SpringBoot - 整合JDBC与默认数据源
对于数据访问层,无论是SQL还是NOSQL,Spring Boot默认采用整合Spring Data的方式进行统一处理,添加大量自动配置,屏蔽了很多设置。引入各种xxxTemplate,xxxRepository来简化我们对数据访问层的操作。对我们来说只需要进行简单的设置即可。这里SpringBoot版本使用1.5.10。
【1】创建项目,引入需要的模块
pom文件如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>【2】配置MySQL并测试
类似于以前项目的config.properties,这将mysql的属性配置在yml文件中。
数据源的所有配置对应类如下:
/**
* Base class for configuration of a data source.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Maciej Walkowiak
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Benedikt Ritter
* @author Eddú Meléndez
* @since 1.1.0
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public class DataSourceProperties
implements BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware, InitializingBean {
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private Environment environment;
/**
* Name of the datasource.
*/
private String name = "testdb";
/**
* Generate a random datasource name.
*/
private boolean generateUniqueName;
/**
* Fully qualified name of the connection pool implementation to use. By default, it
* is auto-detected from the classpath.
*/
private Class type;
/**
* Fully qualified name of the JDBC driver. Auto-detected based on the URL by default.
*/
private String driverClassName;
/**
* JDBC url of the database.
*/
private String url;
/**
* Login user of the database.
*/
private String username;
/**
* Login password of the database.
*/
private String password;
/**
* JNDI location of the datasource. Class, url, username & password are ignored when
* set.
*/
private String jndiName;
/**
* Populate the database using 'data.sql'.
*/
private boolean initialize = true;
/**
* Platform to use in the DDL or DML scripts (e.g. schema-${platform}.sql or
* data-${platform}.sql).
*/
private String platform = "all";
/**
* Schema (DDL) script resource references.
*/
private List schema;
/**
* User of the database to execute DDL scripts (if different).
*/
private String schemaUsername;
/**
* Password of the database to execute DDL scripts (if different).
*/
private String schemaPassword;
/**
* Data (DML) script resource references.
*/
private List data;
/**
* User of the database to execute DML scripts.
*/
private String dataUsername;
/**
* Password of the database to execute DML scripts.
*/
private String dataPassword;
/**
* Do not stop if an error occurs while initializing the database.
*/
private boolean continueOnError = false;
/**
* Statement separator in SQL initialization scripts.
*/
private String separator = ";";
/**
* SQL scripts encoding.
*/
private Charset sqlScriptEncoding;
private EmbeddedDatabaseConnection embeddedDatabaseConnection = EmbeddedDatabaseConnection.NONE;
private Xa xa = new Xa();
private String uniqueName;
//...
} application.yml文件如下:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver在测试类中获取默认数据源,并拿到链接:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class DatasourceApplicationTests {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws Exception {
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass()+"***********");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
}测试结果如下:
class org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource***********
ProxyConnection[PooledConnection[com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@2bfbffb2]]即,数据源默认使用的是org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource(这个与SpringBoot版本有关,这里是1.5.10)。
【3】使用JdbcTemplate访问数据库
SpringBoot默认配置了JdbcTemplate和NamedParameterJdbcTemplate,源码如下:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ DataSource.class, JdbcTemplate.class })
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
public class JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration {
private final DataSource dataSource;
public JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Bean
@Primary
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(JdbcOperations.class)
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() {
return new JdbcTemplate(this.dataSource);
}
@Bean
@Primary
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(NamedParameterJdbcOperations.class)
public NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate() {
return new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(this.dataSource);
}
}编写controller进行测试:
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/hello")
private Map getBook(){
String sql = "select * from book";
List> list = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
return list.get(0);
}
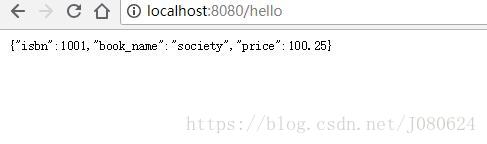
} 浏览器访问结果如下:
这里返回结果为Map,浏览器得到的为JSON。这是因为,首先方法上使用了注解@Responsebody,其次WebMVCAutoConfiguration默认注册了一系列的HttpMessageConverter,该类主要用来做请求响应的转换。
而@Responsebody注解被RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 处理器进行解析。
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 源码如下:
/**
* Resolves method arguments annotated with {@code @RequestBody} and handles return
* values from methods annotated with {@code @ResponseBody} by reading and writing
* to the body of the request or response with an {@link HttpMessageConverter}.
