依图20190823,京东0824,kick start0825,快手0825
依图
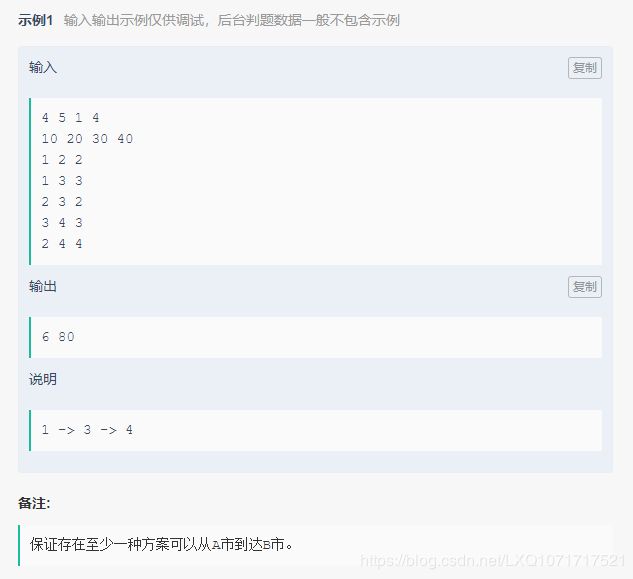
1.地铁进站出站,计算车费
理论上a[n-1],b[0]应该对车费没影响的,但是数据不知道为什么,是有影响的。。。
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int n;
int in[1001];
int out[1001];
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i 2.Dijkstra求最短路径
用邻接矩阵存储的,过了0.6
应该用邻接表
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1005;
const int INF= 1<<30;
int n,m;
int st,ed;
int G[maxn][maxn];
int cake[maxn];
int d[maxn];
int c[maxn];
bool vis[maxn]={false};
void Dijkstra(int s){
fill(d, d+maxn, INF);
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
d[s]=0;
c[s]=cake[s];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int u=-1, MIN=INF;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(vis[j]==false&&d[j]c[v]){
c[v]=c[u]+cake[v];
}
}
}
}
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &n,&m, &st,&ed);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d", &cake[i]);
}
fill(G[0],G[0]+maxn*maxn,INF);
for(int j=0;j 3.组合成3的倍数
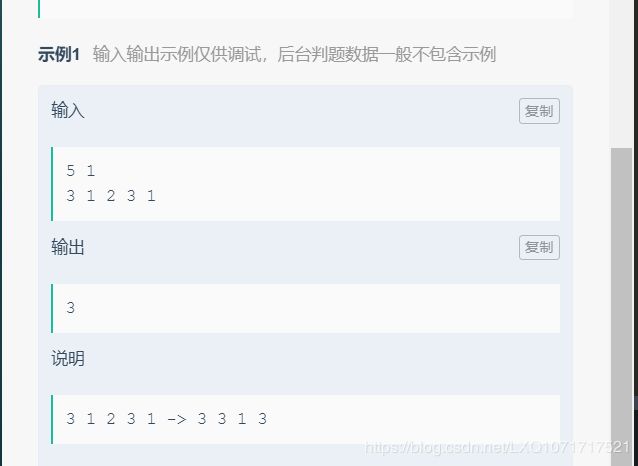
这道题可以不用存储数组元素,一遍遍历就可以做
如果k=0,统计元素为3的倍数的个数ans=n3;
统计元素除3余1的个数n1,除3余2的个数n2,这两种数两两组合就是3的倍数,
如果k 如果k>=min(n1,n2),先计算ans=n3+min(n1,n2), 剩下的元素要么全部都是除3余1的,要么就全部都是除3余2的,他们都是要3个相加才是3的倍数, k=k-min(n1,n2),k=k/2,假设剩下的是除3余1的,n1=n1-n2,n1=n1/3, 然后ans=ans+min(k,n1) 代码如下: python版本:(waple) 神仙题。。。。。。 京东的题有点难顶 上面样例输出是3(消掉1,下落之后消掉2,最后剩余3个数) python代码如下:(Waple) 过了0.73 比如模式为abcc,那么gdff,这个就符合这个模式,tyui就不符合 题目链接 Your friend is recently done with cooking class and now he wants to boast in front of his school friends by making a nice dessert. He has come up with an amazing dessert called Cherries Mesh. To make the dish, he has already collected cherries numbered 1 to N. He has also decided to connect each distinct and unordered pair of cherries with a sweet strand, made of sugar. Sweet strands are either red or black, depending on the sugar content in them. Each black strand contains one units of sugar, and each red strand contains two units of sugar. But it turns out that the dessert is now too sweet, and these days his school friends are dieting and they usually like dishes with less sugar. He is really confused now and comes to your rescue. Can you help him find out which all sweet strands he should remove such that each pair of cherries is connected directly or indirectly via a sugar strand, and the dish has the minimum possible sugar content? The first line of input gives the number of test cases, T. Each test case begins with a line containing two integers N and M, the number of cherries and the number of black sweet strands, respectively. Then M lines follow, each describing a pair of cherries connected to a black strand. The i-th line contains cherries numbered Ci and Di, it indicates that Ci and Di cherry are connected with a black strand of sugar. Note: Any other pair of cherries not present in the input means that they are connected by a red strand. For each test case, output one line containing Time limit: 15 seconds per test set. Test set 1 (Visible) 1 ≤ N ≤ 100. Test set 2 (Hidden) For at least 90% of the test cases: In the first sample case, there are two cherries and they are connected with a black strand. Removing any of the strand causes cherries to get disconnected. Hence, the minimum sugar content is 1. In the second sample case, we can keep the black strand between cherry numbered 2 and cherry numbered 3, and remove any of the red strands, which leads to a minimum sugar content of 3. 主要就是并查集的应用 Umon is a foodie coder. Do you know what two activities that he loves the most? Of course, coding and eating! He always spends the whole day doing only those two activities. However, he thinks that some times of the day are better spent coding, and others are better spent eating. To illustrate this problem, Umon divides his day into S time slots. During the i-th time slot, if Umon codes 100% of the time, he will achieve Ci units of coding. On the other hand, if he eats 100% of the time, he will achieve Eiunits of eating. But of course, Umon can also use only a fraction of the time for coding, and the remaining for eating. Formally, he will choose a real number f (0 ≤ f ≤ 1), code for f of the time, and use the remaining (1 - f) time to eat. This way, he will achieve f × Ci units of coding and (1 - f) × Ei units of eating. The total amount of coding Umon achieves for the day is simply the sum of all units of coding he achieved in each of the time slots. The total amount of eating is calculated in a similar way. Umon needs to plan his schedule for the next D days. On the i-th day, he needs to achieve at least a total amount of Ai units of coding and Bi units of eating. For each day, determine whether there is a way for Umon to achieve his target. The first line of input gives the number of test cases, T. T test cases follow. Each test case begins with a line containing two integers D and S, the number of days and the number of time slots in a day, respectively. Then S lines follow, each describing a time slot. The i-th line contains two integers Ci and Ei, the amount of coding units achieved if Umon codes for 100% of the time slot, and the amount of eating units achieved if he eats for 100% of the time slot, respectively. Then D lines follow, each describing a day. The i-th line contains two integers Ai and Bi, the minimal total amount of coding and eating that needs to be achieved on that day. For each test case, output one line containing Time limit: 20 seconds per test set. Test set 1 (Visible) 1 ≤ S ≤ 2. Test set 2 (Hidden) For at least 90% of the test cases: In the first sample case, there are 4 days and 2 time slots for each day. Thus, the answer should be YYNY. In the second sample case, note that the value of characteristics for the time slots may not necessarily be different from each other. Alice and Bob are playing a new virtual reality team game - Street Checkers. The game is set on a very long street divided into tiles which are numbered from 0 to 109(inclusive of both). At the start of the game, Alice and Bob are standing on tile number 0 and are given a random number X in range [L, R] (both ends are inclusive). Alice only jumps to odd numbered tiles, while Bob only jumps to even numbered tiles. If the number on the tile divides X, then the player landing on it has to color it with their favorite color. The game is over after tile X has been colored. A game is considered interesting by both the players if the absolute difference between the number of tiles painted by each is not greater than 2. Help Alice and Bob find how many numbers in the interval [L, R] could make for an interesting game. The first line of the input gives the number of test cases, T. T lines follow each containing two integers L and R, the start and end of the interval used to generate the random number X. For each test case, output one line containing Time limit: 40 seconds per test set. Test set 1 (Visible) 1 ≤ L ≤ R ≤ 106. Test set 2 (Hidden) 1 ≤ L ≤ R ≤ 109. For the first sample case, let us look at all the possible number in range [5, 10]: Thus, the answer for this test case is 5. In the second sample case, we have only one number 102. Alice would paint 4 tiles : {1, 3, 17, 51} while Bob would paint 4 tiles : {2, 6, 34, 102}. The game would be interesting since the absolute difference is 0. 膜拜大神 (by Waple) 不知道为啥,通过0% python大法好(by Waple) #includefrom collections import defaultdict
n, k = map(int, input().strip().split())
a = list(map(int, input().strip().split()))
d = defaultdict(int)
for num in a:
d[num%3] += 1
res = d[0]
while k > 0 and (d[1] + d[2] > 1):
if d[1] > 0 and d[2] > 0:
d[1] -= 1
d[2] -= 1
res += 1
elif d[1] > 1:
d[1] -= 2
d[2] += 1
elif d[2] > 1:
d[2] -= 2
d[1] += 1
else:
break
k -= 1
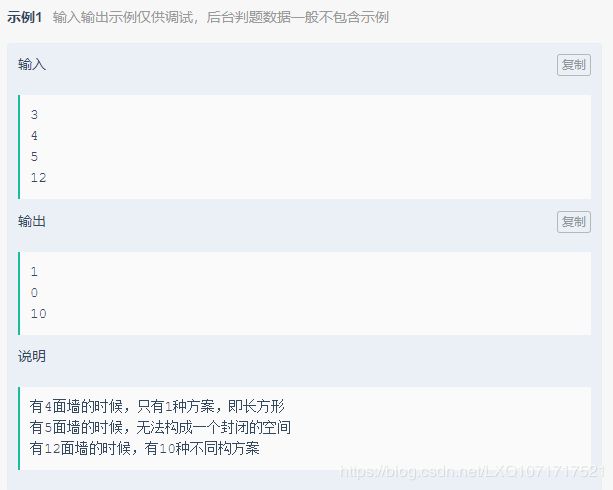
print(res)4.博物馆的墙
京东
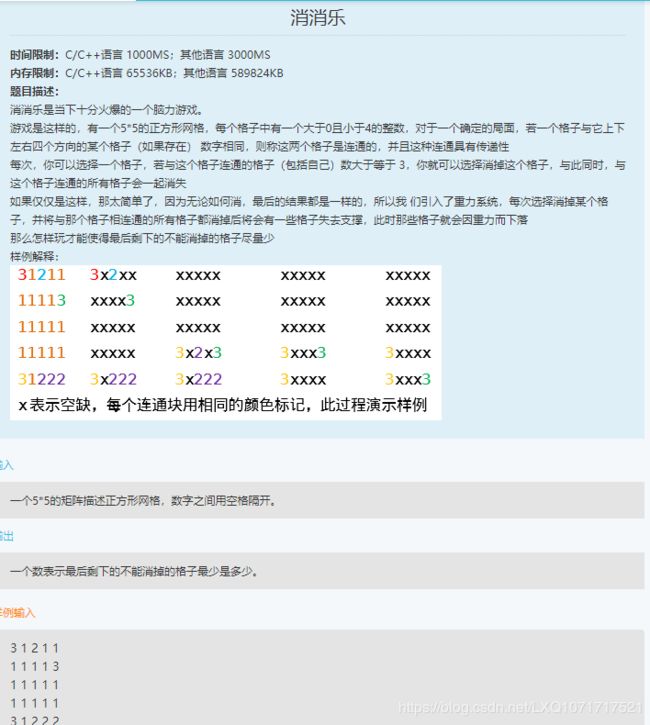
1.消消乐
from copy import deepcopy
b = []
for _ in range(5):
b.append(list(map(int, input().strip().split())))
ans = 25
def dfs(b, i, j, visited):
res = 1
visited[i][j] = False
for m, n in ((0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1)):
new_i, new_j = i+m, j+n
if 0 <= new_i <= 4 and 0 <= new_j <= 4 and b[new_i][new_j] == b[i][j] and visited[new_i][new_j]:
visited[new_i][new_j] = False
res += dfs(b, new_i, new_j, visited)
return res
def op_dfs(b, i, j, visited):
visited[i][j] = False
tmp = b[i][j]
b[i][j] = 'x'
for m, n in ((0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1)):
new_i, new_j = i+m, j+n
if 0 <= new_i <= 4 and 0 <= new_j <= 4 and b[new_i][new_j] == tmp and visited[new_i][new_j]:
op_dfs(b, new_i, new_j, visited)
def sch(b):
candi = []
visited = [[False if b[i][j] == 'x' else True for j in range(5)] for i in range(5)]
for i in range(5):
for j in range(5):
if visited[i][j]:
length = dfs(b, i, j, visited)
if length > 2:
candi.append((i, j))
return candi
def calculate(b):
global ans
res = 0
for line in b:
for num in line:
if num != 'x':
res += 1
ans = min(ans, res)
def drop(b):
ans = []
new_a = []
for j in range(5):
res = []
for i in range(4, -1, -1):
if b[i][j] != 'x':
res.append(b[i][j])
res += ['x'] * (5 - len(res))
new_a.append(res[::-1])
for line in zip(*new_a):
ans.append(list(line))
return ans
def operate(b):
candidates = sch(b)
for i, j in candidates:
visited = [[False if b[i][j] == 'x' else True for j in range(5)] for i in range(5)]
new_a = deepcopy(b)
op_dfs(new_a, i, j, visited)
calculate(new_a)
new_a = drop(new_a)
operate(new_a)
operate(b)
print(ans)2.拼接迷宫
#include面试
给定一个字符串和一个模式,判断字符串属不属于这个模式
#includeKick Start——谷歌
1.Cherries Mesh
Problem
Input
Output
Case #x: y, where x is the test case number (starting from 1) and y is minimum possible sugar content.Limits
Memory limit: 1GB.
1 ≤ T ≤ 100
M ≤ N*(N-1)/2
1 ≤ Ci ≤ N, for all i.
1 ≤ Di ≤ N, for all i.
Ci ≠ Di, for all i.
Every {Ci, Di} is distinct.
0 ≤ M ≤ 100.
1 ≤ N ≤ 1000.
0 ≤ M ≤ 1000.
For all test cases:
1 ≤ N ≤ 105.
0 ≤ M ≤ 105.Sample
Input
Output
2
2 1
1 2
3 1
2 3
Case #1: 1
Case #2: 3
#include2.Code-Eat Switcher
Problem
Input
Output
Case #x: y, where x is the test case number (starting from 1) and y is a string with D characters, where the i-th character is Y if there exists a schedule that can fulfill the target for the i-th day, otherwise it should be N.Limits
Memory limit: 1GB.
1 ≤ T ≤ 100.
1 ≤ Ci ≤ 104, for all i.
1 ≤ Ei ≤ 104, for all i.
0 ≤ Ai ≤ 108, for all i.
0 ≤ Bi ≤ 108, for all i.
1 ≤ D ≤ 10.
1 ≤ S ≤ 103.
1 ≤ D ≤ 103.
For all test cases:
1 ≤ S ≤ 105.
1 ≤ D ≤ 105.Sample
Input
Output
2
4 2
3 8
6 10
0 18
3 13
10 0
7 3
1 2
4 4
4 4
0 0
Case #1: YYNY
Case #2: Y
#include 3.Street Checkers
Problem
Input
Output
Case #x: y, where x is the test case number (starting from 1) and y is the count of numbers in interval [L, R] which results in an interesting game for Alice and Bob.Limits
Memory limit: 1GB.
1 ≤ T ≤ 100.
0 ≤ R - L ≤ 105.Sample
Input
Output
2
5 10
102 102
Case #1: 5
Case #2: 1
#include 快手
1.
N = int(input().strip())
M = int(input().strip())
a = []
pic = []
st = -1
for index in range(M):
tmp = input().strip()
cat, i = tmp.split('_')
if cat == 'V':
a.append(tmp)
else:
if st == -1:
st = index
pic.append(tmp)
res = []
m = st
last = 0
while m > 0:
res.append(a.pop(0))
m -= 1
while a and pic:
if pic:
res.append(pic.pop(0))
last = 0
for _ in range(N-1):
if a:
res.append(a.pop(0))
last += 1
#last
if pic and last >= N-1:
res.append(pic.pop(0))
while a:
res.append(a.pop(0))
print(len(res))
for i in range(len(res)):
print(res[i])2.
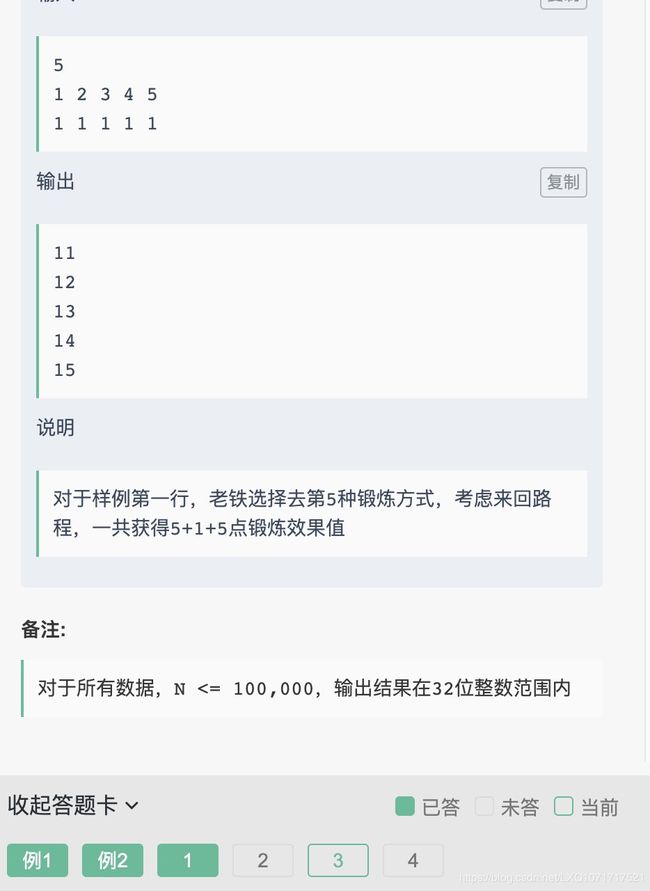
3.健身问题
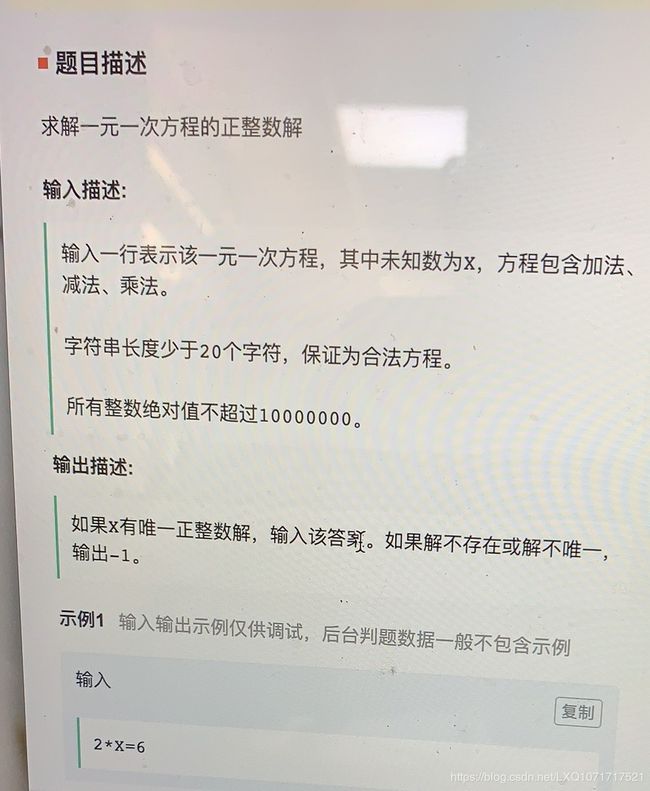
#include4.
res = []
s = input()
for i in range(10000):
tmp = s.replace('X', str(i))
eval1, eval2 = tmp.split('=')
ans1, ans2 = eval(eval1), eval(eval2)
if ans1 == ans2:
res.append(i)
if len(res) == 0 or len(res) > 1:
print(-1)
else:
print(res[0])