C++上机的微薄建议
C++上机实验
对于本次的c++上机考试,我总结和预测了一下考试的内容、考点,希望到对各位有所帮助。在复习的时候能够少走弯路,考试的时候提高做题速度,能做一道是一道。有疏漏的地方还请各位大佬见谅。
有什么没涉及到的经验还请您慷慨解囊,让我们班都考个好成绩。
考试内容及考点
- 类
- 运算符的重载
- 继承(一般为public 公有继承,估计到后面要考虑 virtual虚继承)
- 虚函数
- 抽象类
类的题千万看清楚main函数以及输出的内容,确定出这个类所需要的数据成员和成员函数、要重载那些运算符、以及友元函数(这个是最容易被看错的)。
好了不说废话了,上例题
三个私有成员变量,两个构造函数(根据创建了两个对象,然后输出了两句不同的话可以知道)
两个没有返回值的SetClock(23,59,59) 、Show() 函数。
而这些的具体实现都在输出结果中推测。可考试时先把具体的函数列在纸上,方便实现
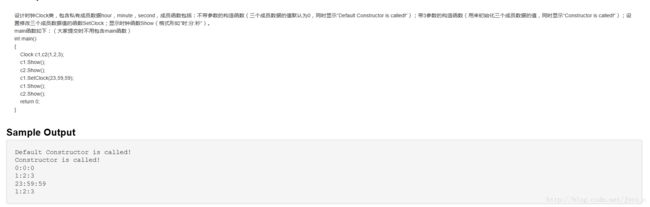
在众多类中,时间类(时、分、秒)算是复杂一点的,举个栗子:
class Clock
{
private:
int hour,minute,second;
public :
Clock(int h=0,int m=0,int s=0)
{
hour=h;minute=m;second=s;
}
void Show()
{
cout<":"<":"<void fun(Clock &t) //fun函数起到一个对传进来的对象的时、分、秒调整规范
{
int sum=t.hour*3600+t.second+t.minute*60;
while(sum<0) //主要对付sum小于0的情况。
{
sum+=3600*24; //回到昨天
}
t.hour=sum/3600;
t.minute=(sum-t.hour*3600)/60;
t.second=sum-t.hour*3600-t.minute*60;
t.hour%=24; //存在sum很大,虽然minute和second 可以取余,但hour>=24
}
Clock operator++() //前置++ 下面会提到
{
this->second++;
fun(*this); //修改完就调整格式
return *this;
}
Clock operator++(int) //后置++
{
Clock old(*this);
this->second++;
fun(*this); //
return old;
}
Clock operator--() //前置++
{
this->second--;
fun(*this); //
return *this;
}
Clock operator--(int ) //后置++
{
Clock old(*this);
this->second--;
fun(*this); //
return old;
}
int operator-(Clock &t) //特别注意这里返回值为int ,因为是两个对象相减得到一个很大的数字,看诡异的输出,就要猜到他的函数是什么样子
{
int sum1=hour*3600+minute*60+second;
int sum2=t.hour*3600+t.minute*60+t.second;
return sum1-sum2;
}
}; class Date
{
private:
int year,month,day;
int IsLeapYear(int y) //返回y年是否闰年,是返回1,否则返回0,可用于DaysOfMonth闰年2月的计算
{
if(y%4==0||y%400==0&&y%100!=0)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int DaysOfMonth(int y,int m) //返回y年m月的天数
{
int d;
switch(m)
{
case 1: case 3:case 5:case 7:case 8:
case 10: case 12:
d=31;break;
case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11:
d=30;break;
case 2:
{
d=28+IsLeapYear(y) ;
}break;
}
return d;
}
public:
Date(int y=2015,int m=5,int d=20)
{
year=y;
month=m;
day=d;
}
void Set(int y,int m,int d)
{
year=y;
month=m;
day=d;
}
void fun(Date & t) //调整日期格式的函数
{
while(true)
{
if(t.day<=DaysOfMonth(t.year,t.month)&&t.day>0&&t.month<=12&&t.month>0) //满足格式就break
break;
if(t.day>DaysOfMonth(t.year,t.month)) //天数超出了这个月的
{
t.day-=DaysOfMonth(t.year,t.month); //调整day
t.month++; //月份++
if(t.month>12) //调整月份
{
t.month=1;
t.year++;
}
}
if(t.day<=0)
{
t.month--;
if(t.month<=0)
{
t.month=12;
t.year--;
}
t.day+=DaysOfMonth(t.year,t.month);
}
}
}
friend ostream & operator<<(ostream &os,Date &t)
{
os<"年"<"月"<"日";
return os;
}
Date operator++(int)
{
Date old(*this);
this->day++;
fun(*this);
return old;
}
Date operator--(int)
{
Date old(*this);
day--;
fun(*this);
return old;
}
Date &operator++()
{
day++;
fun(*this);
return *this;
}
Date &operator--()
{
day--;
fun(*this);
return *this;
}
Date operator+(int n)
{
Date t(*this);
t.day+=n;
fun(t);
return t;
}
Date operator-(int n)
{
Date t(*this);
t.day-=n;
fun(t);
return t;
}
}; 上面两个题目还有一些细节是,
1. 运算符的重载
假设有对象 T,P
前置++,即 P= ++T ,–同样适用
Date &operator++() // 返回引用
{
day++; //先++ 再返回去赋值,原理简单,不存在新创建对象。
return *this;
}后置++ ,即p=T++ ;
Date operator++(int) //特别注意返回值不能是引用,而且(int)
{
Date old(*this); //需要创建一个新的对象。
