解析request.getInputStream()
https://blog.csdn.net/u010018421/article/details/52833346
前几天在做文件上传,当时突然搞不清楚上传原理,没办法下手,所以趁着周末研究了一下:
带有文件上传的form表单:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
由于enctype=”multipart/form-data”,所以不能使用request.getParameter()及相关方法获取,并且form表单具有上传文件功能,离不开io流,所以讲request.getInputStream()取到的输入流输出到指定位置。发现上传的图片已经损坏,并且比原来大了一点。当时感觉很奇怪:因为我的form表单还有普通的文本域,哪里去了?
所以将request.getInputStream()得到的输入流打印到了一个*.txt文本中,
文件开头: 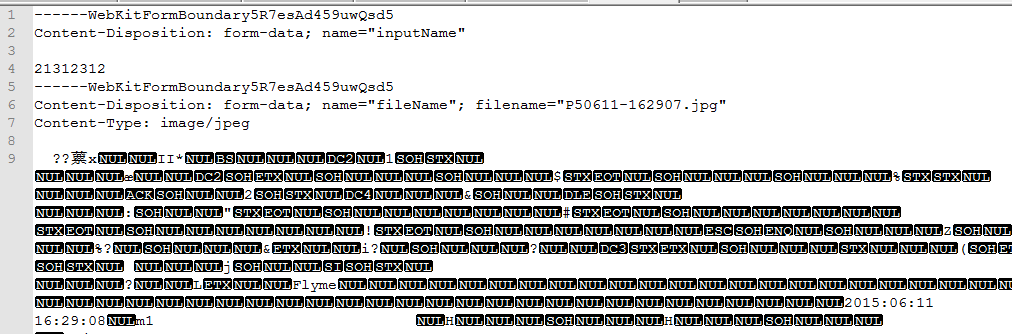
文件结尾: 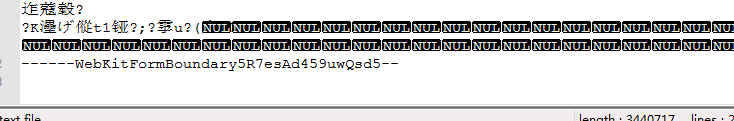
可以发现,前8行可以解析,第9行开始是乱码(实际上乱码才是图片的数据),网上查阅发现:是将form表单的所有提交的内容都在request.getInputStream()中,所以自己编写代码解析了一下整个inputStream。
声明:对*.txt的解析的部分思路来源于网上。具体什么位置没找到。
贴上代码:
private static byte[] subBytes(byte[] b, int from, int end) {
byte[] result = new byte[end - from];
System.arraycopy(b, from, result, 0, end - from);
return result;
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1.判断当前request消息实体的总长度
int totalBytes = request.getContentLength();
System.out.println("当前数据总长度:" + totalBytes);
// 2.在消息头类型中找出分解符,例如:boundary=----WebKitFormBoundaryeEYAk4vG4tRKAlB6
String contentType = request.getContentType();
int position = contentType.indexOf("boundary=");
String startBoundary = "--" + contentType.substring(position+"boundary=".length());
String endBoundary = startBoundary + "--";
//将request的输入流读入到bytes中
InputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(inputStream);
byte[] bytes = new byte[totalBytes];
dataInputStream.readFully(bytes);
dataInputStream.close();
//将字节读入到字符流中
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new StringReader(new String(bytes)));
//开始读取reader(分割form表单内的表单域类型:文本或者文件)
//记录当前的读取行对应的bytes;
int temPosition = 0;
boolean flag = false;
int end = 0;
while(true){
//当读取一次文件信息后
if(flag){
bytes = subBytes(bytes, end, totalBytes);
temPosition = 0;
reader = new BufferedReader(new StringReader(new String(bytes)));
}
//读取一行的信息:------WebKitFormBoundary5R7esAd459uwQsd5,即:lastBoundary
String str = reader.readLine();
System.out.println("this line is:" + str);
//换行算两个字符
temPosition += str.getBytes().length + 2;
//endBoundary:结束
if(str==null||str.equals(endBoundary)){
break;
}
//表示头信息的开始(一个标签,input,select等)
if(str.startsWith(startBoundary)){
//判断当前头对应的表单域类型
str = reader.readLine(); //读取当前头信息的下一行:Content-Disposition行
temPosition += str.getBytes().length+2;
int position1 = str.indexOf("filename="); //判断是否是文件上传
//such as:Content-Disposition: form-data; name="fileName"; filename="P50611-162907.jpg"
if(position1 == -1){//表示是普通文本域上传
}else{//position1!=-1,表示是文件上传
//解析当前上传的文件对应的name(input标签的name),以及fieldname:文件名
int position2 = str.indexOf("name=");
//去掉name与filename之间的"和;以及空格
String name = str.substring(position2 + "name=".length() + 1, position1-3);
//去掉两个"
String filename = str.substring(position1 + "filename=".length() + + 1,str.length() - 1);
//读取行,such as:Content-Type: image/jpeg,记录字节数,此处两次换行
temPosition += (reader.readLine().getBytes().length + 4);
end = this.locateEnd(bytes, temPosition, totalBytes, endBoundary);
String path = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
DataOutputStream dOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(path + "/test.jpg")));
dOutputStream.write(bytes, temPosition, end-temPosition-2);
dOutputStream.close();
flag = true;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 定位当前头信息的结束位置
* @param bytes
* @param start :开始位置
* @param end :结束位置
* @param endStr :比较字符串
* @return
* TODO
*/
public int locateEnd(byte[] bytes,int start,int end,String endStr){
byte[] endByte = endStr.getBytes();
for(int i=start+1;iif(bytes[i]==endByte[0]){
int k = 1;
while(kif(bytes[i+k] != endByte[k]){
break;
}
k++;
}
System.out.println(i);
if(i==3440488){
System.out.println("start");
}
//返回结束符的开始位置
if(k == endByte.length){
return i;
}
}
}
return 0;
} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
运行完此代码,可以发现文件已上传到指定位置,可以正常打开,哈哈,不枉我今天凌晨两点才睡觉。
以上是我对request.getInpuStream()的理解。希望对大家有帮助。
最后说一下,没有对同时上传多个文件进行测试,文件的上传位置也是随意指定的.