Android输入系统解析及Native层模拟按键方案
Android输入系统解析及Native层模拟按键方案
目录
1 Android输入系统
1.1 Android Input核心交互
1.1.1 文件节点读写
1.1.2 Framework层抓取事件
1.1.2 节点传输协议
1.2 模拟按键方式
1.2.1 Java层方案
1.2.2 C层方案
2 Amlogic模拟按键实践
2.1基于鼠标的本地模拟
2.2 Framework层实践案列简述
1 Android输入系统
Android输入系统涉及到驱动,HAL|C 及Framework层,这里聚焦于驱动与本地执行层间的交互。其架构参考如下
1.1 Android Input核心交互
如上图,本篇分析聚焦于Native层与Kernel交互,帮助梳理c/c++层模拟按键技术支持。这里分为两个部分,文件节点读写及节点传输协议解析
1.1.1 文件节点读写
这里来分析下Android系统针对输入设备的读写逻辑,先来看下驱动写输入事件到文件节点
定位文件到drivers/input/input.c,这是Android input子系统核心实现
subsys_initcall(input_init);
module_exit(input_exit);这里可以看到,input是内核加载即加载的核心驱动,下面来看下其引导函数
很明显,这里主要做了几件事,在sys文件系统及proc文件系统建立对应目录,申请字符设备号等。这块涉及到input子系统初始化,不展开。这里关注驱动写事件到文件节点(文件节点在对应的设备注册时创建)。
一般的设备中断时,从其寄存器读取事件通过input系统input_report_abs函数上传,如下
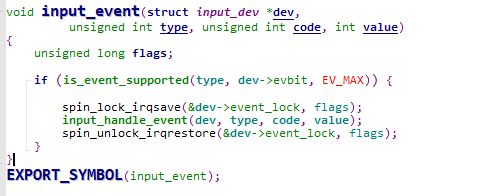
其在input.h中以inline实现,下面来看下input_event函数
这里通过自旋锁禁用本地中断,完成一次中断处理(此时处于中断上下文),在调用input_handle_event数据前,通过is_event_supported来查看硬件设备支持的事件类型,在adb中可以通过命令getevent –p查看,编者的amlogic平台如下:
下面来看input_handle_event函数
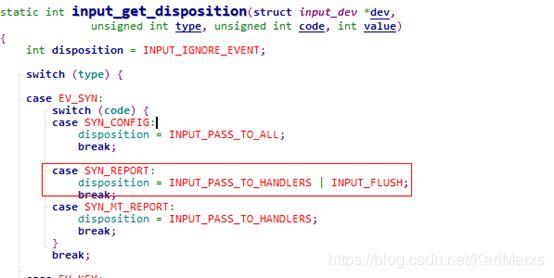
这里首先获取对此事件的处理策略,再处理,这里简单来看下此函数
可以看到对tpye=ev_syn的事件,其处理flag为INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS | INPUT_FLUSH,同理查看ev_rel的处理flag为INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS
此时回到input_handle_event函数,来分析
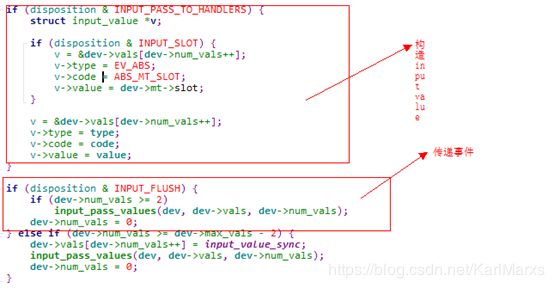
这里有个重点,就是普通的事件上报,在第一步完成后,面临两个策略:
1 如果flag中有inpu_flush,则完成此事件上报
