抽象代数入门(二)
Field(域)
Dfn: ”Field“ is a commutative ring ![]() , s.t. every non-zero element has inverse.
, s.t. every non-zero element has inverse.
这个交换环对于乘法和加法都满足交换性,而且对于所有非零元素都存在逆。
- 对加法逆,即
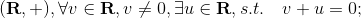
- 对乘法逆,即
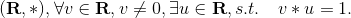
这两个都满足,u是对应元素的逆。加法的逆写成-v, 乘法的逆写成![]() 都是可以的,都是符号表示。
都是可以的,都是符号表示。
Polynomials over a field
Dfn: Let ![]() be a field. A polynomial over a field
be a field. A polynomial over a field ![]() is an equation of the form :
is an equation of the form :![]() , where the coefficients
, where the coefficients ![]() . The set of all polynomials over a field
. The set of all polynomials over a field ![]() is denoted
is denoted ![]() .
.
ideal(理想)
Dfn: "Idela" of ![]() is a subset
is a subset ![]() of
of ![]() s.t. it is closed under addition and closed under multiplication by any element of
s.t. it is closed under addition and closed under multiplication by any element of ![]() .
.
- closed under addition:
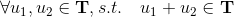
- closed under multiplication:
![\exists r\in \mathbb{F}[z], \forall u\in\mathbf{T}, s.t. \quad r*u\in\mathbf{T}](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ace2e10b4dc84dec8412c491cfeab5e7.gif)
i.e. the set of even integers is an ideal in the ring of integers ![]() . Given an ideal
. Given an ideal ![]() , it is possible to define a quotient ring
, it is possible to define a quotient ring ![]() .
.
i.e. ![]() is ideal.
is ideal.
Module(模)
Dfn: a module is one of the fundamental algebraic structures used in abstract algebra. A module over a ring is a generalization of the notion of vector space over a field.
环上的一个模,域上的一个向量空间。在模中的系数是来自于环的,而向量空间中的系数是来自于域的。(域的定义更为严格,比之于环),系数的寻去空间更为通用,因此说模是向量空间的泛化。
Integral Domain(整域)
Dfn: 也叫整环,指的是不含零因子(divisor)的交换环。环中乘法的单位元通常和加法的单位元不同,整环是整数环的抽象化。关于交换环(commutative ring)的定义可以参看抽象代数入门(一)。
- multiplicative identity element:
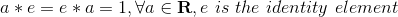 .
. - No divisors of 0,
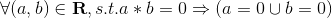 or
or 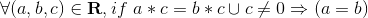
i.e. ![]()
![]() is an intergral domain.
is an intergral domain.
Principal Ideal Ring(主理想环)
Dfn: 每个理想都可以由单个元素生成的环,写成left ideal xR or right ideal Rx 的形式,其中 x 是 环 R 中的一个元素。
Dfn: 如果交换的理想环R 同时也是整环,那么称之为主理想域(principal ideal domain), 简写成 P.I.D.
i.e. 整数环是主理想域,Eucildean Ring 一般都是。
Polynomial Ring(多项式环)
多项式环是对初等数学中多项式的泛化,通常表示成 ![]() 。
。
Dfn: The polynomial ring, ![]() , in
, in ![]() over
over ![]() is defined as:
is defined as:
![]() ,
, ![]() is the coefficient of
is the coefficient of ![]() ,
, ![]() 只是一个符号,
只是一个符号,![]() 称为 powers of
称为 powers of ![]() .
.
The ideal generated by a finite set of polynomials ![]() defined as:
defined as:
![]()
Monoic Polynomial(单多项式)
Dfn: a single-variable polynomial(univariate polynomial) in which the leading coefficient is equal to 1. Which can be written in the form:
![]()
Unique Factorization Domain(唯一分解环)
Dfn: 唯一分解环是一个整环(integral domain), 其元素都可以表示成有限个不可约元素乘积的形式,并在允许重排下唯一,相当于满足基本算术定理的整环。简写为UFD.
A integral domain R is said to be a unique factorization domain if it has the following factorization properties:
- Every nonzero nonunit element
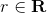 can be written as a product of a finite number of irreducible elements
can be written as a product of a finite number of irreducible elements 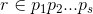 .
. - The factorization into irreducible elements is unique in the sense that if
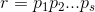 and
and 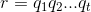 are two factorizations. Then s=t and after a suitable reindexing of the factor,
are two factorizations. Then s=t and after a suitable reindexing of the factor, 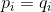 .
.
Every principal ideal domain R is a unique factorization domain.