*
* An {@code @RequestBody} method argument is also validated if it is annotated
* with {@code @javax.validation.Valid}. In case of validation failure,
* {@link MethodArgumentNotValidException} is raised and results in an HTTP 400
* response status code if {@link DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver} is configured.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
*/
public class RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor extends AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor {
//...
public void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage = createInputMessage(webRequest);
ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage = createOutputMessage(webRequest);
// Try even with null return value. ResponseBodyAdvice could get involved.
writeWithMessageConverters(returnValue, returnType, inputMessage, outputMessage);
}
//...
}
其中 writeWithMessageConverters用来转换返回内容。
跟踪源码如下:
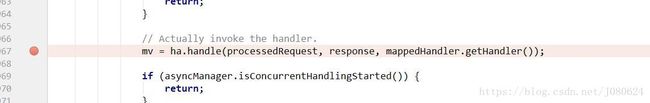
② AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}③ RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
④ ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
try {
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(getReturnValueHandlingErrorMessage("Error handling return value", returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
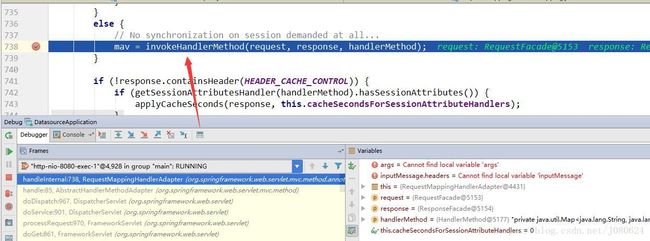
⑤ InvocableHandlerMethod
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking '" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(getMethod(), getBeanType()) +
"' with arguments " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
Object returnValue = doInvoke(args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method [" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(getMethod(), getBeanType()) +
"] returned [" + returnValue + "]");
}
return returnValue;
}⑥ 调用目标方法
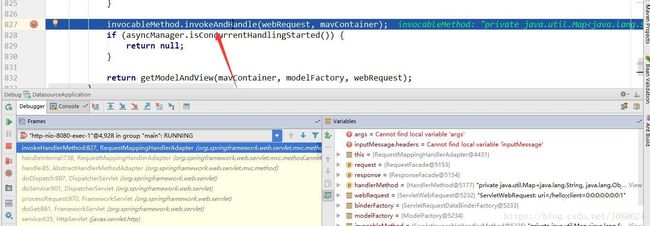
⑦ ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
//开始从这里执行
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
try {
//对返回结果开始进行处理
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(getReturnValueHandlingErrorMessage("Error handling return value", returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
⑧ HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite
注意:这里的handler是RequestReponseBodyMethonProcessor !
⑨ RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
public void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage = createInputMessage(webRequest);
ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage = createOutputMessage(webRequest);
// Try even with null return value. ResponseBodyAdvice could get involved.
// 注意这里!
writeWithMessageConverters(returnValue, returnType, inputMessage, outputMessage);
}⑩ AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor
/**
* Writes the given return type to the given output message.
* @param value the value to write to the output message
* @param returnType the type of the value
* @param inputMessage the input messages. Used to inspect the {@code Accept} header.