2 如果flag中午inpu_flush,但vals数组个数如果是max-1,则也需要分段上报。这里假设满足上面中的任何一条件,继续来看
这里首先通过rcu_read_lock(),进入读端临界区读取变量,之后通过input_to_handler来处理事件。这里先不关注重复事件处理,接着来看input_to_handler
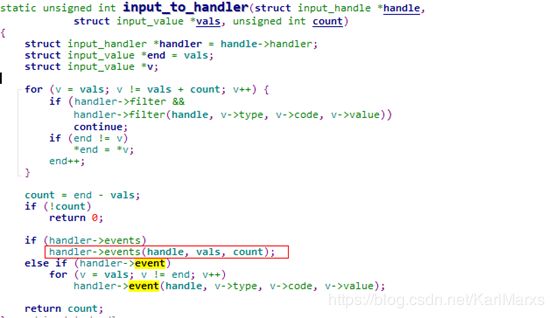
这个函数,整体逻辑就是先filter事件,对于有效事件再通过handle来传递。
这里需要注意下,输入事件过滤的连续性,否则for循环处理逻辑就有问题
这里调用handler->events函数处理,这里需要说明下,此函数指针注册在evdec.c中,这里简单提一下,可深入如下:
接上文,这里来分析evdev-event函数,其内部又调用evdev-events函数,展开来看
这里可以看到数据通过数组指针传递到evdev子系统,待其处理,接下来看下evdev是如何处理这一组输入事件的
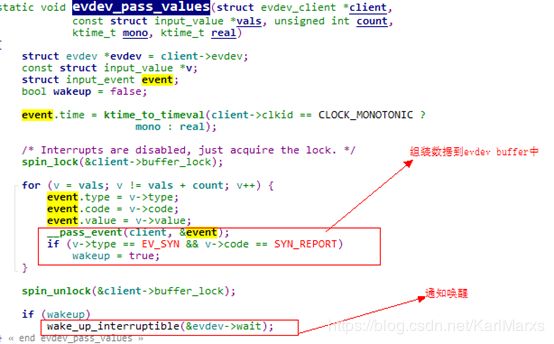
如注释,这里主要分为两步,即是组装事件到evdev的buffer中,第二部通知唤醒
先来看下如何组装批量数据
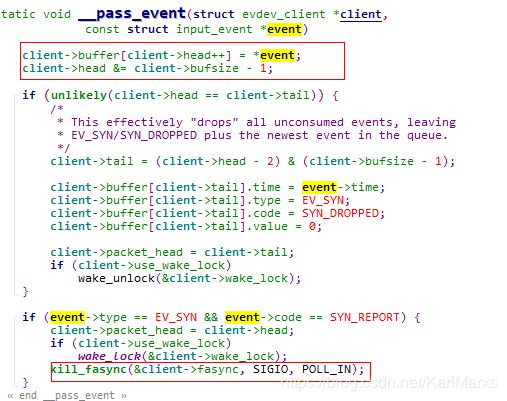
这里主要是把数据放入client->buffer。(kill_fasync异步通知机制这里暂不涉及)
接上文在组装完事件数据后,通过wake_up_interruptible通知唤醒到注册在等待队列上的进程。该函数不能直接的立即唤醒进程,而是由调度程序转换上下文,调整为可运行状态。在这个语境下次进程就是当前进程,由于内核写文件节点逻辑处于中断上下文,猜测应该在进程上下文进程因为一些条件阻塞在此等待队列中,此时就被唤醒了,来处理evdev_client中的buffer数组了。简单参考如下(evdev_read函数):
1.1.2 Framework层抓取事件
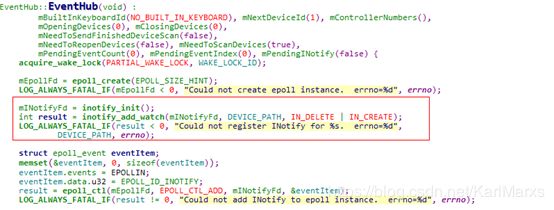
下个阶段来简单分析下输入事件的读取,基于input系统框架图,完成事件收发的是EventHub对象,这里来看下其构造方法
这里,device_path为/dev/input,此时将监控此目录的inotify fd加入到epoll中。
在INPUT-READER系统中通过EventHub.getevents()来获取事件,这个函数比较复杂,这里分步来描述下,怎么读取事件的,这涉及到后期的模拟按键
第一步:
这里声明了event 及 capacity,为后期循环读取事件的标杆。
第二步:
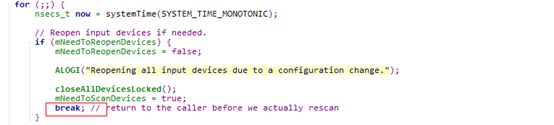
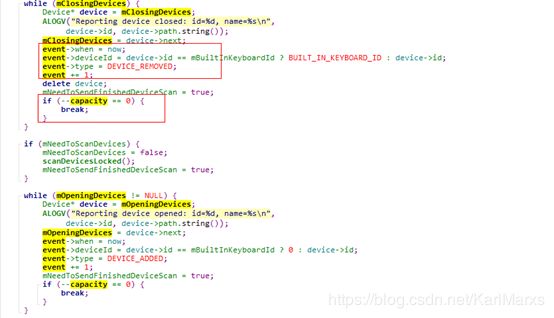
判断,是否有需要打开设备,如果有,直接跳出循环进行对应逻辑,可以看到此处理优先级比较高
第三步:
这里可以看到在一次循环中优先处理设备打开及关闭,同步的构造event事件。
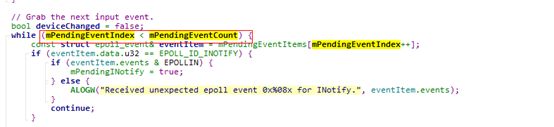
