Reluplex代码阅读
本文来源:Reluplex: An Efficient SMT Solver for Verifying Deep Neural Work
Guy Katz, Clark Barrett, David L. Dill, Kyle Julian, and Mykel J. Kochenderfer
Stanford University, Stanford USA
解决的主要问题
在安全性很高的系统中应用DNN需要为DNN的行为提供“formal guarantees”,验证DNN的特性或者提供反例。
算法的主要实现过程
与单纯形法相同,Reluplex允许变量临时违反边界,因为它反复查找可行的变量赋值。 不仅如此,Reluplex还允许属于ReLU对的变量临时违反ReLU约束。然后,在迭代时,Reluplex会反复选择超出范围或违反ReLU约束的变量,并使用Pivot和Update操作对其进行纠正。
对于一组给定的变量 χ={x1,...,xn} χ = { x 1 , . . . , x n } ,它的配置规则是一组区别符号 {SAT,UNSAT} { S A T , U N S A T } 或者一个元组 <B,T,l,u,α,R> < B , T , l , u , α , R > , B⊆χ B ⊆ χ 是一组基本变量;T,代表tableau,包含每一 xi∈B x i ∈ B ,有方程 xi=∑xj∉Bcjxj x i = ∑ x j ∉ B c j x j ; l,u l , u 是对应每一个变量 x∈χ x ∈ χ 赋值的下界和上界; R∈χxχ R ∈ χ x χ 是Relu连接的集合。初始赋值全都是0,保证所有的方程能够保持(不过上下界的约束可能会被违反)。
具体的操作有:

Updateb和Updatef U p d a t e b 和 U p d a t e f 规则允许通过分别更新向后或向前的变量来纠正损坏的ReLU连接,前提是这些变量是非基本的变量。 PivotForRelu P i v o t F o r R e l u 规则允许在ReLU中出现的基本变量被交换,以便可以应用 Updateb和Updatef U p d a t e b 和 U p d a t e f (当ReLU中的两个变量都是基本的并且它们的赋值不满足ReLU语义时,这是需要进一步操作的)。ReluSplit规则用于拆分某些ReLU连接。首先尝试使用 Updateb和Updatef U p d a t e b 和 U p d a t e f 规则来修复不满足条件的ReLU对,并且只在特定ReLU对的更新次数超过某个阈值时才进行splits。 直观地说,这可能会限制拆分为“有问题”的ReLU对,同时仍保证终止。
例子:

设定的基本变量初始为 a1,a2,a3 a 1 , a 2 , a 3 ,根据DNN有下面的3个方程:
(1)a1=vb21−v11 ( 1 ) a 1 = v 21 b − v 11
(2)a2=vb22+v11 ( 2 ) a 2 = v 22 b + v 11
(3)a3=−vf21−vf22+v31 ( 3 ) a 3 = − v 21 f − v 22 f + v 31
基本变量集合为 a1,a2,a3 a 1 , a 2 , a 3 ,ReLU连接集合R= {<vb21,vf21>,<vb22,vf22>} { < v 21 b , v 21 f > , < v 22 b , v 22 f > }
所有变量的初始值均赋值为0。基本变量的上界和下界设为0.输入输出变量的上下界需要根据具体的条件设置,在此处因为没有上下文所以我们自己初始化了一个上下界。

配置步骤:
- 变量 v31 v 31 是非基本变量而且越界了。所以我们要Update,把它设置成0.5。
根据方程(3), v31=0.5 v 31 = 0.5 意味着 a3=0.5 a 3 = 0.5 - a3=0.5 a 3 = 0.5 → a3 a 3 越界,需要执行PivotForRelu操作,把 vf21 v 21 f 变成基本变量,把 a3 a 3 重新设置为0,而此时 vf21=1 v 21 f = 1
- 因为此时 α(vf21)=0.5≠0=max(0,α(vb21)) α ( v 21 f ) = 0.5 ≠ 0 = m a x ( 0 , α ( v 21 b ) ) 。所以要执行 Updateb U p d a t e b 的操作,使得 α(vb21)=0.5 α ( v 21 b ) = 0.5
- 根据方程(1), vb21=0.5 v 21 b = 0.5 意味着 a1=0.5 a 1 = 0.5
- a1=0.51 a 1 = 0.51 → a1 a 1 越界,需要执行PivotForRelu操作,把 v11 v 11 变成基本变量,把 a1 a 1 重新设置为0,而此时 v11=0.5 v 11 = 0.5
- 此时有: α(v11)=0.5,α(vf21)=0.5,α(vb21)=0.5,α(v31)=0.5,α(a2)=0.5 α ( v 11 ) = 0.5 , α ( v 21 f ) = 0.5 , α ( v 21 b ) = 0.5 , α ( v 31 ) = 0.5 , α ( a 2 ) = 0.5 ,因为 a2 a 2 的值太大了,所以需要执行PivotForRelu操作,把 vb22 v 22 b 变成基本变量,把 a2 a 2 重新设置为0,而此时 v11=−0.5 v 11 = − 0.5 ,最后结果为:

