(九)利用processing展示简单函数的使用
随机绘制直线:
void setup(){
size(480, 120);
smooth();
frameRate(2);
}
void draw(){
background(204);
for(int x = 20; x < width; x+=20){
float mx = mouseX/10;
float offsetA = random(-mx, mx);
float offsetB = random(-mx, mx);
line(x+offsetA, 20, x-offsetB, 100);
}
saveFrame("Shape.png");
}
随机移动图像:
float speedX = 10.0;
float speedY = 2.5;
int diameter = 20;
float x;
float y;
void setup(){
size(640, 120);
smooth();
x = width/2;
y = height/2;
randomSeed(20);
}
void draw(){
x += random(-speedX, speedX);
y += random(-speedY, speedY);
x = constrain(x, 0, width);
y = constrain(y, 0, height);
ellipse(x, y, diameter, diameter);
}
函数使用说明:
randomSeed(Auto) //设置种子数, Auto 相同的话生成的种子数相同,随机数也就是相同的
random(-x, x) //在-x 到 x 之间随机成生一个数字
constrain(x, 0, width) //将x 的值设置在(0, width)这范围中
//通过计时器实现一个圆形的向左向右移动
int timer1 = 2000;
int timer2 = 4000;
float x;
void setup(){
size(640, 120);
smooth();
x = width/2;
}
void draw(){
int currentTime = millis();
background(204);
if(currentTime > timer2){
x -= 0.5;
}else if(currentTime > timer1){
x += 0.5;
}
ellipse(x, 60, 90, 90);
}
函数使用说明:
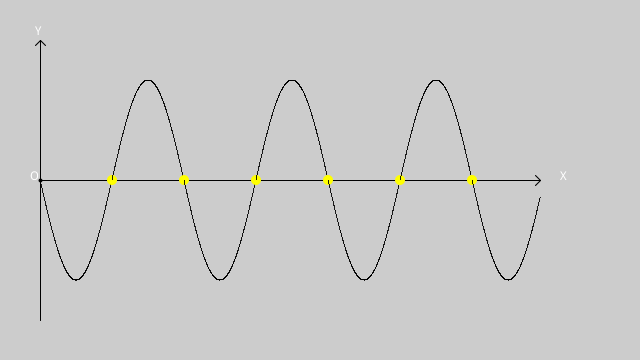
millis() //返回当前程序的运行时间,单位为毫秒实现sin函数的图形化显示:
float angle = 0.0;
float x;
float y;
float stepX = 0.2;
int rate = 0;
void display_XY(){
line(40, 40, 40, 320);
line(40, height/2, width-100, height/2);
text("Y", 35, 35);
line(40, 40, 35, 45);
line(40, 40, 45, 45);
text("O", 30, height/2);
text("X", 560, height/2);
line(width-105, height/2-5,width-100, height/2);
line(width-105, height/2+5, width-100, height/2);
x = 40;
y = height/2;
strokeWeight(4);
point(x, y);
strokeWeight(1);
}
void setup(){
size(640, 360);
smooth();
background(204);
frameRate(120);
display_XY();
}
void draw(){
rate++;
if(rate == 60){
rate = 0;
}
angle += 0.5;
y = sin(radians(angle))*100+height/2;
x += stepX;
point(x, y);
if(y>-0.01+height/2 && y < 0.01 + height/2){
noStroke();
fill(255, 255, 0);
ellipse(x, y, 10, 10);
noFill();
stroke(0);
}
if(x >= 540){
saveFrame("Shape.png");
noLoop();
//exit();
}
}
函数说明:
sin(float) //读入弧度值,函数结果 位于 -1,1之间
float angle = 0.0;
float offset = 60;
float scalar = 2;
float speed = 0.05;
void setup(){
size(120, 120);
fill(0);
smooth();
}
void draw(){
float x = offset + cos(angle) * scalar;
float y = offset + sin(angle) * scalar;
ellipse(x, y, 2, 2);
angle += speed;
scalar += speed;
}程序运行结果:
图形的平移,旋转和缩放:
float angle = 0.0;
float angleDirection = 1;
float speed = 0.005;
void setup(){
size(200, 200);
smooth();
}
void draw(){
background(204);
translate(100, 100);
rotate(angle);
strokeWeight(12);
line(0, 0, 40, 0);
translate(40, 0);
rotate(angle * 2.0);
strokeWeight(6);
line(0, 0, 30, 0);
translate(30, 0);
rotate(angle * 3.0);
strokeWeight(3);
line(0, 0, 20, 0);
angle += speed*angleDirection;
if((angle > QUARTER_PI) || (angle < 0)){
angleDirection *= -1;
}
saveFrame("Shape.png");
}函数使用说明:
translate(x, y) //设置x, y为新的 0,0点
rotate(angle) //将坐标系统进行旋转,angle为旋转的角度,旋转是绕着原点进行的
scale(num) //num 为缩放比例,同时笔画的粗细也会进行缩放,strokeWeight(1.0/num)修改笔画的权重
nf(i, 4) //nf(1, 4)指(0001), nf(11, 4)指(0011)