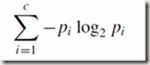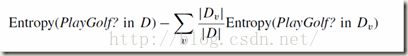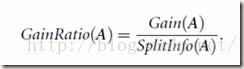C4.5算法(一)代码实现
入门学习机器学习的十大算法,第一站就是C4.5算法。C4.5是一种决策树算法,属于监督学习。先给一个样本集,从而建立一棵决策树,然后根据这个决策树来对后续的数据做决策。
作为没有相关背景知识和系统学习过的人,当然要边学边记啦。C4.5算法我的学习步骤是这样:
因为个人认为C4.5算法中比较难和重要的两个点就是对连续变量的离散化,和剪枝策略,所以会单独着重学习下。因为我终归是做hadoop和spark的,所以还会看看C4.5在spark上的应用和实现(C4.5显然不适合MapReduce模型)。本文只是step1,算法逻辑和编程实现的总结。step 1: 了解清楚算法的逻辑,以及编程实现
step 2: 其中对连续变量的离散化处理
step 3: C4.5的剪枝
step 4: C4.5算法的spark实现
算法逻辑
1. 先明确几个概念:
熵: 朴素点说,就是信息的不确定性,多样性,包含的信息量的大小,需要用多少bit来传递这个信息。比如,抛一枚银币3次,得到的可能结果有8种,我们知道计算机要用3bit来传递,所以熵就是log2(8)=3。wiki上这样解释“你需要用 log2(n) 位来表示一个可以取 n 个值的变量。”
信息增益: 熵的减小量。决策树的期望是尽快定位,也就是说我们希望数据集的多样性越小越好,越小说明结果越稳定,越能定位到准确的结果。信息增益越大,则熵会变的越小,说明结果越好。信息增益的计算方式,是原数据集的熵,减去依照属性划分后,每个属性值的概率 * 对应的子数据集的熵。
信息增益率:对信息增益进行修正。信息增益会优先选择那些属性值多的属性,为了克服这种倾向,用一个属性计算出的信息增益,除以该属性本身的熵(SplitInfo),得到信息增益率。
2. C4.5算法逻辑:
先给一个来自网上的算法步骤:
我的概括:
(1) 先查看是否为“纯”数据集(即结果一致)
(2) 选择信息增益率最大的属性bestAttr
(3) 根据bestAttr属性,把数据集划分成几个子数据集
(4) 对每个子数据集,递归C4.5算法
把整个C4.5算法的属性划分轨迹记录下来,就形成了一棵C4.5决策树。然后就能用这棵树做决策了。
Java代码实现
把这四段代码拷贝到四个java文件中,然后就直接可以运行了。
下面的代码实现决策树的主要逻辑。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class DecisionTree {
InfoGainRatio infoGainRatio = new InfoGainRatio();
public TreeNode createDecisionTree(List attribute, List> dataset) {
TreeNode tree = new TreeNode();
//check if it is pure
if(DataSetUtil.isPure(DataSetUtil.getTarget(dataset))) {
tree.setLeaf(true);
tree.setTargetValue(DataSetUtil.getTarget(dataset).get(0));
return tree;
}
//choose the best attribute
int bestAttr = getBestAttribute(attribute, dataset);
//create a decision tree
tree.setAttribute(attribute.get(bestAttr));
tree.setLeaf(false);
List attrValueList = DataSetUtil.getAttributeValueOfUnique(bestAttr, dataset);
List subAttribute = new ArrayList();
subAttribute.addAll(attribute);
subAttribute.remove(bestAttr);
for(String attrValue : attrValueList) {
//更新数据集dataset
List> subDataSet = DataSetUtil.getSubDataSetByAttribute(dataset, bestAttr, attrValue);
//递归构建子树
TreeNode childTree = createDecisionTree(subAttribute, subDataSet);
tree.addAttributeValue(attrValue);
tree.addChild(childTree);
}
return tree;
}
/**
* 选出最优属性
* @param attribute
* @param dataset
* @return
*/
public int getBestAttribute(List attribute, List> dataset) {
//calculate the gainRatio of each attribute, choose the max
int bestAttr = 0;
double maxGainRatio = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < attribute.size(); i++) {
double thisGainRatio = infoGainRatio.getGainRatio(i, dataset);
if(thisGainRatio > maxGainRatio) {
maxGainRatio = thisGainRatio;
bestAttr = i;
}
}
System.out.println("The best attribute is \"" + attribute.get(bestAttr) + "\"");
return bestAttr;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
//eg 1
String attr = "age income student credit_rating";
String[] set = new String[12];
set[0] = "youth high no fair no";
set[1] = "youth high no excellent no";
set[2] = "middle_aged high no fair yes";
set[3] = "senior low yes fair yes";
set[4] = "senior low yes excellent no";
set[5] = "middle_aged low yes excellent yes";
set[6] = "youth medium no fair no";
set[7] = "youth low yes fair yes";
set[8] = "senior medium yes fair yes";
set[9] = "youth medium yes excellent yes";
set[10] = "middle_aged high yes fair yes";
set[11] = "senior medium no excellent no";
List> dataset = new ArrayList>();
List attribute = Arrays.asList(attr.split(" "));
for(int i = 0; i < set.length; i++) {
String[] s = set[i].split(" ");
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for(int j = 0; j < s.length; j++) {
list.add(s[j]);
}
dataset.add(list);
}
DecisionTree dt = new DecisionTree();
TreeNode tree = dt.createDecisionTree(attribute, dataset);
tree.print("");
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class InfoGainRatio {
/**
* 获取某个属性的熵
* = -∑ p(xi)log(2,p(xi))
* @param list
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public double getEntropy(List list) {
//概率统计
Map probability = DataSetUtil.getProbability(list);
//熵计算
double entropy = 0;
Set set = probability.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Entry) iterator.next();
double prob = (double) entry.getValue();
entropy -= prob * (Math.log(prob) / Math.log(2));
}
return entropy;
}
/**
* 获取某个属性的信息增益 = Entropy(U) − ∑(|Di|/|D|)Entropy(Di)
*
离散属性
* @param attrId
* @param dataset
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public double getGain(int attrId, List> dataset) {
List targetList = DataSetUtil.getTarget(dataset);
List attrValueList = DataSetUtil.getAttributeValue(attrId, dataset);
double totalEntropy = getEntropy(targetList);
Map probability = DataSetUtil.getProbability(attrValueList);
double subEntropy = 0;