this->day++; //是先赋值,后++,就是返回的这个值是未++之前的,++后的值改变的原来这个*this。
return old;
}还有就是重载输出>>运算符 如果看到输出调用的不是show而是cout<<"Date 1:"<
那么需要重载<<运算符函数 而且必须是友元函数
friend ostream & operator<<(ostream &os,Date &t)
{
os<"年"<"月"<"日"; //确立好输出格式
return os; //返回这个对象,返回这个对象,返回这个对象
}`
如果看到`cin>>T` T为对象,需要重载>>运算符,但一般不常见
`friend istream & operator>>(istream &is,Date &t)
{
is>>t.year>>t.month>>t.day;
return is;
} 额,需要注意的是 不要 = 的重载 还有其他的重载就不过多说明了
还有就是如果有成员函数有char a[100] 字符串类型,include
#include接下来是继承。一般都是public 公有继承,
#include0;y=0;
}
Point(int xx,int yy)
{
x=xx;y=yy;
cout<<"Function #2 is called!"<void Show()
{
cout<<"("<","<")"<cout<<"Function #3 is called!"<class Circle:public Point //注意基类的私有成员不能在派生类拿出来用,而且考试一般不会让你把基类的私有变为保护。
{
private:
int radius;
public:
Circle():Point(1000,1000) //需要注意输出结果,对应哪种构造函数,因为参数可能会有差异
{
cout<<"Function #4 is called!"<0;
}
Circle(int x,int y,int r):Point(x,y)
{
radius=r;
cout<<"Function #5 is called!"<int r):Point(p)
{
radius=r;
cout<<"Function #6 is called!"<int r):Point(100,100)
{
radius =r;
cout<<"Function #7 is called!"<10;
cout<<"Function #8 is called!"<void Show()
{
cout<<" Radius="<" "<<"Center=";
Point::Show(); //要调用基类的同名函数,用基类名::去访问
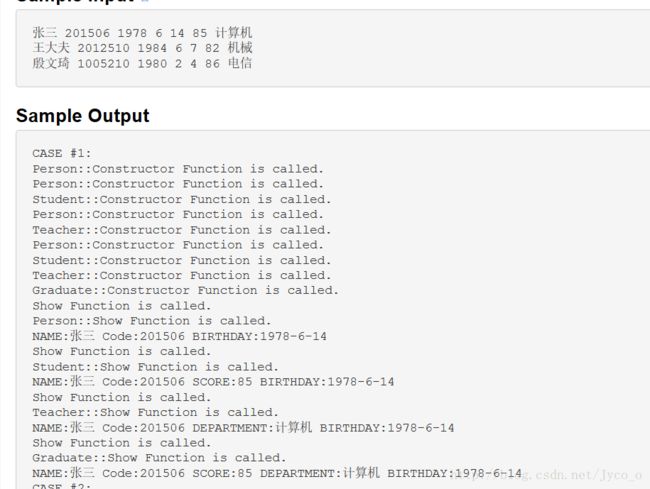
cout<<"Function #9 is called!"< 多个类继承的时候,有一种叠加的效果,四个类
#includevirtual void Show()
{
cout<<"Person::Show Function is called."<cout<<"NAME:"<" Code:"<" BIRTHDAY:"<"-"
<"-"<class Student: virtual public Person //虚继承
{
private:
string name;
int code;
int year,month,day;
int score;
public:
Student(string n,int c,int y,int m,int d,int s):Person(n,c,y,m,d)
{
name=n;
code=c;
year=y;
month=m;
day=d;
score=s;
cout<<"Student::Constructor Function is called."<virtual void Show()
{
cout<<"Student::Show Function is called."<cout<<"NAME:"<" Code:"<" SCORE:"<" BIRTHDAY:"<"-"
<"-"<class Teacher:virtual public Person //虚继承
{
private:
string name;
int code;
int year,month,day;
string department;
public:
Teacher(string n,int c,int y,int m,int d,string dd):Person(n,c,y,m,d)
{
name=n;
code=c;
year=y;
month=m;
day=d;
department=dd;
cout<<"Teacher::Constructor Function is called."<virtual void Show()
{
cout<<"Teacher::Show Function is called."<cout<<"NAME:"<" Code:"<" DEPARTMENT:"<" BIRTHDAY:"<"-"<"-"<class Graduate :public Student,public Teacher
{
private:
string name;
int code;
int year,month,day;
string department;
int score;
public:
Graduate(string n,int c,int y,int m,int d,int s,string dd)
:Person(n,c,y,m,d), //特别注意这里的对所有基类的构造函数,因为输出结果“Person::Constructor Function is called. ··········
”顺序是从基类往下的
Student(n,c,y,m,d,s),
Teacher(n,c,y,m,d,dd)
{
name=n;
code=c;
year=y;
month=m;
day=d;
score=s;
department=dd;
cout<<"Graduate::Constructor Function is called."<void Show()
{
cout<<"Graduate::Show Function is called."<cout<<"NAME:"<" Code:"<" SCORE:"<" DEPARTMENT:"<" BIRTHDAY:"<"-"<"-"<void Show(Person *p)
{
cout<<"Show Function is called."<Show();
} 这是多重继承。

如果是虚继承,在你、你爸、你妈 的类里设置了你爷的名字都是同一个人。

这里的话,设置爷爷辈的名字,你需要分开情况,因为你爸你妈各自带着一个。
这只是在说明virtual对于基类的修改关系,并不意味着Graduate 上面有三种不同的对象,归根到底,是Graduate 的三种特有的属性,加virtual 会让这种属性的联系更加符合实际。
最后一定要注意空格,空格,空格。最后上传的时候一定要盯清楚,自己的输出和题目的输出。
好了就说这么多了。希望能对大家有所帮助。也希望大家能多多贡献自己的力量,让我们班更强大。
有诸多毛病和遗漏还请多多包涵,找我商讨。我定改之。