* @param outputMessage the output message to write to
* @throws IOException thrown in case of I/O errors
* @throws HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException thrown when the conditions indicated
* by the {@code Accept} header on the request cannot be met by the message converters
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
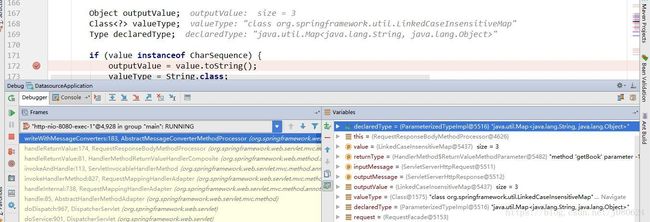
protected void writeWithMessageConverters(T value, MethodParameter returnType,
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage, ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
Object outputValue;
Class valueType;
Type declaredType;
if (value instanceof CharSequence) {
outputValue = value.toString();
valueType = String.class;
declaredType = String.class;
}
else {
outputValue = value;
valueType = getReturnValueType(outputValue, returnType);
declaredType = getGenericType(returnType);
}
HttpServletRequest request = inputMessage.getServletRequest();
//从请求中拿到MediaType
List requestedMediaTypes = getAcceptableMediaTypes(request);
//拿到producibleMediaTypes
List producibleMediaTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, valueType, declaredType);
if (outputValue != null && producibleMediaTypes.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No converter found for return value of type: " + valueType);
}
Set compatibleMediaTypes = new LinkedHashSet();
//循环遍历requestedType ,producibleType 拿到compatibleMediaTypes
for (MediaType requestedType : requestedMediaTypes) {
for (MediaType producibleType : producibleMediaTypes) {
//对比判断是否相容
if (requestedType.isCompatibleWith(producibleType)) {
compatibleMediaTypes.add(getMostSpecificMediaType(requestedType, producibleType));
}
}
}
if (compatibleMediaTypes.isEmpty()) {
if (outputValue != null) {
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(producibleMediaTypes);
}
return;
}
//所有相容的mediaTypes
List mediaTypes = new ArrayList(compatibleMediaTypes);
//对mediaTypes进行排序
MediaType.sortBySpecificityAndQuality(mediaTypes);
MediaType selectedMediaType = null;
//对MediaType 进行循环遍历判断
for (MediaType mediaType : mediaTypes) {
//判断该mediaType是否是具体的类型
if (mediaType.isConcrete()) {
selectedMediaType = mediaType;
break;
}
else if (mediaType.equals(MediaType.ALL) || mediaType.equals(MEDIA_TYPE_APPLICATION)) {
selectedMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM;
break;
}
}
if (selectedMediaType != null) {
//移除权重,如application/json;q=0.8(权重)
selectedMediaType = selectedMediaType.removeQualityValue();
//循环遍历messageConverters
for (HttpMessageConverter messageConverter : this.messageConverters) {
//对messageConverter 进行判断
if (messageConverter instanceof GenericHttpMessageConverter) {
//判断该messageConverter可以处理declaredType,valueType,selectedMediaType,
if (((GenericHttpMessageConverter) messageConverter).canWrite(
declaredType, valueType, selectedMediaType)) {
outputValue = (T) getAdvice().beforeBodyWrite(outputValue, returnType, selectedMediaType,
(Classextends HttpMessageConverter>) messageConverter.getClass(),
inputMessage, outputMessage);
if (outputValue != null) {
addContentDispositionHeader(inputMessage, outputMessage);
// 向响应中写数据
((GenericHttpMessageConverter) messageConverter).write(
outputValue, declaredType, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Written [" + outputValue + "] as \"" + selectedMediaType +
"\" using [" + messageConverter + "]");
}
}
return;
}
}
else if (messageConverter.canWrite(valueType, selectedMediaType)) {
outputValue = (T) getAdvice().beforeBodyWrite(outputValue, returnType, selectedMediaType,
(Classextends HttpMessageConverter>) messageConverter.getClass(),
inputMessage, outputMessage);
if (outputValue != null) {
addContentDispositionHeader(inputMessage, outputMessage);
((HttpMessageConverter) messageConverter).write(outputValue, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Written [" + outputValue + "] as \"" + selectedMediaType +
"\" using [" + messageConverter + "]");
}
}
return;
}
}
}
if (outputValue != null) {
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(this.allSupportedMediaTypes);
