Matlab数据可视化(3):一维数据绘图 I
以下介绍一维数据的可视化。
一. 饼状图、根状图和梯形图
1) 饼状图
(源代码:pie_stem_stairs.m)
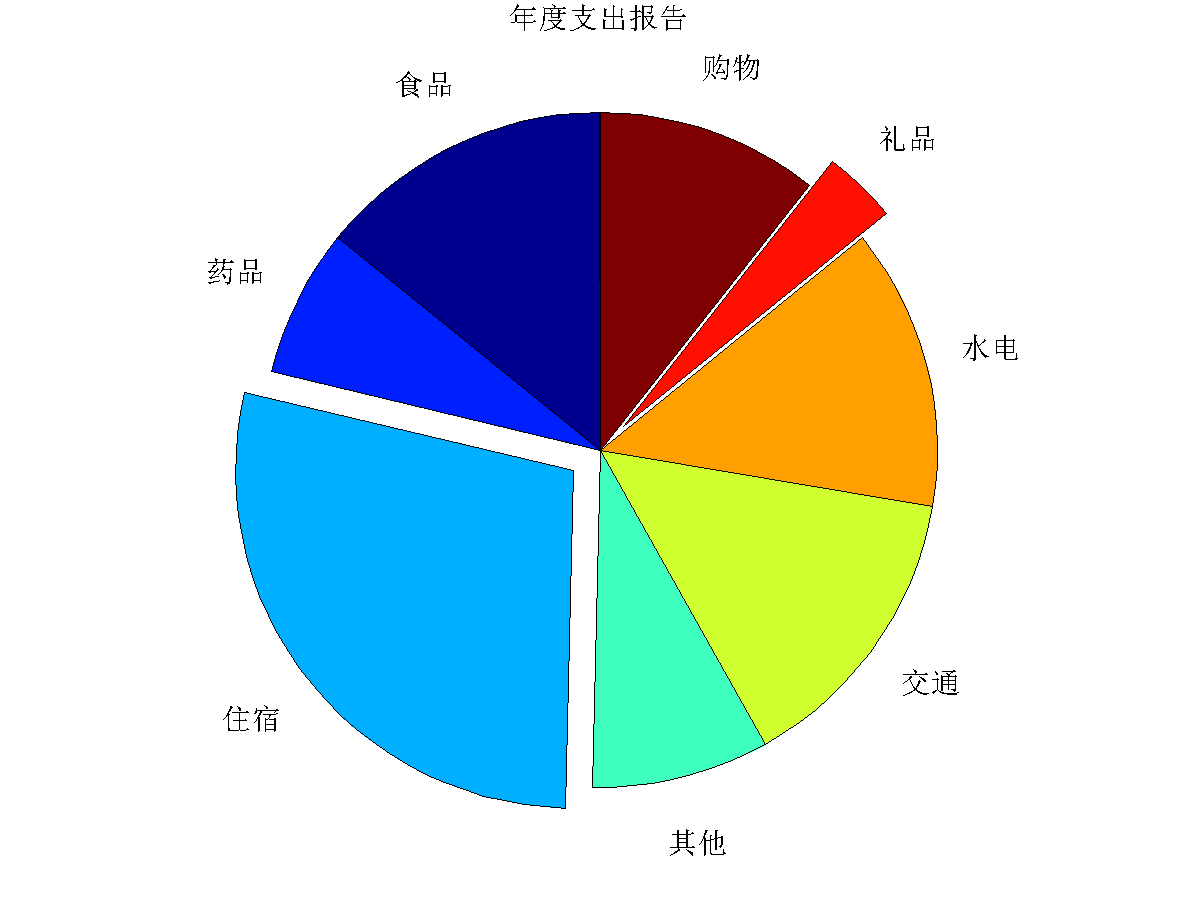
饼状图可以直观地表示百分比的相对大小。饼状图可以由matlab的pie命令绘制。其中,我们可以将某些数据从饼中分离以强调显示(图1)。
Expenses = [20 10 40 12 20 19 5 15];
ExpenseCategories = {'食品','药品','住宿','其他','交通',...
'水电','礼品','购物'};
MostLeastExpensive = ...