到这一步才开始处理正式的设备事件,判断条件依赖mPendingEventIndex < mPendingEventCount,此循环通过这个来处理事件处理。
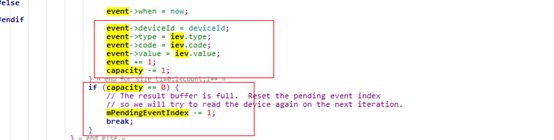
此时判断,buffer缓存是否用完,若用完,则直接完成此一轮循环,直到从kernel上报那一批数据都处理完,这个是核心点。
第四步:
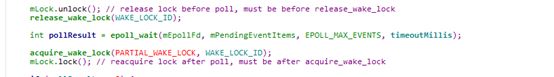
如果经过前面三步处理,还没有跳出循环,说明已经没有了设备插拔事件,以及没有正式事件上报事件。此时开始进入epoll_wait函数显示阻塞函数,以等待kernel或者模拟端事件来临,开启下一批事件上报。
以上四步,目前来看有几点需要重点注意:
1 提取数据通过一个大循环来处理底层同一批次事件,类似一个水磊,循环不觉。
2 同一批次数据如果处理不完,需要经过几个循环处理,处理完才可以处理下一批次事件。
3 同一批次数据,优先处理设备插拔。
至此在Native层就完成了设备节点数据读取,其数据会通过管道过滤模式,最终到达App端。
1.1.2 节点传输协议
上一节简述了文件节点读写,重点聚焦在数据的传递,但是输入系统传递的数据格式是如何的,如何支持input业务,这个就涉及到input系统的节点传输协议。
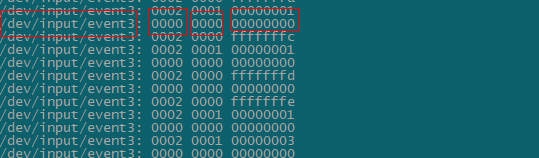
在正式开始前,这里先基于编者amalogic平台,来实时看下输入事件
第一列代表设备节点,后面三列明显是上报数据,具体格式,具体可以参考下input.h中关于input_event的定义
struct input_event {
struct timeval time;
__u16 type;
__u16 code;
__s32 value;
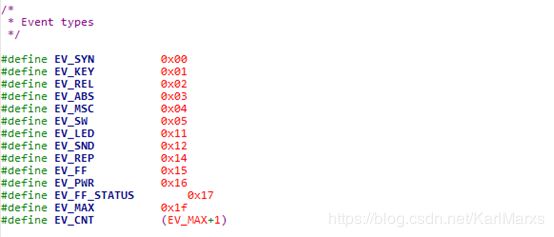
};任何输入事件,最终都通过此结构体来上报信息,怎么来区分大批量数据代表什么输入事件内容?这个就涉及到文件节点传输协议,具体查案input.h定义就可以了。这里仅仅对type做下注释
types对应于一个相同逻辑输入结构的一组Codes。每个type都有一组可用的codes用于产生输入事件。每个type可用的codes的详细信息请参考Codes一节的内容。
* EV_SYN:
- 用于事件间的分割标志。事件可能按时间或空间进行分割,就像在多点触摸协议中的例子。
* EV_KEY:
- 用来描述键盘,按键或者类似键盘设备的状态变化。
* EV_REL:
- 用来描述相对坐标轴上数值的变化,例如:鼠标向左方移动了5个单位。
* EV_ABS:
-用来描述相对坐标轴上数值的变化,例如:描述触摸屏上坐标的值。
* EV_MSC:
- 当不能匹配现有的类型时,使用该类型进行描述。
* EV_SW:
- 用来描述具备两种状态的输入开关。
* EV_LED:
- 用于控制设备上的LED灯的开和关。
* EV_SND:
- 用来给设备输出提示声音。
* EV_REP:
-用于可以自动重复的设备(autorepeating)。
* EV_FF:
- 用来给输入设备发送强制回馈命令。(震动?)