}
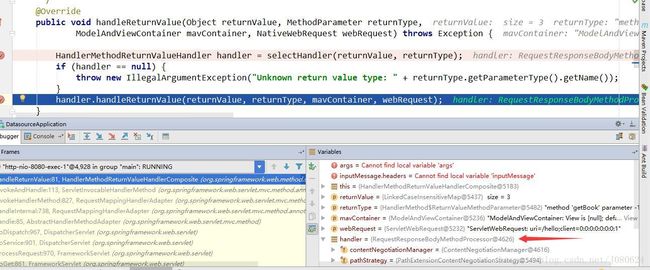
} - 返回值,值类型,方法返回声明类型如下图:
- 从请求头中拿到MediaType:
List requestedMediaTypes = getAcceptableMediaTypes(request);HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy.resolveMediaTypes()
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @throws HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException if the 'Accept' header cannot be parsed
*/
@Override
public List resolveMediaTypes(NativeWebRequest request)
throws HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException {
String[] headerValueArray = request.getHeaderValues(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT);
if (headerValueArray == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List headerValues = Arrays.asList(headerValueArray);
try {
List mediaTypes = MediaType.parseMediaTypes(headerValues);
MediaType.sortBySpecificityAndQuality(mediaTypes);
return mediaTypes;
}
catch (InvalidMediaTypeException ex) {
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(
"Could not parse 'Accept' header " + headerValues + ": " + ex.getMessage());
}
} 结果如下图:
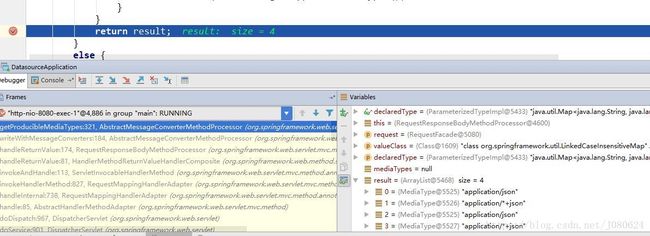
- 拿到producibleMediaTypes
List producibleMediaTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, valueType, declaredType);AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor.getProducibleMediaTypes
/**
* Returns the media types that can be produced:
*
* - The producible media types specified in the request mappings, or
*
- Media types of configured converters that can write the specific return value, or
*
- {@link MediaType#ALL}
*
* @since 4.2
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected List getProducibleMediaTypes(HttpServletRequest request, Class valueClass, Type declaredType) {
//首先从requestMapping尝试拿到mediaType,如produce="application/json;charset=utf-8"
Set mediaTypes = (Set) request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
//如果mediaTypes 不为空,直接返回
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(mediaTypes)) {
return new ArrayList(mediaTypes);
}
//如果mediaTypes 为空,则从allSupportedMediaTypes进行尝试获取
else if (!this.allSupportedMediaTypes.isEmpty()) {
List result = new ArrayList();
//对所有的messageConverters进行遍历
for (HttpMessageConverter converter : this.messageConverters) {
if (converter instanceof GenericHttpMessageConverter && declaredType != null) {
if (((GenericHttpMessageConverter) converter).canWrite(declaredType, valueClass, null)) {
//将判断后合适的converter支持的MediaType放到result中
result.addAll(converter.getSupportedMediaTypes());
}
}
else if (converter.canWrite(valueClass, null)) {
result.addAll(converter.getSupportedMediaTypes());
}
}
return result;
}
else {
return Collections.singletonList(MediaType.ALL);
}
} 从requestMapping中拿到的MediaType如下图:
- 判断类型相容
MediaType.isCompatibleWith()
/**
* Indicate whether this {@code MediaType} is compatible with the given media type.
* For instance, {@code text/*} is compatible with {@code text/plain}, {@code text/html}, and vice versa.
* In effect, this method is similar to {@link #includes(MediaType)}, except that it is symmetric.
* @param other the reference media type with which to compare
* @return {@code true} if this media type is compatible with the given media type; {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean isCompatibleWith(MediaType other) {
return super.isCompatibleWith(other);
}
如果 RequestMapping中没有写produce="application/json;charset=utf-8",则从messageConverts中拿到所有支持的MediaType返回,如下图:
此时返回的producibleMediaTypes如下:
HttpMessageConverter其他知识参考博客:
HttpMessageConverter与返回JSON;
SpringMVC的默认配置与修改
【4】SpringBoot内置数据源
DataSourceConfiguration 源码如下:
/**
* Actual DataSource configurations imported by {@link DataSourceAutoConfiguration}.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
*/
abstract class DataSourceConfiguration {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T createDataSource(DataSourceProperties properties,
Classextends DataSource> type) {
return (T) properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().type(type).build();
}
/**
* Tomcat Pool DataSource configuration.