(Expenses==max(Expenses)|Expenses==min(Expenses));
figure();
h=pie(gca,Expenses,MostLeastExpensive,ExpenseCategories);
% 命令为每一个数据项返回一个文本句柄(text handle,h的偶数项)
% 可以通过句柄改变字体大小
for i =2:2:16;set(h(i),'fontsize',14);end
% 添加标注
title('年度支出报告','fontsize',14);
图 1
2) 根状图
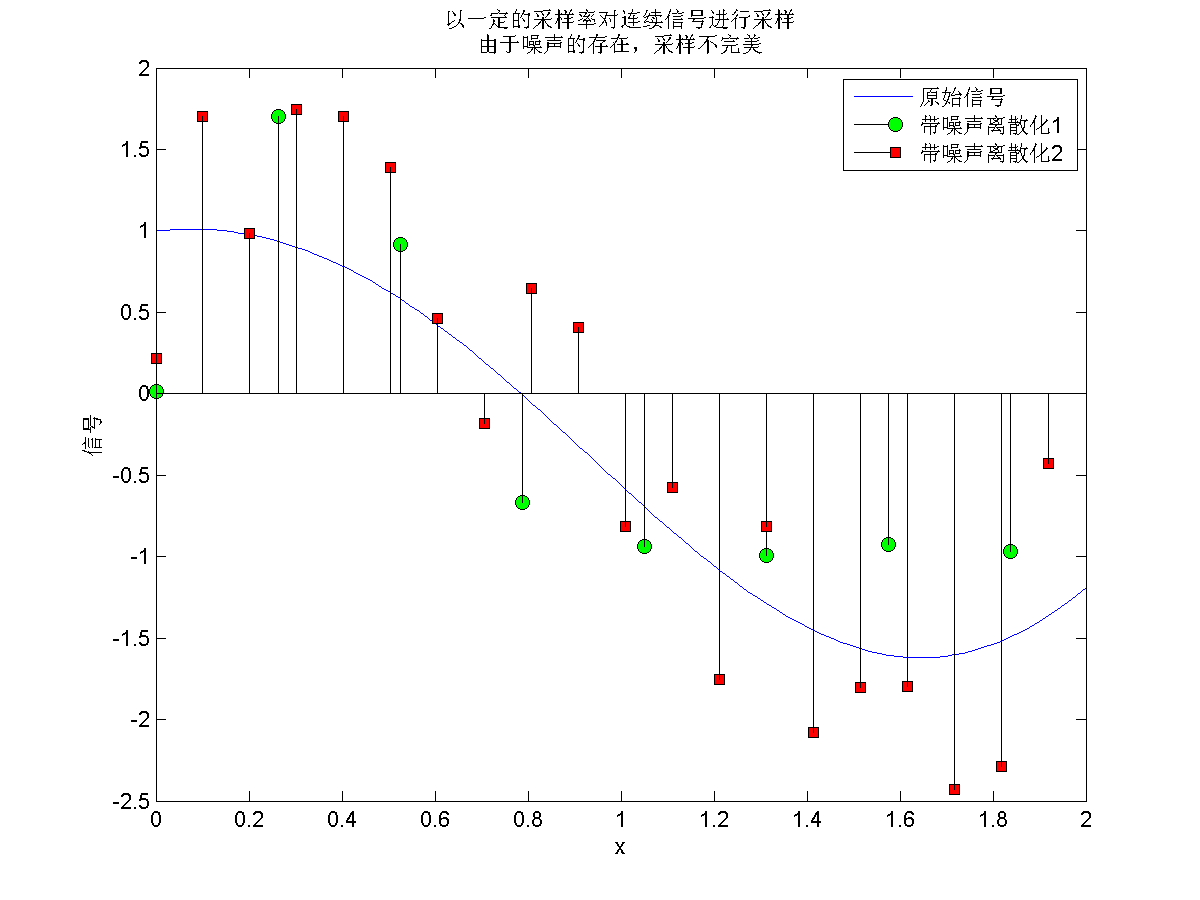
根状图可由stem命令绘制,根状图常用来表示连续信号的离散采样数据(图2)。
%% 根状图
figure;
x = linspace(0,2,100);
x1 = x(1:13:end);
x2 = x(1:5:end);
y = exp(.3*x).*cos(-2*x);
yy = round(rand(1,length(x1)));yy(yy==0)=-1;
y1 = exp(.3*x1).*cos(-2*x1)+yy.*rand(1,length(x1));
yy = round(rand(1,length(x2)));yy(yy==0)=-1;
y2 = exp(.3*x2).*cos(-2*x2)+yy.*rand(1,length(x2));
plot(x,y); hold on;
h1 = stem(x1,y1);
h2 = stem(x2,y2);
% 设置标志的大小和样式
set(h1,'MarkerFaceColor','green','Marker','o','Markersize',7,'Color',[0 0 0]);