* EV_PWR:
- 特别用于电源开关的输入。.
* EV_FF_STATUS:
- 用于接收设备的强制反馈状态。关于code,有兴趣可自行查看input.h文件。Android input系统在数据上报时,通过tpye |code |value组合就可以完成全部信息的整合上报了。这里的文件节点协议对于后面c端模拟实现由重要的参考意义。
1.2 模拟按键方式
关于Android端模拟按键实现,其实在熟悉了input框架后,就可以有多种方案,一般来讲分为java端方案及本地Native方案
1.2.1 Java层方案
类比adb input keyevent value+ 这条命令,可以在源代码找到参考代码,如下,定位到源代码中frameworks/base/cmds/input/src/com/android/commands/input/Input
文件,其核心代码是
private void sendKeyEvent(int inputSource, int keyCode, boolean longpress) {
long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
injectKeyEvent(new KeyEvent(now, now, KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN, keyCode, 0, 0,
KeyCharacterMap.VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD, 0, 0, inputSource));
if (longpress) {
injectKeyEvent(new KeyEvent(now, now, KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN, keyCode, 1, 0,
KeyCharacterMap.VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD, 0, KeyEvent.FLAG_LONG_PRESS,
inputSource));
}
injectKeyEvent(new KeyEvent(now, now, KeyEvent.ACTION_UP, keyCode, 0, 0,
KeyCharacterMap.VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD, 0, 0, inputSource));
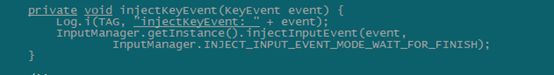
}其核心是调用了injectKeyEvent方法:
可以看到,这里直接调用了IMS的方法,这样子实现起来就比较简单了。
1.2.2 C层方案
参考1.1节描述,可以通过直接在文件节点写入模拟按键事件即可,EventHub在检测到事件后会处理对应的事件,下文基于amalogic来实现native层模拟按键
2 Amlogic模拟按键实践
2.1基于鼠标的本地模拟
基于第二节分析,在amlogic平台基于鼠标设备来构造点击 移动 滑动事件,实现本地模拟,基于方案,模拟头文件如下:
#ifndef _ANALOG_H
#define _ANALOG_H
#include
#include
// from /linux/input.h
typedef struct input_event {
struct timeval time;
__u16 type;
__u16 code;
__s32 value;
} input_event;
typedef struct analog_event {
char *type;
char *code;
char *value;
bool isSync;
} analog_event;
typedef struct analog_motion {
int x;
int y;
} analog_motion;
// 宏定义
// method for analog with scene
int init_analog();
int close_analog();
int send_analog_event(analog_event *event);
int analog_click_event();
int analog_motion_event(analog_motion *motion);
int analog_whell_event(bool is_up);
#endif 这里主要是一些方法声明,及业务结构体定义,下面来看下具体实现,基本就是对头文件的实现。这里贴出一些核心实现,次要的忽略
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define MOUSE_KEY_TPYE "1"
#define MOUSE_LEFT_KEY_CODE "272"
#define REPORT_TYPE 0
#define REPORT_CODE 0
#define MOUSE_REL_TYPE "2"
#define MOUSE_REL_X_CODE "0"
#define MOUSE_REL_Y_CODE "1"
#define MOUSE_REL_WHEEL_CODE "8"
#define WHELL_DOWN "4294967295"
#define WHELL_UP "1"
#define LOG_TAG "iflytek_hal"
static const char *MOUSE_NAME = "/dev/input/event3";
static const char *MOUSE_NAME1 ="/dev/input/event4";
int fd = -99;
static char* get_string(int value);
int init_analog()
{
if(fd < 0) {
fd = open(MOUSE_NAME,O_RDWR);
}
if(fd < 0) {
ALOGI("init_analog_with mouse1");
fd = open(MOUSE_NAME1,O_RDWR);
}
if(fd < 0) {
fprintf(stderr,"could not open %s,%s\n",MOUSE_NAME,strerror(errno));
ALOGE("could not open%s,%s\n",MOUSE_NAME,strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
ALOGI("init_analog_success");
return fd;
}
int close_analog() {
if(fd > 0) {
close(fd);
}
ALOGI("close_analog");
return 0;
}
int send_analog_event(analog_event *event)
{
int ret;
if(fd < 0 || event == NULL) {
ALOGE("fd is not open or event is null");
return -1;
}
ALOGI("send_analog_event type is %s,code is %s,value is %s\n",event->type,event->code,event->value);
input_event _event;
memset(&_event,0,sizeof(_event));