*/
@ConditionalOnClass(org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.datasource.type", havingValue = "org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource", matchIfMissing = true)
static class Tomcat extends DataSourceConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.tomcat")
public org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource dataSource(
DataSourceProperties properties) {
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource dataSource = createDataSource(
properties, org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource.class);
DatabaseDriver databaseDriver = DatabaseDriver
.fromJdbcUrl(properties.determineUrl());
String validationQuery = databaseDriver.getValidationQuery();
if (validationQuery != null) {
dataSource.setTestOnBorrow(true);
dataSource.setValidationQuery(validationQuery);
}
return dataSource;
}
}
/**
* Hikari DataSource configuration.
*/
@ConditionalOnClass(HikariDataSource.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.datasource.type", havingValue = "com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource", matchIfMissing = true)
static class Hikari extends DataSourceConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.hikari")
public HikariDataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
return createDataSource(properties, HikariDataSource.class);
}
}
/**
* DBCP DataSource configuration.
*
* @deprecated as of 1.5 in favor of DBCP2
*/
@ConditionalOnClass(org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.datasource.type", havingValue = "org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource", matchIfMissing = true)
@Deprecated
static class Dbcp extends DataSourceConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.dbcp")
public org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource dataSource(
DataSourceProperties properties) {
org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource dataSource = createDataSource(
properties, org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource.class);
DatabaseDriver databaseDriver = DatabaseDriver
.fromJdbcUrl(properties.determineUrl());
String validationQuery = databaseDriver.getValidationQuery();
if (validationQuery != null) {
dataSource.setTestOnBorrow(true);
dataSource.setValidationQuery(validationQuery);
}
return dataSource;
}
}
/**
* DBCP DataSource configuration.
*/
@ConditionalOnClass(org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.datasource.type", havingValue = "org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource", matchIfMissing = true)
static class Dbcp2 extends DataSourceConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.dbcp2")
public org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource dataSource(
DataSourceProperties properties) {
return createDataSource(properties,
org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource.class);
}
}
/**
* Generic DataSource configuration.
*/
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(DataSource.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.datasource.type")
static class Generic {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
}
}
}
【5】SpringBoot加载项目路径下的SQL
SpringBoot另一个特性是可以加载项目路径下的SQL脚本,比如建表语句,insert语句等等。
DataSourceAutoConfiguration 类如下:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ DataSource.class, EmbeddedDatabaseType.class })
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DataSourceProperties.class)
@Import({ Registrar.class, DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration.class })
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class);
//这里注册了DataSourceInitializer
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public DataSourceInitializer dataSourceInitializer(DataSourceProperties properties,
ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
return new DataSourceInitializer(properties, applicationContext);
}
//...
}DataSourceInitializer类如下:
/**
* Bean to handle {@link DataSource} initialization by running {@literal schema-*.sql} on
* {@link PostConstruct} and {@literal data-*.sql} SQL scripts on a
* {@link DataSourceInitializedEvent}.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Eddú Meléndez
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Kazuki Shimizu
* @since 1.1.0
* @see DataSourceAutoConfiguration
*/
class DataSourceInitializer implements ApplicationListener {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(DataSourceInitializer.class);
private final DataSourceProperties properties;
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private DataSource dataSource;
private boolean initialized = false;
DataSourceInitializer(DataSourceProperties properties,
ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.properties = properties;
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
//对象初始化方法
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
if (!this.properties.isInitialize()) {
logger.debug("Initialization disabled (not running DDL scripts)");
return;
}
if (this.applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(DataSource.class, false,
false).length > 0) {
this.dataSource = this.applicationContext.getBean(DataSource.class);
}
if (this.dataSource == null) {
logger.debug("No DataSource found so not initializing");
return;
}
//运行Schema脚本
runSchemaScripts();
}
private void runSchemaScripts() {
//获取项目下的Schema脚本
List scripts = getScripts("spring.datasource.schema",
this.properties.getSchema(), "schema");
if (!scripts.isEmpty()) {
String username = this.properties.getSchemaUsername();
String password = this.properties.getSchemaPassword();
runScripts(scripts, username, password);
try {
this.applicationContext
.publishEvent(new DataSourceInitializedEvent(this.dataSource));
// The listener might not be registered yet, so don't rely on it.