set(h2,'MarkerFaceColor','red','Marker','s','Color',[0 0 0]);
xlabel('x');ylabel('信号');
title({'以一定的采样率对连续信号进行采样','由于噪声的存在,采样不完美'});
legend({'原始信号','带噪声离散化1','带噪声离散化2'});
print(gcf,'-dpng','./stem.png');
图 2
3) 梯形图
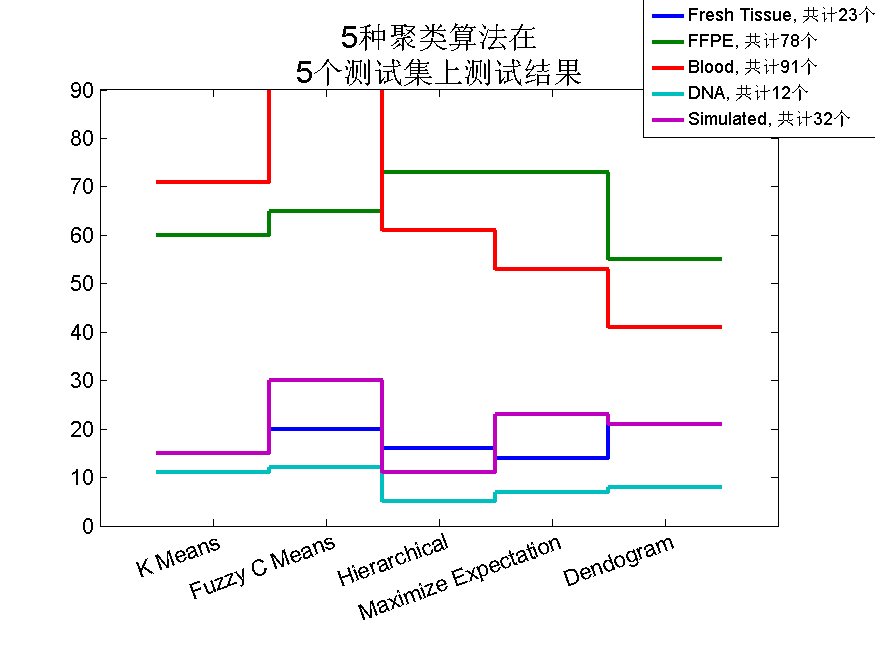
梯形图可由stairs命令得到,它常常用于数据之间连线并无意义的情况下的绘图,在数据密集的情况下,也可以用梯形图代替柱状图。(图3)
%% 梯形图
%figure('units','normalized','position',[0.1 0.1 0.6 0.6]);
figure;
% 加载数据
load algoResultsData.mat
% 增加一行NaN,以使最梯形图最后是一条水平线(而非上升线)
h=stairs([MethodPerformanceNumbers nan(5,1)]');
legendMatrix = {'Fresh Tissue','FFPE',...
'Blood','DNA','Simulated'};
for i = 1:5;
set(h(i),'linewidth',2); % 加粗线条
% y在图例说明后面加注“共计…个”
legendMatrix{i} = [legendMatrix{i} ...
', 共计' num2str(CategoryTotals(i)) '个'];
end
set(gca,'xlim',[0.5 6.5],...
'XTick',1.5:nosOfMethods+1,...
'XTickLabel',{'K Means','Fuzzy C Means',...