_event.type = atoi(event->type);
_event.code = atoi(event->code);
_event.value = atoi(event->value);
ret = write(fd,&_event,sizeof(_event));
if(ret < sizeof(_event)) {
ALOGE("write event error,%s\n",strerror(errno));
return -1;
}else {
ALOGI("write event size is,%d\n",ret);
}
if(event->isSync) {
memset(&_event,0,sizeof(_event));
_event.type = REPORT_TYPE;
_event.code = REPORT_CODE;
_event.value = 0;
ret = write(fd,&_event,sizeof(_event));
if(ret < sizeof(_event)) {
ALOGE("write event error,%s\n",strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
}
ALOGI("send event write event success");
return 0;
}
int analog_click_event()
{
int ret;
ALOGI("start analog click event");
analog_event event;
memset(&event,0,sizeof(event));
event.type = MOUSE_KEY_TPYE;
event.code = MOUSE_LEFT_KEY_CODE;
event.value = "1";
event.isSync = true;
ret = send_analog_event(&event);
if(ret < 0) {
return -1;
}
memset(&event,0,sizeof(event));
event.type = MOUSE_KEY_TPYE;
event.code = MOUSE_LEFT_KEY_CODE;
event.value = "0";
event.isSync = true;
ret = send_analog_event(&event);
if(ret < 0) {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int analog_whell_event(bool is_up)
{
int ret;
fprintf(stdout,"start analog whell event");
ALOGI("start analog whell event");
analog_event event;
memset(&event,0,sizeof(event));
char *down = WHELL_DOWN;
char *up = WHELL_UP;
event.type = MOUSE_REL_TYPE;
event.code = MOUSE_REL_WHEEL_CODE;
event.value = (!is_up) ? down : up;
event.isSync = true;
ret = send_analog_event(&event);
if(ret < 0) {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int analog_motion_event(analog_motion *motion)
{
bool valid = false;
int ret;
if(motion == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"analog_motion is NULL");
ALOGE("analog_motion is NULL");
return -1;
}
analog_event event;
memset(&event,0,sizeof(event));
if(motion->x > 0) {
valid = true;
event.type = MOUSE_REL_TYPE;
event.code = MOUSE_REL_X_CODE;
event.value = get_string(motion->x);
}
if(motion->y > 0) {
if(valid) {
ret = send_analog_event(&event);
if(ret < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
valid = true;
memset(&event,0,sizeof(event));
event.type = MOUSE_REL_TYPE;
event.code = MOUSE_REL_Y_CODE;
event.value = get_string(motion->y);
}
if(valid) {
event.isSync = true;
ret = send_analog_event(&event);
if(ret < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int test_main(int argc ,char *argv[])
{
int ret;
ret = init_analog();
if(ret < 0) {
return -1;
}
if(argc == 2) {
if(!strncmp(argv[1],"click",5)) {
analog_click_event();
return 0;
}else if(!strncmp(argv[1],"up",2)) {
return analog_whell_event(true);
}else if(!strncmp(argv[1],"down",4)) {
return analog_whell_event(false);
}
return -1;
}else if(argc == 3) {
analog_motion motion;
event.value = get_string(motion->x);
}
if(motion->y > 0) {
if(valid) {
ret = send_analog_event(&event);
if(ret < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
valid = true;
memset(&event,0,sizeof(event));
event.type = MOUSE_REL_TYPE;
event.code = MOUSE_REL_Y_CODE;
event.value = get_string(motion->y);
}
if(valid) {
event.isSync = true;
ret = send_analog_event(&event);
if(ret < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
} 下面是Android4.4平台下的mk编译文件,目前测试已经通过。
LOCAL_PATH:= $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_SRC_FILES:= analog.c
