基于python+whoosh的全文检索实现
whoosh的官方介绍:http://whoosh.readthedocs.io/en/latest/quickstart.html
因为做的是中文的全文检索需要导入jieba工具包以及whoosh工具包
直接上代码吧
from whoosh.qparser import QueryParser
from whoosh.index import create_in
from whoosh.index import open_dir
from whoosh.fields import *
from jieba.analyse import ChineseAnalyzer
from get_comment import SQL
from whoosh.sorting import FieldFacet
analyser = ChineseAnalyzer() #导入中文分词工具
schema = Schema(phone_name=TEXT(stored=True, analyzer=analyser), price=NUMERIC(stored=True),
phoneid=ID(stored=True))# 创建索引结构
ix = create_in("path", schema=schema, indexname='indexname') #path 为索引创建的地址,indexname为索引名称
writer = ix.writer()
writer.add_document(phone_name='name',price ="price",phoneid ="id") # 此处为添加的内容
print("建立完成一个索引")
writer.commit()
# 以上为建立索引的过程
new_list = []
index = open_dir("indexpath", indexname='comment') #读取建立好的索引
with index.searcher() as searcher:
parser = QueryParser("要搜索的项目,比如“phone_name", index.schema)
myquery = parser.parse("搜索的关键字")
facet = FieldFacet("price", reverse=True) #按序排列搜索结果
results = searcher.search(myquery, limit=None, sortedby=facet) #limit为搜索结果的限制,默认为10,详见博客开头的官方文档
for result1 in results:
print(dict(result1))
new_list.append(dict(result1))
注:
Whoosh 有一些很有用的预定义 field types,你也可以很easy的创建你自己的。
whoosh.fields.ID
这个类型简单地将field的值索引为一个独立单元(这意味着,他不被分成单独的单词)。这对于文件路径、URL、时间、类别等field很有益处。
whoosh.fields.STORED
这个类型和文档存储在一起,但没有被索引。这个field type不可搜索。这对于你想在搜索结果中展示给用户的文档信息很有用。
whoosh.fields.KEYWORD
这个类型针对于空格或逗号间隔的关键词设计。可索引可搜索(部分存储)。为减少空间,不支持短语搜索。
whoosh.fields.TEXT
这个类型针对文档主体。存储文本及term的位置以允许短语搜索。
whoosh.fields.NUMERIC
这个类型专为数字设计,你可以存储整数或浮点数。
whoosh.fields.BOOLEAN
这个类型存储bool型
whoosh.fields.DATETIME
这个类型为 datetime object而设计(更多详细信息)
whoosh.fields.NGRAM 和 whoosh.fields.NGRAMWORDS
这些类型将fiel文本和单独的term分成N-grams(更多Indexing & Searching N-grams的信息)
---------------------
出处:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21149391/article/details/79509251
#coding=utf-8
from whoosh.qparser import QueryParser
from whoosh.index import create_in
from whoosh.index import open_dir
from whoosh.fields import *
from jieba.analyse import ChineseAnalyzer
#from get_comment import SQL
from whoosh.sorting import FieldFacet
analyser = ChineseAnalyzer() #导入中文分词工具
schema = Schema(phone_name=TEXT(stored=True, analyzer=analyser), price=NUMERIC(stored=True),
phoneid=ID(stored=True))# 创建索引结构ix = create_in("/home/jack/manage.py", schema=schema, indexname='indexname') #path 为索引创建的地址,indexname为索引名称
ix = create_in("path", schema=schema, indexname='indexname') #path 为索引创建的地址,indexname为索引名称
writer=ix.writer()
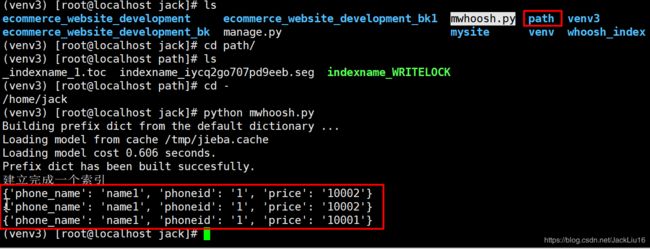
writer.add_document(phone_name='name1',price ="10001",phoneid ="1") # 此处为添加的内容
writer.add_document(phone_name='name1',price ="10002",phoneid ="1") # 此处为添加的内容
writer.add_document(phone_name='name1',price ="10002",phoneid ="1") # 此处为添加的内容
writer.add_document(phone_name='name3',price ="10003",phoneid ="1") # 此处为添加的内容
writer.add_document(phone_name='name4',price ="10004",phoneid ="1") # 此处为添加的内容
print("建立完成一个索引")
writer.commit()
# 以上为建立索引的过程
new_list = []
index = open_dir("path", indexname='indexname') #读取建立好的索引
with index.searcher() as searcher:
parser = QueryParser("phone_name", index.schema)
myquery = parser.parse("name1")
facet = FieldFacet("price", reverse=True) #按序排列搜索结果
results = searcher.search(myquery, limit=None, sortedby=facet) #limit为搜索结果的限制,默认为10,详见博客开头的官方文档
for result1 in results:
print(dict(result1))
new_list.append(dict(result1))