'Hierarchical','Maximize Expectation','Dendogram'});
% 添加标注
title({'5种聚类算法在','5个测试集上测试结果'},'fontsize',15);
legendflex(h,... %handle to plot lines
legendMatrix,... %corresponding legend entries
'ref', gcf, ... %which figure
'anchor', {'ne','ne'}, ...%location of legend box
'buffer',[0 0], ... % an offset wrt the location
'fontsize',8,... %font size
'xscale',.5); %a scale factor for symbols
rotateXLabels(gca,20);
set(gca,'position',[0.1139 0.1989 0.7750 0.6638]);
set(gcf,'color',[1 1 1],'paperpositionmode','auto');
图 3
二. 盒形图
(源代码boxplots.m)
盒形图(box plot)又名盒须图(box-and-whisker diagram)。它能在一副图中同时表示多种统计信息。具体而言,包括如下五种统计量:中位数(median,Q2)
上下四分位数(Q1、Q3)和最大最小值。其中,Q1和Q3构成盒子,胡须分别向上和向下延伸到最大值和最小值处。
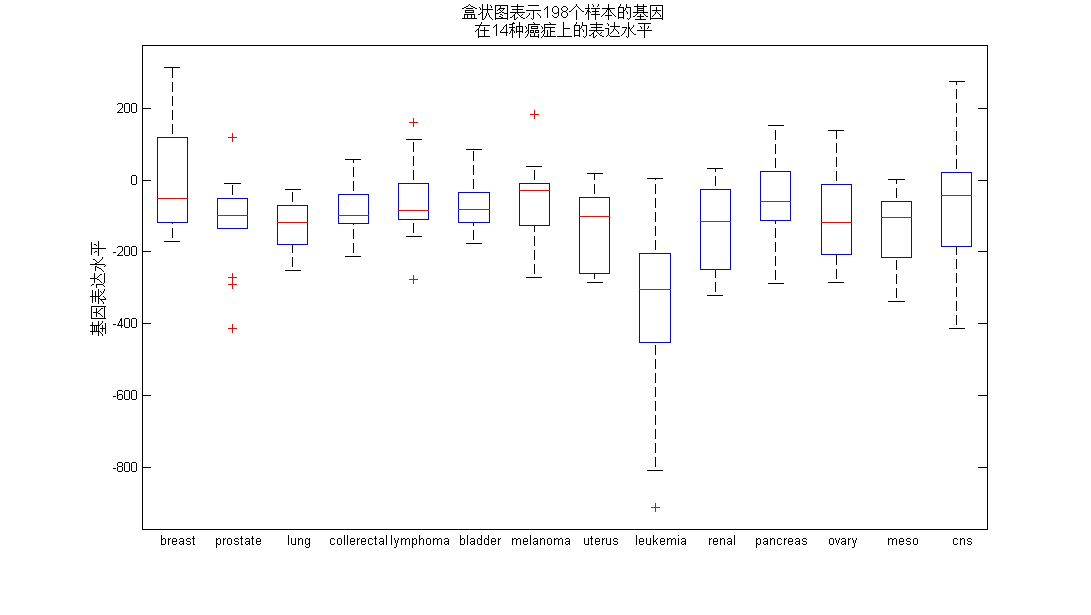
接下来,我们利用matlab自带的命令plotbox,绘制14种癌症的第105号基因表达水平的盒形图(图4)。
% 加载14种癌症基因表达数据,共16063组基因,144+54=198个样本
load 14cancer.mat
figure('units','normalized','Position',[0 0 0.8 0.8]);
data = [Xtrain(:,0105); Xtest(:,0105)];
labels = [ytrainLabels ytestLabels];
boxplot(data,labels,'labels',classLabels);
ylabel('基因表达水平','fontsize',12);
title({'盒状图表示198个样本的基因','在14种癌症上的表达水平'},'fontsize',12);
图 4
第三方函数aboxplot,提供了更高级的功能,我们可以为盒形图上色,同时绘制多组盒形图等。
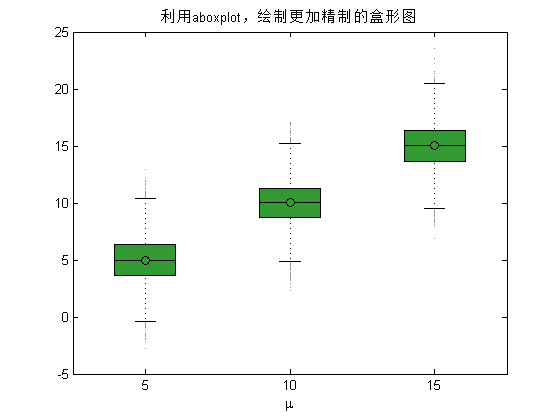
首先,绘制单独一组盒形图(图5)。
figure;
x1 = normrnd(5,2,10000,1); % 期望为5,方差为2的正态分布的10000个数据
x2 = normrnd(10,2,10000,1); % 期望为10,方差为2的正态分布的10000个数据