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES:= bionic/libc/bionic
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := \
libcutils \
liblog \
libc \
libusbhost
LOCAL_MODULE:= analog
include $(BUILD_EXECUTABLE)
~
2.2 Framework层实践案列简述
上文基于Native完成了C端的input测试,为了最终支持App可以应用此接口,针对其逻辑,把它的核心功能分解为HAL及JNI支持模块。
同步的来看下Hal层支持代码,首先看下test.h,它主要定义了hal模块的核心结构体。如下
#ifndef ANDROID_TEST_INTERFACE_H
#define ANDROID_TEST_INTERFACE_H
#include
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"{
#endif
#include "analog.h"
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
__BEGIN_DECLS
/**
* the id of this module
*/
#define TEST_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID "iflytek"
#define ANALOG_DEVICE_ID "analog"
#define DEV_MOUSE_INPUT "/dev/input/event4"
typedef struct iflytek_module_t {
struct hw_module_t common;
} iflytek_module_t;
typedef struct analog_device_t {
struct hw_device_t common;
int (*send)(analog_event *event);
int (*motion)(analog_motion *motion);
int (*init)();
int (*close)();
} analog_device_t;
static inline int test_open(const struct hw_module_t* module,struct analog_device_t** device) {
return module->methods->open(module,ANALOG_DEVICE_ID,(struct hw_device_t**)device);
}
static inline int test_close(struct analog_device_t* device) {
return device->common.close(&device->common);
}
__END_DECLS
#endif test.c文件主要是基于test.h 在Android框架下的实现。如下,其核心功能依赖上文贴出来的analog.C实现,具体如下:
#define LOG_TAG "test_hal"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define MODULE_NAME "test controll module"
#define MODULE_AUTHOR "xx"
static int test_module_open(const hw_module_t* module,const char* name,hw_device_t** device);
static int test_module_close(hw_device_t* device);
static struct hw_module_methods_t iflytek_module_methods = {
open: test_module_open
};
test_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
common: {
tag: HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
version_major: 1,
version_minor: 0,
id: TEST_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
name: MODULE_NAME,
author: MODULE_AUTHOR,
methods: &test_module_methods
}
};
static int test_module_open(const hw_module_t* module,const char* name,hw_device_t** device) {
int status = -EINVAL;
if(!strcmp(name,ANALOG_DEVICE_ID)) {
analog_device_t *dev;
dev = (analog_device_t*)malloc(sizeof(analog_device_t));
if(!dev) {
ALOGE("failed malloc analog_device\n");
status = -ENOMEM;
return status;
}
memset(dev,0,sizeof(analog_device_t));
dev->common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->common.version = 0;
dev->common.module = (hw_module_t*)module;
dev->common.close = iflytek_module_close;
dev->send = send_analog_event;
dev->motion = analog_motion_event;
dev->init = init_analog;
dev->close = close_analog;
*device = &dev->common;
status =0;
}else {
ALOGE("faile find %s module\n",name);
}
ALOGE("open testmodule success\n");
return status;
}
static int itest_module_close(hw_device_t* device) {
analog_device_t *dev = (analog_device_t*) device;
dev->close();
return 0;
} 这里面重要的是必须定义HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM变量,其内部初始化了这里定义的模块的各种变量。
其对应的Android.mk文件如下。
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE_PATH := $(TARGET_OUT_SHARED_LIBRARIES)/hw
LOGCAL_MODULE_TAG := optional
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := \
liblog \
libcutils \
libc
