_size=None,
num_heads=1,
loop_function=None,
dtype=None,
scope=None,
initial_state_attention=False):
if not decoder_inputs:
raise ValueError("Must provide at least 1 input to attention decoder.")
if num_heads < 1:
raise ValueError("With less than 1 heads, use a non-attention decoder.")
if attention_states.get_shape()[2].value is None:
raise ValueError("Shape[2] of attention_states must be known: %s" %
attention_states.get_shape())
if output_size is None:
output_size = cell.output_size
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
scope or "attention_decoder", dtype=dtype) as scope:
dtype = scope.dtype
batch_size = array_ops.shape(decoder_inputs[0])[0] # Needed for reshaping.
attn_length = attention_states.get_shape()[1].value
if attn_length is None:
attn_length = array_ops.shape(attention_states)[1]
attn_size = attention_states.get_shape()[2].value
# To calculate W1 * h_t we use a 1-by-1 convolution, need to reshape before.
hidden = array_ops.reshape(attention_states,
[-1, attn_length, 1, attn_size])
hidden_features = []
v = []
attention_vec_size = attn_size # Size of query vectors for attention.
for a in xrange(num_heads):
k = variable_scope.get_variable("AttnW_%d" % a,
[1, 1, attn_size, attention_vec_size])
hidden_features.append(nn_ops.conv2d(hidden, k, [1, 1, 1, 1], "SAME"))
v.append(
variable_scope.get_variable("AttnV_%d" % a, [attention_vec_size]))
state = initial_state
def attention(query):
"""Put attention masks on hidden using hidden_features and query."""
ds = [] # Results of attention reads will be stored here.
if nest.is_sequence(query): # If the query is a tuple, flatten it.
query_list = nest.flatten(query)
for q in query_list: # Check that ndims == 2 if specified.
ndims = q.get_shape().ndims
if ndims:
assert ndims == 2
query = array_ops.concat(query_list, 1)
for a in xrange(num_heads):
with variable_scope.variable_scope("Attention_%d" % a):
y = linear(query, attention_vec_size, True)
y = array_ops.reshape(y, [-1, 1, 1, attention_vec_size])
# Attention mask is a softmax of v^T * tanh(...).
s = math_ops.reduce_sum(v[a] * math_ops.tanh(hidden_features[a] + y),
[2, 3])
a = nn_ops.softmax(s)
# Now calculate the attention-weighted vector d.
d = math_ops.reduce_sum(
array_ops.reshape(a, [-1, attn_length, 1, 1]) * hidden, [1, 2])
ds.append(array_ops.reshape(d, [-1, attn_size]))
return ds
outputs = []
prev = None
batch_attn_size = array_ops.stack([batch_size, attn_size])
attns = [
array_ops.zeros(
batch_attn_size, dtype=dtype) for _ in xrange(num_heads)
]
for a in attns: # Ensure the second shape of attention vectors is set.
a.set_shape([None, attn_size])
if initial_state_attention:
attns = attention(initial_state)
for i, inp in enumerate(decoder_inputs):
if i > 0:
variable_scope.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
# If loop_function is set, we use it instead of decoder_inputs.
if loop_function is not None and prev is not None:
with variable_scope.variable_scope("loop_function", reuse=True):
inp = loop_function(prev, i)
# Merge input and previous attentions into one vector of the right size.
input_size = inp.get_shape().with_rank(2)[1]
if input_size.value is None:
raise ValueError("Could not infer input size from input: %s" % inp.name)
x = linear([inp] + attns, input_size, True)
# Run the RNN.
cell_output, state = cell(x, state)