x3 = normrnd(15,2,10000,1); % 期望为15,方差为2的正态分布的10000个数据
x = cat(2,x1,x2,x3); % 将三组数据连接成 10000 x 3 的矩阵
aboxplot(x,'labels',[5,10,15],'Colorgrad','green_down','OutlierMarker','*','OutlierMarkerSize',1,'WidthE',0.2,'WidthS',0.6); % 利用aboxplot绘图
xlabel('\mu'); % X轴标签
title('利用aboxplot,绘制更加精制的盒形图');
图5
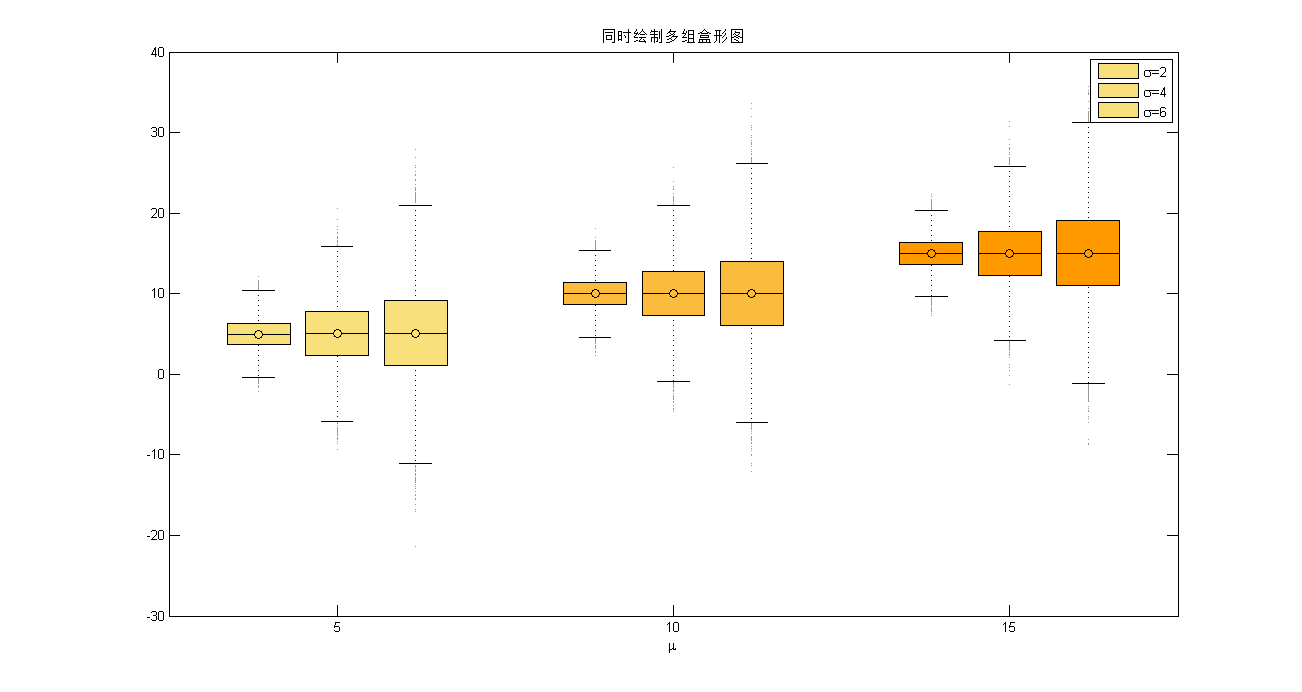
然后,我们绘制含有三组数据的盒形图(图6)。
figure;
% 第一组标准差都为2
x1 = normrnd(5,2,10000,1);
x2 = normrnd(10,2,10000,1);
x3 = normrnd(15,2,10000,1);
% 第二组标准差都为4
y1 = normrnd(5,4,10000,1);
y2 = normrnd(10,4,10000,1);
y3 = normrnd(15,4,10000,1);
% 第三组标准差都为6
z1 = normrnd(5,6,10000,1);
z2 = normrnd(10,6,10000,1);
z3 = normrnd(15,6,10000,1);
% 将每组数据连接成 10000 x 3 的矩阵
x = cat(2,x1,x2,x3);
y = cat(2,y1,y2,y3);
z = cat(2,z1,z2,z3);
% 将三组数据连接成 3 x 10000 x 3 的矩阵
h = cat(1, reshape(x,[1 size(x)]), reshape(y,[1 size(y)]), reshape(z,[1 size(z)]));
aboxplot(h,'labels',[5,10,15],'colorgrad','orange_down','colorrev',true); % 绘图; 颜色默认为蓝色,这里设为橙色; colorrev默认为false,可以改为默认值观察变化
xlabel('\mu'); % X轴标签
legend('\sigma=2','\sigma=4','$\sigma=6'); % 添加图例
title('同时绘制多组盒形图');图 6
三. 迷你图(sparkline)
(源代码:sparklines.m)sparkline最初是由Edward Tufte(爱德华塔夫特)提出的,是一类信息体积小和数据密度高的图表。目前它被用作一些测量,相关的变化的信息呈现的方式,如平均温度,股市交投活跃。sparkline也常常以一组多条的形式出现在柱状图,折线图当中。
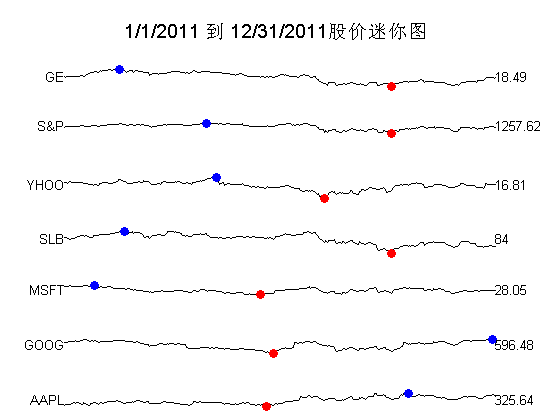
以下我们用迷你图绘制谷歌等7家公司2011年全年的股价信息。(图7)