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := test.cpp analog.c
LOCAL_MODULE := test.default
include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
最后若想在App端复用此结果,需要jni层周转,基于amalogic平台测试代码如下,这里仅做参考:
/**
* 1 define constant
* 2 define function
* 3 register protel
*/
#define LOG_TAG "iflytek_jni"
#include "JNIHelp.h"
#include "jni.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define CHECK_DEVICE() do{ \
if(!g_device) { \
return; \
} \
while(0)
#define MOUSE_KEY_TPYE "1"
#define MOUSE_LEFT_KEY_CODE "272"
#define REPORT_TYPE 0
#define REPORT_CODE 0
#define MOUSE_REL_TYPE "2"
#define MOUSE_REL_X_CODE "0"
#define MOUSE_REL_Y_CODE "1"
#define MOUSE_REL_WHEEL_CODE "8"
#define WHELL_DOWN "4294967295"
#define WHELL_UP "1"
namespace android {
static struct {
jclass clazz;
} gMotionClassInfo;
static analog_device_t* g_device = NULL;
static jint android_server_init(JNIEnv* env,jclass clazz) {
iflytek_module_t* module;
ALOGI("init iflytek hal ...");
if(hw_get_module(IFLYTEK_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,(const struct hw_module_t**)&module) != 0) {
ALOGE("iflytek module is not found");
return -EFAULT;
}
if(iflytek_open(&module->common,&g_device) != 0) {
ALOGE("open iflytek module failed");
return -EFAULT;
}
return g_device->init();
}
static void android_server_click(JNIEnv* env,jclass calzz) {
ALOGI("start click analog click");
if(!g_device) {
ALOGE("g_device is NULL");
return;
}
analog_event event;
memset(&event,0,sizeof(event));
event.type = MOUSE_KEY_TPYE;
event.code = MOUSE_LEFT_KEY_CODE;
event.value = "1";
event.isSync = true;
g_device->send(&event);
memset(&event,0,sizeof(event));
event.type = MOUSE_KEY_TPYE;
event.code = MOUSE_LEFT_KEY_CODE;
event.value = "0";
event.isSync = true;
g_device->send(&event);
return;
}
static void android_server_long_click(JNIEnv* env,jclass clazz,jint time) {
return;
}
static void android_server_tap(JNIEnv* env,jclass clazz,jboolean is_up) {
ALOGI("start analog tap");
if(!g_device) {
ALOGE("g_device is NULL");
return;
}
analog_event event;
memset(&event,0,sizeof(event));
char *down = WHELL_DOWN;
char *up = WHELL_UP;
event.type = MOUSE_REL_TYPE;
event.code = MOUSE_REL_WHEEL_CODE;
event.value = (!is_up) ? down : up;
event.isSync = true;
g_device->send(&event);
return;
}
static void android_server_motion(JNIEnv* env,jclass clazz,jint x_pos,jint y_pos) {
ALOGI("start analog motion");
if(!g_device) {
ALOGE("g_device is NULL");
return;
}
analog_motion motion;
memset(&motion,0,sizeof(motion));
motion.x = x_pos;
motion.y = y_pos;
g_device->motion(&motion);
return;
}
#define FIND_CLASS(var, className) \
var = env->FindClass(className); \
LOG_FATAL_IF(! var, "Unable to find class " className);
static JNINativeMethod sMethods[] = {
{"analogInit","()I",(void*) android_server_init},
{"analogClick","()V",(void*) android_server_click},
{"analogLongClick","(I)V",(void*) android_server_long_click},
{"analogTap","(Z)V",(void*) android_server_tap},
{"analogMotion","(II)V",(void*) android_server_motion},
// {"analogMotion","(Lcom/android/MotionEvent;)V",(void*) android_server_iflytek_IflytekService_motion},
};
int register_android_server_TestService(JNIEnv* env) {
FIND_CLASS(gMotionClassInfo.clazz,"com/android/MotionEvent");
return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env,"com/android/server/iflytek/TestService",sMethods,NELEM(sMethods));
}
}