# Run the attention mechanism.
if i == 0 and initial_state_attention:
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
variable_scope.get_variable_scope(), reuse=True):
attns = attention(state)
else:
attns = attention(state)
with variable_scope.variable_scope("AttnOutputProjection"):
output = linear([cell_output] + attns, output_size, True)
if loop_function is not None:
prev = output
outputs.append(output)
return outputs, state在网上大概搜了一下,关于attention的解释都模棱两可,有的甚至都是错的。首先希望来看源码的同学首先确保已经将NEURAL MACHINE TRANSLATION
BY JOINTLY LEARNING TO ALIGN AND TRANSLATE论文中的公式理解清楚,seq2seq模型详解:
 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
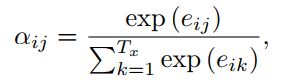 (4)
(4)
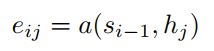 (5)
(5)
其次,在工程实现中,使用的多的是Grammar as a foreign language中的公式,也请各位确保理解。
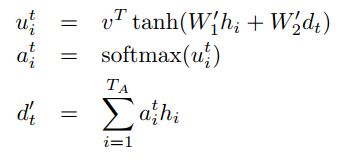 (6)
(6)
encoder输出的隐层状态 h1,...,hTA ,decoder的隐层状态 d1,...,dTB 。 vT,W′1,W′2 是模型要学的参数。所谓的attention,就是在每个解码的时间步,对encoder的隐层状态进行加权求和,针对不同信息进行不同程度的注意力。那么我们的重点就是求出不同隐层状态对应的权重。源码中的attention机制里是最常见的一种,可以分为三步走:(1)通过当前隐层状态(d_{t})和关注的隐层状态 hi 求出对应权重 uti ;(2)softmax归一化为概率;(3)作为加权系数对不同隐层状态求和,得到一个的信息向量 d′t 。后续的 d′t 使用会因为具体任务有所差别。
再来看看attention_decoder的参数:
和基本的rnn_decoder相比(rnn_decoder(decoder_inputs, initial_state, cell, loop_function=None, scope=None))
多了几个参数:
attention_states:即图中的hi。attention_states的shape为[batch_size,atten_length,seq_size]。其中atten_length就是encoder的句长,atten_size就是每个cell的attention的size。
output_size=None:如果是None的话默认为cell.output_size
num_heads=1 :attention就是对信息的加权求和,一个attention head对应了一种加权求和方式,这个参数定义了用多少个attention head去加权求和。用多个head加权求和可以避免一个attention关注出现偏差的情况。
initial_state_attention=False:如果是True的话,attention由state和attention_states进行初始化,如果False,则attention初始化为0。
W1∗hi 用的是卷积的方式实现,返回的tensor的形状是[batch_size, attn_length, 1, attention_vec_size]
# To calculate W1 * h_t we use a 1-by-1 convolution, need to reshape before.
hidden = array_ops.reshape(attention_states,
[-1, attn_length, 1, attn_size])
hidden_features = []
v = []
attention_vec_size = attn_size # Size of query vectors for attention.
for a in xrange(num_heads):
k = variable_scope.get_variable("AttnW_%d" % a,
[1, 1, attn_size, attention_vec_size])
hidden_features.append(nn_ops.conv2d(hidden, k, [1, 1, 1, 1], "SAME"))
v.append(
variable_scope.get_variable("AttnV_%d" % a, [attention_vec_size]))
W2∗dt ,此项是通过下面的线性映射函数linear实现。
然后计算 uti=VT∗tanh(W1∗hi+W2∗dt) ,即下面代码中的s=…
然后计算softmax
然后计算 d‘t 。至此,公式(6)中的结果都已经计算完毕。
for a in xrange(num_heads):
with variable_scope.variable_scope("Attention_%d" % a):
y = linear(query, attention_vec_size, True)
y = array_ops.reshape(y, [-1, 1, 1, attention_vec_size])
# Attention mask is a softmax of v^T * tanh(...).
s = math_ops.reduce_sum(v[a] * math_ops.tanh(hidden_features[a] + y),
[2, 3])
a = nn_ops.softmax(s)
# Now calculate the attention-weighted vector d.
d = math_ops.reduce_sum(
array_ops.reshape(a, [-1, attn_length, 1, 1]) * hidden, [1, 2])
ds.append(array_ops.reshape(d, [-1, attn_size]))
return ds公式(6)计算完毕,就得到了公式(3)中的ci。然后计算时间步长i的隐藏状态si。
即对于时间步i的隐藏状态,由时间步i-1的隐藏状态si-1,由attention计算得到的输入内容ci和上一个输出yi-1得到。
x = linear([inp] + attns, input_size, True)
# Run the RNN.
cell_output, state = cell(x, state)
# Run the attention mechanism.
if i == 0 and initial_state_attention:
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
variable_scope.get_variable_scope(), reuse=True):
attns = attention(state)
else:
attns = attention(state)然后得到了si,接下来要计算yi。即公式(1),对于时间步i的输出yi,由时间步i的隐藏状态si,由attention计算得到的输入内容ci和上一个输出yi-1得到。
with variable_scope.variable_scope("AttnOutputProjection"):
output = linear([cell_output] + attns, output_size, True)到这里,embedding_attention_seq2seq的核心代码都已经解读完毕了。在实际的运用,可以根据需求灵活使用各个函数,特别是attention_decoder函数。相信坚持阅读下来的小伙伴们,能对这个API有更深刻的认识。
参考文献:
(1)seq2seq模型详解
(2)dynamic_rnn详解
(3)NEURAL MACHINE TRANSLATION BY JOINTLY LEARNING TO ALIGN AND TRANSLATE
(4)Grammar as a foreign language
(5)Tensorflow源码解读(一):Attention Seq2Seq模型
(6)tensorflow的legacy_seq2seq(这篇文章错误较多)
(7)Seq2Seq with Attention and Beam Search