%% 加载数据
[dt{1} dateD{1}] = xlsread('AAPL_090784_012412.csv');
[dt{2} dateD{2}] = xlsread('GOOG_090784_012412.csv');
[dt{3} dateD{3}] = xlsread('MSFT_090784_012412.csv');
[dt{4} dateD{4}] = xlsread('SLB_090784_012412.csv');
[dt{5} dateD{5}] = xlsread('YHOO_090784_012412.csv');
[dt{6} dateD{6}] = xlsread('S&P_090784_012412.csv');
[dt{7} dateD{7}] = xlsread('GE_090784_012412.csv');
stocks = {'AAPL','GOOG','MSFT','SLB','YHOO','S&P','GE'};
rangeMIN = datenum('1/1/2011');
rangeMAX = datenum('12/31/2011');
%% 数据预处理
for i = 1:length(dt)
% 数据处理
% 将日期转化为数字形式
dateD{i} = datenum({dateD{i}{2:end,1}});
% 查找日期区间
idx = find(dateD{i} >= rangeMIN & dateD{i} <= rangeMAX);
dt{i} = dt{i}(idx);
% 提取区间内的数据
dateD{i} = dateD{i}(idx);
% 标准化数据
dtn{i} = dt{i}./max(dt{i});
clear idx
labels2{i} = num2str(dt{i}(end));
end
%% 绘制迷你图
sparkline(dateD,dtn,stocks,labels2);
图7
实际的绘制工作由sparkline命令完成,方法是将7条表示股价信息的曲线绘制在同一个figure中,高度分别相关若干距离。代码如下:
function sparkline(xdata,ydata,labels1,labels2)
%SPARKLINE(XDATA,YDATA,LABELS1,LABELS2) creates a graph with sparklines
% XDATA and YDATA are cell arrays of vectors of x and corresponding y
% values. LABELS1 give the labels you want corresponding to each sparkline
% to be located at the start of the line. LABELS2 give the labels you want
% corresponding to each sparkline to be located at the end of the line.