此时恰好满足所有条件,停机!
代码
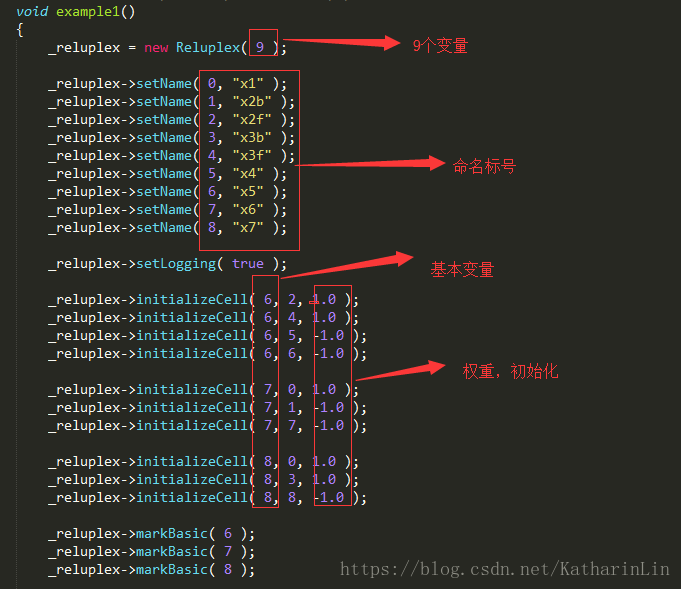
reluplex/Reluplex.h:
The main class, implementing the core Reluplex algorithm.glpk-4.60: (folder)
The glpk open-source LP solver, plus some modifications.
The patches applied to the pristine GLPK appear under the “glpk_patch”
folder (no need to re-apply them).reluplex/SmtCore.h:
A simple SmtCore, in charge of the search stack.nnet/:
This folder contains the ACAS Xu neural networks that we used, and
code for loading and accessing them.


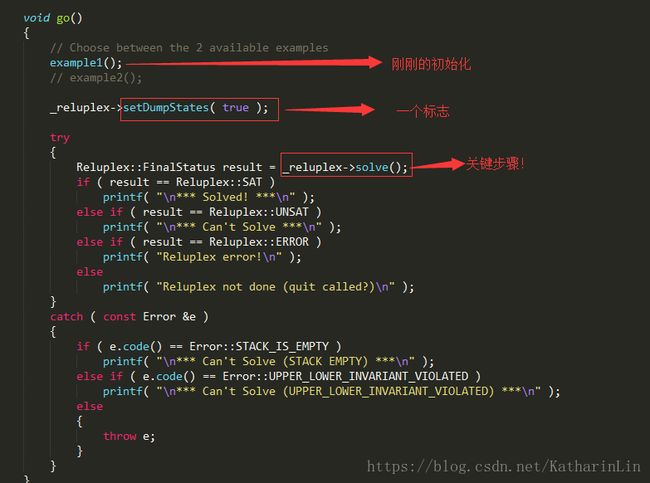

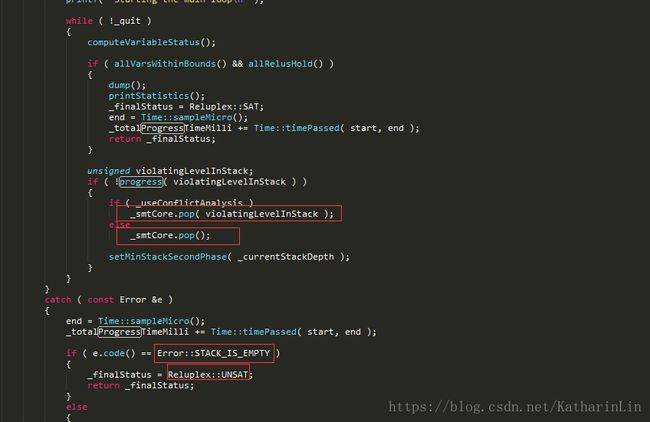
the main loop is implemented in the progress() method. This loop:
A. Invokes GLPK in order to fix any out-of-bounds variables
B. If all variables are within bounds, attempts to fix a broken ReLU constraint.

如果没有OutOfBounds的变量就来调整Relu变量。
![]()
invoking GLPK
in order to fix all out-of-bound variables.
The method translates the current tableau into a GLPK instance, invokes GLPK, and then extracts the solution tableau and assignment from GLPK.【大概就是tableau和求解器的相互转化过程】

如果不需要分裂就直接调用fixBrokenRelu() method。
fixing a specific ReLU constraint that is currently broken.
We first try to fix the b variable to agree with the f variable, and only if that fails attempt to fix f to agree with b. If both fail, the problem is infeasible, and the method returns false. Otherwise, the pair is fixed, and the method returns true.
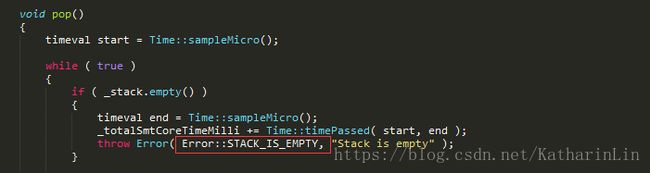
fixBrokenRelu()的返回值就是progress()的返回值,如果不成功的话就会调用smt中的pop(),然后继续while循环。如果调用pop()是栈已经空了,那么会抛出栈空异常,solve()里catch到后得出结果UNSAT。

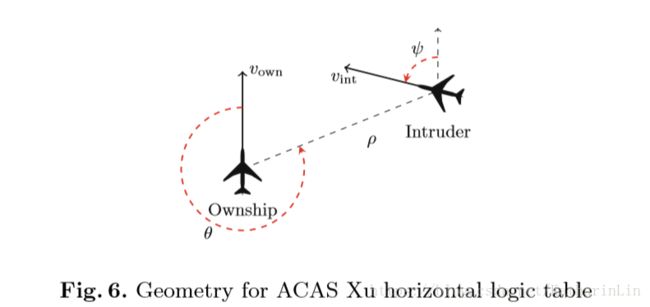
ACAS Xu System(无人机载避碰系统)
证明过程处理整个神经网络, 而不做任何简化假设。
机载避碰系统(ACAS X)采用的方法包括解决部分可观测的马尔可夫决策过程, 以优化报警逻辑, 进一步降低空中碰撞的概率, 同时尽量减少不必要的警报。ACAS Xu会产生水平机动警告。
ACAS 的发展重点是使用一个大型的查找表, 将传感器测量数据映射到警告。但是, 此表需要超过2GB 的内存,使得航空电子硬件的内存需求不足。所以, DNN 的表示法被探讨为查找表的一个潜在替代。初步结果显示, 在不危及安全性的情况下, 内存需求急剧减少。事实上, 由于它的持续性质, DNN 方法有时会胜过离散查找表 。最近, 为了减少查找时间, DNN 方法得到了进一步的改进, 单个DNN 被 45个DNNs 的数组所取代。因此, 原始2GB 表现在可以替换为需要少于3MB内存的高效神经网络。
证明一组输入不能产生错误警报对于验证系统在安全关键设置中的使用至关重要。
以前的验证方法包括在150万模拟碰撞中对系统进行彻底测试, 但这在验证连续 DNNs 中不存在错误行为的时候是效率很低的。所以我们要采取Reluplex的方法。
ACAS 系统将输入变量映射到操作报告。每个报告被分配一个分数, 与最佳的操作对应的是最低分数。
45个DNNs通过离散 τ和aprev τ 和 a p r e v , 并通过每个离散组合生成一个网络产生。因此, 每个网络都有5个输入和five 输出。DNNs是完全连接的, 使用 ReLU激励函数, 并有6个隐层, 总共有300个 ReLU节点。
在代码中,有45个DNN的文件,每一个文件定义了一个DNN。


代码中网络都是已经训练好的。
我们需要验证 ACAS Xu网络是否为不同输入域中的输出报告分配了正确的分数。

图中有五种输出:COC、SL、SR、WL、WS。
在这个例子中我们要验证的property是:
(i) The system does not give unnecessary turning advisories; (ii) Alerting regions are uniform and do not contain inconsistent alerts; and (iii) Strong alerts do not appear for high τ values.
For each property, we looked for an input that would violate it;
an UNSAT result indicates that a property holds
a SAT result indicates that it does not hold.
In the SAT case, the satisfying assignment is an example of an input that violates the property.
eg.
property1:如果intruder很远并且比本机慢得多,COC建议的分数总是低于某个固定的阈值
我们目前存在的问题:
1.input、output具体指代及来源
2.properties列举十个是否能有效证明
3.properties每一个代表什么没有具体说明,补充材料的链接并没有东西
4.为什么有的property只验证了一个网络
5.没有给出和其他SMT求解器比较的代码,无法得知是如何将传感器数值转换成SMT输入
6.45个DNNs的产生,离散化是怎么做的并没有说明
7.如何将property映射成问题的输入,没有说明,Readme中提到,These 10 benchmarks are organized under the “check_properties” folder, in numbered folders. Property 6 is checked in two parts, and so it got two folders: property6a and property6b. Within these folders, the properties are given in Reluplex format (in main.cpp).但是看代码它是直接读取DNN中的相关参数。