Set set = probability.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Entry) iterator.next();
double prob = (double) entry.getValue();
List subTargetList = DataSetUtil.getTargetByAttribute((String) entry.getKey(), attrValueList, targetList);
double entropy = getEntropy(subTargetList);
subEntropy += prob * entropy;
}
return totalEntropy - subEntropy;
}
/**
* 获取某个属性的信息增益率 = Gain(A) / SplitInfo(A)
*
离散属性
* @param attrId
* @param dataset
* @return
*/
public double getGainRatio(int attrId, List> dataset) {
List attrValueList = DataSetUtil.getAttributeValue(attrId, dataset);
double gain = getGain(attrId, dataset);
double splitInfo = getEntropy(attrValueList);
return splitInfo == 0 ? 0 : gain/splitInfo;
}
} 下面的代码是数据集处理的相关操作。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class DataSetUtil {
/**
* 获取数据集中的结果列
* @param dataset
* @return
*/
public static List getTarget(List> dataset) {
List target = new ArrayList();
int targetId = dataset.get(0).size() - 1;
for(List element : dataset) {
target.add(element.get(targetId));
}
return target;
}
/**
* 获取属性值
* @param attrId
* @param dataset
* @return
*/
public static List getAttributeValue(int attrId, List> dataset) {
List attrValue = new ArrayList();
for(List element : dataset) {
attrValue.add(element.get(attrId));
}
return attrValue;
}
/**
* 获取属性值,唯一值
* @param bestAttr
* @param dataset
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
public static List getAttributeValueOfUnique(int attrId, List> dataset) {
Set attrSet = new HashSet();
List attrValue = new ArrayList();
for(List element : dataset) {
attrSet.add(element.get(attrId));
}
Iterator iterator = attrSet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
attrValue.add((String) iterator.next());
}
return attrValue;
}
/**
* for test
* 输出数据集
* @param attribute
* @param dataset
*/
public static void printDataset(List attribute, List> dataset) {
System.out.println(attribute);
for(List element : dataset) {
System.out.println(element);
}
}
/**
* 数据集纯度检测
*/
public static boolean isPure(List data) {
String result = data.get(0);
for(int i = 1; i < data.size(); i++) {
if(!data.get(i).equals(result))
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 对一列进行概率统计
* @param list
* @return
*/
public static Map getProbability(List list) {
double unitProb = 1.00/list.size();
Map probability = new HashMap();
for(String key : list) {
if(probability.containsKey(key)) {
probability.put(key, unitProb + probability.get(key));
}else{
probability.put(key, unitProb);
}
}
return probability;
}
/**
* 根据属性值,分离出结果列target
* @param attrValue
* @param attrValueList
* @param targetList
* @return
*/
public static List getTargetByAttribute(String attrValue,
List attrValueList, List targetList) {
List result = new ArrayList();
for(int i=0; i> getSubDataSetByAttribute(
List> dataset, int attrId, String attrValue) {
List> subDataset = new ArrayList>();
for(ArrayList list : dataset) {
if(list.get(attrId).equals(attrValue)) {
ArrayList cutList = new ArrayList();
cutList.addAll(list);
cutList.remove(attrId);
subDataset.add(cutList);
}
}
System.out.println(subDataset);
return subDataset;
}
} import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TreeNode {
public String attribute;
public List attributeValue;
public List child;
//for leaf node
public boolean isLeaf;
public String targetValue;
TreeNode() {
attributeValue = new ArrayList();
child = new ArrayList();
}
public String getAttribute() {
return attribute;
}
public void setAttribute(String attribute) {
this.attribute = attribute;
}
public List getAttributeValue() {
return attributeValue;
}
public void setAttributeValue(List attributeValue) {
this.attributeValue = attributeValue;
}
public void addAttributeValue(String attributeValue) {
this.attributeValue.add(attributeValue);
}
public List getChild() {
return child;
}
public void setChild(List child) {
this.child = child;
}
public void addChild(TreeNode child) {
this.child.add(child);
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return isLeaf;
}
public void setLeaf(boolean isLeaf) {
this.isLeaf = isLeaf;
}
public String getTargetValue() {
return targetValue;
}
public void setTargetValue(String targetValue) {
this.targetValue = targetValue;
}
public void print(String depth) {
if(!this.isLeaf){
System.out.println(depth + this.attribute);
depth += "\t";
for(int i = 0; i < this.attributeValue.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(depth + "---(" + this.attributeValue.get(i) + ")---" );
this.child.get(i).print(depth + "\t");
}
} else {
System.out.println(depth + "[" + this.targetValue + "]");
}
}
} 这是很简单的实现,当然代码还是有很需要完善的地方。比如,数据集和相关的操作其实可以放在一个类里来实现,这里没有添加对连续变量的处理,剪枝也还没实现。anyway,C4.5算法的主要逻辑毕竟已经实现了,其余的用到的时候再慢慢扩充吧。