% No borders necessary - span the axes out to total available space
% make the plots by bumping up each sparkline with an arbitrary unit of
% separation. Here unitOfSep=1;
unitOfSep=1;
figure; axes('position',[0 0 1 .9]);hold on;
endPt = -1;
startPt = 1e100;
for i = 1:length(xdata)
% Plot SparkLines
plot(xdata{i}, ydata{i}+ (i-1)*+unitOfSep,'k');
maxp{i} = find(ydata{i}==max(ydata{i}));
minp{i} = find(ydata{i}==min(ydata{i}));
plot(xdata{i}(maxp{i}),ydata{i}(maxp{i})+ (i-1)*+unitOfSep,'bo','MarkerFaceColor','b');
plot(xdata{i}(minp{i}),ydata{i}(minp{i})+ (i-1)*+unitOfSep,'ro','MarkerFaceColor','r');
text(xdata{i}(end), mean(ydata{i})+ (i-1)*+unitOfSep,labels1{i},'HorizontalAlignment','right');
text(xdata{i}(1), mean(ydata{i})+ (i-1)*+unitOfSep,labels2{i},'HorizontalAlignment','left');
endPt = max([xdata{i}(1) endPt]);
startPt= min([xdata{i}(end) startPt]);
end
text(startPt+50, i*unitOfSep+.7,'1/1/2011 到 12/31/2011股价迷你图','fontsize',14);
set(gca,'visible','off','ylim',[0+unitOfSep/2 i*unitOfSep+unitOfSep/2],...
'yticklabel',[],'xlim',[startPt-.15*(endPt-startPt) endPt+.15*(endPt-startPt)],...
'xticklabel',[],'TickLength',[0 0]);
set(gcf,'Color',[1 1 1],'Paperpositionmode','auto');
四. 堆叠折线图(stacked line graph)
(源代码:stackedlines.m)
堆叠折线图可以表示多组数据变化趋势。以下我们利用绘制面积图的area命令制作堆叠折线图。我们已有15个名字的受欢迎程度在各个年份的排名,我们即要用图像表示出这个趋势。(图8)
%% 加载数据
[ranksoverdecades names] = xlsread('MockDataNameVoyager.xlsx');
sex = names(2:end,2);
names = names(2:end,1);
years = ranksoverdecades(1,:);
ranksoverdecades = ranksoverdecades(2:end,:);
ranksoverdecades = ranksoverdecades';
% 将男孩名字和女孩名字分开
males = find(strcmp(sex,'M'));
fmales = find(strcmp(sex,'F'));
ymax=max(max(cumsum(ranksoverdecades,2)));
% 计算名字标签的位置的y坐标
nameLoc = cumsum(ranksoverdecades(end,:));
nameLoc = [0 nameLoc];
nameLoc = (nameLoc(1:end-1) + nameLoc(2:end))/2;
%% 布局
figure('units','normalized','Position',[ 0.3432 0.1472 0.6542 0.7574]);
% 创建主坐标轴
axes('position',[.05,.1,.87,.85],'ylim',[0 ymax],'xlim',[min(years) max(years)],'YAxisLocation','right',...
'ytick',nameLoc,'yticklabel',names,'ticklength',[0.01 0.05],'tickdir','out','fontsize',14);
% 另建一个坐标轴,绘制面积图
axes('Position',get(gca,'Position'));
% 绘制拆线
h = area(years,ranksoverdecades);
% 按性别设定颜色,男孩为蓝色,女孩为粉色
set(h(males),'FaceColor',[100 149 237]/255)
set(h(fmales),'FaceColor',[255 192 203]/255);
% fix edgecolor and x and y limits
set(h,'edgecolor',[.5 .5 .5]) % Set all to same value
set(gca,'ylim',[0 ymax],'xlim',[min(years) max(years)],'xticklabel',[],'fontsize',14);
box on;
% annotate the graph
title('婴儿名字趋势图','Fontsize',14);
ylabel('排名随年份的变化','Fontsize',14);
text(mean(get(gca,'xlim')),-11,'年份','Fontsize',14);
图 8