if (!this.initialized) {
runDataScripts();
this.initialized = true;
}
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
logger.warn("Could not send event to complete DataSource initialization ("
+ ex.getMessage() + ")");
}
}
}
//监听机制
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(DataSourceInitializedEvent event) {
if (!this.properties.isInitialize()) {
logger.debug("Initialization disabled (not running data scripts)");
return;
}
// NOTE the event can happen more than once and
// the event datasource is not used here
if (!this.initialized) {
//运行数据脚本
runDataScripts();
this.initialized = true;
}
}
private void runDataScripts() {
//获取项目路径下的数据脚本
List scripts = getScripts("spring.datasource.data",
this.properties.getData(), "data");
String username = this.properties.getDataUsername();
String password = this.properties.getDataPassword();
runScripts(scripts, username, password);
}
private List getScripts(String propertyName, List resources,
String fallback) {
if (resources != null) {
return getResources(propertyName, resources, true);
}
String platform = this.properties.getPlatform();
List fallbackResources = new ArrayList();
fallbackResources.add("classpath*:" + fallback + "-" + platform + ".sql");
fallbackResources.add("classpath*:" + fallback + ".sql");
return getResources(propertyName, fallbackResources, false);
}
private List getResources(String propertyName, List locations,
boolean validate) {
List resources = new ArrayList();
for (String location : locations) {
for (Resource resource : doGetResources(location)) {
if (resource.exists()) {
resources.add(resource);
}
else if (validate) {
throw new ResourceNotFoundException(propertyName, resource);
}
}
}
return resources;
}
private Resource[] doGetResources(String location) {
try {
SortedResourcesFactoryBean factory = new SortedResourcesFactoryBean(
this.applicationContext, Collections.singletonList(location));
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to load resources from " + location,
ex);
}
}
private void runScripts(List resources, String username, String password) {
if (resources.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ResourceDatabasePopulator populator = new ResourceDatabasePopulator();
populator.setContinueOnError(this.properties.isContinueOnError());
populator.setSeparator(this.properties.getSeparator());
if (this.properties.getSqlScriptEncoding() != null) {
populator.setSqlScriptEncoding(this.properties.getSqlScriptEncoding().name());
}
for (Resource resource : resources) {
populator.addScript(resource);
}
DataSource dataSource = this.dataSource;
if (StringUtils.hasText(username) && StringUtils.hasText(password)) {
dataSource = DataSourceBuilder.create(this.properties.getClassLoader())
.driverClassName(this.properties.determineDriverClassName())
.url(this.properties.determineUrl()).username(username)
.password(password).build();
}
DatabasePopulatorUtils.execute(populator, dataSource);
}
}
默认Schema脚本名字:
classpath*:schema.sql;
classpath*:schema-all.sql;默认Data脚本名字:
classpath*:data.sql;
classpath*:data-all.sql;如果想使用自定义脚本名字,在yml文件中配置:
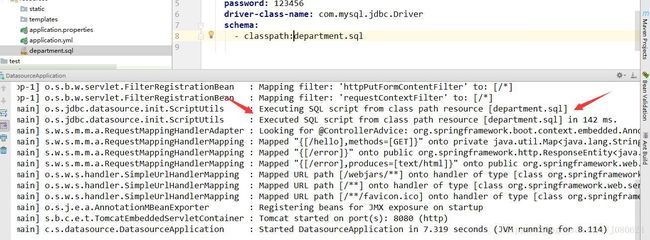
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
schema:
- classpath:department.sql如下图所示: