leetcode算法
59. 滑动窗口最大值
给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,找出所有滑动窗口里数值的最大值。
例如,如果输入数组{2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1}及滑动窗口的大小3。
那么一共存在6个滑动窗口,分别是: {[2,3,4],2,6,2,5,1}, {2,[3,4,2],6,2,5,1}, {2,3,[4,2,6],2,5,1}, {2,3,4,[2,6,2],5,1}, {2,3,4,2,[6,2,5],1}, {2,3,4,2,6,[2,5,1]}。
他们的最大值分别为{4,4,6,6,6,5};
【注】:并不复杂,注意最开头特殊情况的处理即可(题目没讲清楚)。
class Solution {
public:
vector maxInWindows(const vector& num, unsigned int size)
{
int len = num.size();
vector res;
if(len==0 || size==0 || len 58. 动态规划,求连续子数组的最大和
给一个数组,返回它的最大连续子序列的和。
例如:{6,-3,-2,7,-15,1,2,2},连续子向量的最大和为8(从第0个开始,到第3个为止)。
class Solution {
public:
int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(vector array) {
int len = array.size();
vector dp(len,0);
dp[0] = array[0];
int max_sum = dp[0];
for(int i=1; i0 ? dp[i-1]+array[i] : array[i]);
max_sum = ( dp[i]>max_sum ? dp[i] : max_sum);
}
return max_sum;
}
};
57. 用两个栈实现队列
这样Solution对外表现得行为,就和队列一样。我们可以使用Solution.push 将元素压入队列尾部,Solution.pop() 弹出并返回队首得元素。
实际上,C++中queue有四条指令,
q.push(item)压入队尾,q.back()访问队尾,q.pop()弹出队首,q.front()访问队首。 把访问和添加删除元素分开了。
class Solution
{
public:
void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
int pop() {
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.top());
stack1.pop();
}
int temp = stack2.top();
stack2.pop();
while(!stack2.empty()){
stack1.push(stack2.top());
stack2.pop();
}
return temp;
}
private:
stack stack1;
stack stack2;
};
56. 二叉搜索树中第k小的结点
给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中的第k小的结点。
例如, (5,3,7,2,4,6,8) 中,按结点数值大小顺序第三小结点的值为4。
【思路】:编写递归程序的精髓是什么?!
class Solution {
public:
int index = 0;
TreeNode* KthNode(TreeNode* pRoot, int k)
{
if(pRoot != NULL){
TreeNode* node = KthNode(pRoot->left, k);
if(node != NULL)
return node;
index++;
if(index == k)
return pRoot;
node = KthNode(pRoot->right, k);
if(node != NULL)
return node;
}
return NULL;
}
};
55. 二叉树的 序列化 与反序列化
请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
【思路】:整体上来说,这个题相对比较难。读大神的代码,并参照着写下来的。不过,学到并理解了 二级指针,巩固了函数重载,有收获!
class Solution {
public:
char* Serialize(TreeNode *root) {
if(root==NULL)
return NULL;
string str;
Serialize(root, str);
char* ret = new char[str.length()+1];
int i;
for(i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
ret[i] = str[i];
ret[i] = '\0';
return ret;
}
void Serialize(TreeNode *root, string& str){
if(root == NULL){
str += '#';
return; // void 函数的返回方式
}
string r = to_string(root->val);
str += r;
str += ',';
Serialize(root->left, str);
Serialize(root->right, str);
}
TreeNode* Deserialize(char *str) {
if(str == NULL)
return NULL;
TreeNode* ret = Deserialize(&str);
return ret;
}
TreeNode* Deserialize(char **str){
if(**str == '#'){
++(*str);
return NULL;
}
int num = 0;
while(**str != '\0' && **str != ','){
num = num*10 + ((**str)-'0');
++(*str);
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(num);
if(**str == '\0')
return root;
else
++(*str);
root->left = Deserialize(str);
root->right = Deserialize(str);
return root;
}
};
54. 从左向右层次遍历
从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层结点从左至右输出。每一层输出一行。
【思路】:和53题几乎完全一致,此处用两个queue实现。
(当然之前有使用一个queue实现的代码)
class Solution {
public:
vector > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) {
queue queue1, queue2;
vector > result;
if(pRoot!=NULL)
queue1.push(pRoot);
TreeNode* node;
while(!queue1.empty() || !queue2.empty()){
vector data;
if(!queue1.empty()){
while(!queue1.empty()){
node = queue1.front();
data.push_back(node->val);
queue1.pop();
if(node->left!=NULL)
queue2.push(node->left);
if(node->right!=NULL)
queue2.push(node->right);
}
}
else if(!queue2.empty()){
while(!queue2.empty()){
node = queue2.front();
data.push_back(node->val);
queue2.pop();
if(node->left!=NULL)
queue1.push(node->left);
if(node->right!=NULL)
queue1.push(node->right);
}
}
result.push_back(data);
}
return result;
}
};
53. 之字形打印二叉树
请实现一个函数按照之字形打印二叉树。
即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右至左的顺序打印,第三行按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
【思路】:利用两个栈来实现,非常巧妙。避免了队列实现时的reverse<见54题>
class Solution {
public:
vector > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) {
stack stack1, stack2;
vector > result;
if(pRoot!=NULL)
stack1.push(pRoot);
TreeNode* node;
while(!stack1.empty() || !stack2.empty()){
vector data;
if(!stack1.empty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
node = stack1.top();
stack1.pop();
data.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left!=NULL)
stack2.push(node->left);
if(node->right!=NULL)
stack2.push(node->right);
}
}
else if(!stack2.empty()){
while(!stack2.empty()){
node = stack2.top();
stack2.pop();
data.push_back(node->val);
if(node->right!=NULL)
stack1.push(node->right);
if(node->left!=NULL)
stack1.push(node->left);
}
}
result.push_back(data);
}
return result;
}
};
52. 对称二叉树
请实现一个函数,用来判断一颗二叉树是不是对称的。参考了一篇图文并茂博客

利用了函数的重载,非常巧妙。
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* pRoot)
{
if(pRoot == NULL)
return true;
return isSymmetrical(pRoot->left, pRoot->right);
}
private:
bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* pLeftRoot, TreeNode* pRightRoot)
{
if(pLeftRoot==NULL && pRightRoot==NULL)
return true;
if(pLeftRoot==NULL || pRightRoot==NULL)
return false;
if(pLeftRoot->val != pRightRoot->val)
return false;
return isSymmetrical(pLeftRoot->left, pRightRoot->right)
&& isSymmetrical(pLeftRoot->right, pRightRoot->left);
}
};
51. 二叉树的下一个结点
给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。
注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
【思路】:强行中序遍历可行,但不是最优; 找到中序遍历的本质。
/*
struct TreeLinkNode {
int val;
struct TreeLinkNode *left;
struct TreeLinkNode *right;
struct TreeLinkNode *next; // 指的是父结点
TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode)
{
if(!pNode) return NULL;
TreeLinkNode* res = pNode;
if(res->right!=NULL){
res = res->right;
while(res->left!=NULL) res = res->left;
return res;
}
res = pNode;
while(res->next!=NULL){
if(res->next->left == res) return res->next;
res = res->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};
50. 删除链表中的重复元素
【思路】:用两个指针实现,(有一种智能指针的东西也特别秀!)
请删除一个排序的链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。
例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
有两个注意!
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead)
{
ListNode* Head = new ListNode(0);
Head->next = pHead; // 注意
ListNode* slow = Head;
ListNode* fast = pHead;
while(fast){
if(fast->next!=NULL && fast->val==fast->next->val){
while(fast->next!=NULL && fast->val==fast->next->val)
fast = fast->next;
slow->next = fast->next; //注意
fast = fast->next;
}
else{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
}
return Head->next;
}
};
49.链表的入口点
给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
此处是有一个数学关系的(详见博客),顿时感觉数学真强大!
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead)
{
if(!pHead->next) return NULL;
ListNode* slow = pHead;
ListNode* fast = pHead;
while(fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast){
fast = pHead;
while(slow!=fast){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
48. 字符流中第一个不重复的字符
待解决
47. 检查为数值 字符串
【思路】:1. if else;2.正则表达式,建立规则;3.状态迁移(很新奇)
请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。
例如,字符串"+100",“5e2”,"-123",“3.1416"和”-1E-16"都表示数值。 但"12e",“1a3.14”,“1.2.3”,"±5"和"12e+4.3"都不是。
非常秀的代码!!
class Solution {
public:
char arr[10] = "+-n.ne+-n";
int turn[10][9] = {
//+ - n . n e + - n
{1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, // # start
{0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, // +
{0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, // -
{0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}, // n
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}, // .
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, // n
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, // e
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1}, // +
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1}, // -
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1} // n
};
bool isNumeric(char* string)
{
int cur = 0;
for(int i = 0, j; string[i]!='\0'; i++){
for(j = 0; j<9; j++){
if(turn[cur][j]){
if(('0' <= string[i] && string[i] <= '9' && arr[j] == 'n') ||
(string[i] == 'E' && arr[j] == 'e')||
string[i] == arr[j]){
cur = j+1;
break;
}
}
}
if(j>=9) return false;
}
if(cur == 3 || cur == 4 || cur == 5 || cur == 9) return true;
return false;
}
};
46.正则表达式
正则表达式(规则表达式)式对字符串操作的一种逻辑公式。 就是用 事先定义好的一些字符,及这些字符的组合,组成一个“规则字符串”,
这个“规则字符串”用来表达对字符串的一种过滤逻辑。
请实现一个函数用来匹配包括'.'和'*'的正则表达式。
模式中的字符'.'表示任意一个字符,
'*'表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(包含0次)。
在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式。
例如,字符串"aaa"与模式"a.a"和"abaca"匹配,但是与"aa.a"和"ab*a"均不匹配。
class Solution {
public:
bool match(char* str, char* pattern)
{//C 风格的字符串,结束的标志是 '\0'
if(*str == '\0' && *pattern == '\0')
return true;
if(*(pattern+1) != '*'){
if(*str == *pattern||(*str != '\0' && *pattern == '.'))
return match(str+1,pattern+1);
else return false;
}
else {
if(*str == *pattern||(*str != '\0' && *pattern == '.'))
return match(str,pattern+2)||match(str+1,pattern+2)||match(str+1,pattern);
else // 以上三种情况分别对应着,*前面的字符出现,0,1,多次
return match(str,pattern+2);
}
}
};
45. 构建乘积数组
给定一个数组A[0,1,...,n-1],请构建一个数组B[0,1,...,n-1],其中B中的元素B[i]=A[0]*A[1]*...*A[i-1]*A[i+1]*...*A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
【思路】:非常巧妙的构建方法,两遍for循环解决问题。
class Solution {
public:
vector multiply(const vector& A) {
int length = A.size();
vector B(length,1);
for(int i = 1; i < length; i++){
B[i] = B[i-1]*A[i-1];
}
int temp = 1;
for(int j = length-2; j>=0; j--){
temp *= A[j+1];
B[j] *= temp;
}
return B;
}
};
44.输出给定数组中第一个重复的数字
如:输入长度为7的数组{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字2。
class Solution {
public:
bool duplicate(int numbers[], int length, int* duplication) {
if(length==0) return false;
map M;
for(int i=0; i1){
*duplication = numbers[i];
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
43. 字符串转换成整形
【思路】:需要一次遍历与转换,比较简单,重点在于编程落实上。for循环的3句写的都很好。
class Solution {
public:
int StrToInt(string str) {
int n = str.size(), s = 1;
if(!n) return 0;
long long res = 0;
if(str[0] == '-') s = -1;
for(int i = (str[0] == '+'||str[0] == '-') ? 1:0; i42. 位运算两整数相加
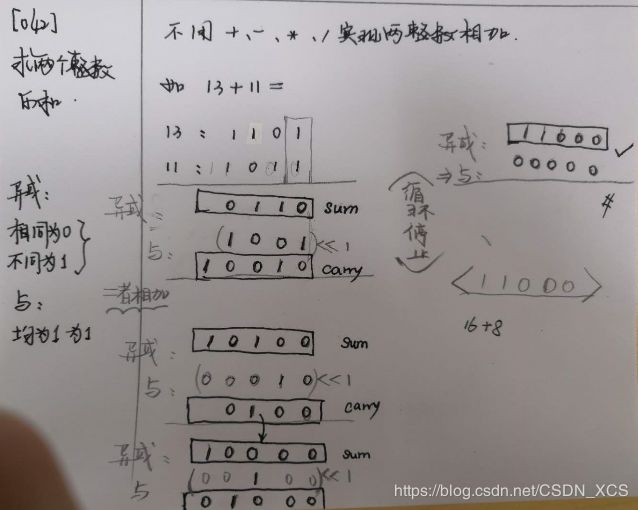
求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用+、-、*、/四则运算符号。
class Solution {
public:
int Add(int num1, int num2)
{
while(num2){
int sum = num1 ^ num2;
int carry = (num1 & num2)<<1;
num1 = sum;
num2 = carry;
}
return num1;
}
};
41. 短路特性
求1+2+3+…+n,要求不能使用乘除法、for、while、if、else、switch、case等关键字及条件判断语句(A?B:C)。
class Solution {
public:
int Sum_Solution(int n) {
int ans = n;
(ans>0) && (ans += Sum_Solution(n-1));
return ans;
}
};
使用判断的递归版应该是这样的:
class Solution {
public:
int Sum_Solution(int n) {
return n>0 ? n+Sum_Solution(n-1) : n;
}
};
40. 约瑟夫环
【思路】:圆圈中最后剩下的数字[算法]
数学分析之后,得到了一个递推公式:对于给定的m,长度为n的序列最后剩余的数字,可以由长度为n-1的序列最后剩余的数字确定。
class Solution {
public:
int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m)
{
if(n==0) return -1; // 返回值必须是-1,否则报错
int res = 0, Num = 1;
while(Num【思路2】:使用链表模拟一个约瑟夫环,从中不断剔除元素,直到最后剩余一个元素。
39. 扑克牌顺子
暂时没调通
38. 反转字符串
“student. a am I” ==> “I am a student.”
【注意】整体上反转后,单词也要反转一下。
【思路】:反转使用reverse,所要作的就是判断空格(分隔符)
class Solution {
public:
string ReverseSentence(string str) {
if(str.empty()) return str;
auto beg = str.begin(),beg1 = ++str.begin(),end = str.end();
reverse(beg,end);
while(true){
if(beg1==end){
reverse(beg,beg1);
break;
}
if(*beg1==' '){
reverse(beg,beg1);
++beg1;
beg = beg1;
}
else
++beg1;
}
return str;
}
};
37. 循环左移字符串
汇编语言中有一种移位指令叫做循环左移(ROL)。对于一个给定的字符序列S,请你把其循环左移K位后的序列输出。
例如,字符序列S=”abcXYZdef”,要求输出循环左移3位后的结果,即“XYZdefabc”。
class Solution {
public:
string LeftRotateString(string str, int n) {
int size = str.size();//一开始就要处理最特殊的情况,输入保护
if(size == 0) return str;
string str1 = str+str;
return str1.substr(n,size);
}
};
36. 找到递增序列中和为S积最小的两个数
输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字S,在数组中查找两个数,使得他们的和正好是S,如果有多对数字的和等于S,输出两个数的乘积最小的。
【思路】:距离最远的积最小自然满足,从两头向中间遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector FindNumbersWithSum(vector array,int sum) {
vector res;
if(array.size()<2) return res;
auto beg = array.begin(), end = --array.end();
while(beg!=end){
if(*beg+*end==sum){
res.push_back(*beg);
res.push_back(*end);
return res;
}
else if(*beg+*end>sum) --end;
else if(*beg+*end 35. 求取和为S的所有序列
输出所有和为S的连续正数序列。序列内按照从小至大的顺序,序列间按照开始数字从小到大的顺序
【思路1】:利用了序列和的规律!
3点需要注意,1.逻辑与或的优先级(不加括号报错);2.整型除法int/int;3.二维数组添加元素(元素推入一维数组,一维数组推入二维数组)
class Solution {
public:
vector > FindContinuousSequence(int sum) {
vector > res;
if(sum<3) return res;
for(int n = (int)sqrt(2*sum); n>1; n--){
if(((n&1)==1 && sum%n==0) || (sum%n)*2==n){ // n为奇数
vector temp;
for(int i = 0, k=sum/n-(n-1)/2; i 34. 找到数组中出现一次的两个数
一个整型数组里除了两个数字之外,其他的数字都出现了偶数次。请写程序找出这两个只出现一次的数字。
【思路1】:用map,虽然有点暴力。(熟悉了map的迭代器)<这种方法没有充分利用其他数字都出现了偶数次这个条件>
【思路2】:评论里有一种巧妙的解法
class Solution {
public:
void FindNumsAppearOnce(vector data,int* num1,int *num2) {
// 返回值通过 指针带回
int Num1 = *num1, Num2 = *num2;
int length = data.size();
map M;
for(int i = 0; isecond == 1 && count == 0){
*num1 = iter->first;
count++;
}
else if(iter->second == 1 && count == 1){
*num2 = iter->first;
}
}
}
};
33. 判断是否是 平衡二叉树
【非常巧妙的做法】
class Solution {
public:
bool IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode* pRoot) {
return getDepth(pRoot) != -1;
}
private: // 感觉这个函数实现了 求取深度之外的另一个任务!
int getDepth(TreeNode* pRoot){
if(pRoot==NULL) return 0;
int left = getDepth(pRoot->left);
if(left == -1) return -1;
int right = getDepth(pRoot->right);
if(right == -1) return -1;
return abs(left-right) > 1 ? -1 : max(left,right)+1;
}
};
32. 树的深度
输入一棵二叉树,求该树的深度。
从根结点到叶结点依次经过的结点(含根、叶结点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。
【思路1】:递归(比较简洁)
【思路2】:层次遍历
class Solution {
public:
int TreeDepth(TreeNode* pRoot)
{
if(pRoot == NULL)
return 0;
int left = TreeDepth(pRoot->left);
int right = TreeDepth(pRoot->right);
return max(left,right)+1;
}
};
思路2的实现:
class Solution {
public:
int TreeDepth(TreeNode* pRoot)
{
if(pRoot == NULL)
return 0;
queue que; // 注意 类型
que.push(pRoot);
int depth = 0;
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
depth++;
for(int i = 0; ileft) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};
31. 有序数组中,某元素的长度
统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数。
【思路】:使用二分查找 找到元素位置,由该位置出发,向左、向右确定区域上下限。
class Solution {
public:
int GetNumberOfK(vector data ,int k) {
// 找到K出现的位置
int index = getK(data, k);
if (index==-1) return 0;
int Lower = index, Upper = index;
for(;Lower>=0;Lower--){
if(data[Lower]k)
break;
}
return (Upper-1)-(Lower+1)+1;
}
int getK(vector data,int k){
int start = 0,end = data.size()-1;
int mid = (start + end)>>1;
while(start <= end){
if(data[mid] < k) start = mid + 1;
else if(k < data[mid]) end = mid - 1;
else return mid;
mid = (start + end)>>1;
}
return -1;
}
};
30. 找到字符串中出现一次的字符所在的位置
【感悟】:本质上是个统计(map)+遍历 (比较简单)
class Solution {
public:
int FirstNotRepeatingChar(string str) {
//统计需要遍历一遍 //查找位置又遍历一遍
if(str.size()==0)
return -1;
auto beg = str.begin(), end = str.end();
map char_dict;
while(beg!=end){
++char_dict[*beg];
++beg;
}
for(int i = 0; i 29. 求前N个丑数
求按从小到大的顺序的第N个丑数,约定1是第一个丑数。其中,丑数(Ugly Number)是指只包含质因子2、3和5的数。
例如6、8都是丑数,但14不是,因为它包含质因子7。
【方案】:维护了三个队列,分别有序,取队首元素的最小值。
存在优化版,可以使用一个vector完成,待学习。
class Solution {
public:
int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
if (index < 7)
return index;
queue q2, q3, q5;
vector result{1};
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < index; i++) {
q2.push(result[i] * 2);
q3.push(result[i] * 3);
q5.push(result[i] * 5); // 队列的添加元素是.push,向量的添加元素是.push_back
int minNum = min(q2.front(), q3.front()); //参数只能是两个值(或是一个数组)
minNum = min(minNum, q5.front());
result.push_back(minNum);
if (q2.front() == minNum) q2.pop();
if (q3.front() == minNum) q3.pop();
if (q5.front() == minNum) q5.pop();
}
return result.back();
}
};
28. 给定数组,拼出最小的数
输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。
例如输入数组{3,32,321},则打印出这三个数字能排成的最小数字为321323。
【感悟】:有序,比无序更好处理
【技巧】:重载了sort函数的 比较器。
#include "pch.h"
#include
#include
#include // 包含进来这两个标准库
using namespace std;
static int compare(const string& st1, const string& st2); //重载比较器
string PrintMinNumber(vector numbers);
int main()
{
vector numbers;
numbers.push_back(3); numbers.push_back(32); numbers.push_back(321);
string str1 = PrintMinNumber(numbers);
cout << str1 << endl;
return 0;
}
static int compare(const string& st1, const string& st2) {
string s1 = st1 + st2;
string s2 = st2 + st1;
return s1 < s2;
}
string PrintMinNumber(vector numbers) {
string result;
if (numbers.size() == 0)
return result;
vector vec_str;
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.size(); i++) {
vec_str.push_back(std::to_string(numbers[i]));
}
auto beg = vec_str.begin(), end = vec_str.end();
sort(beg, end, compare);
while (beg != end) {
result = result.append(*beg);
++beg;
}
return result;
}
27. 找规律题(求1到n之间,1出现的次数)
很快的求出任意非负整数区间中X出现的次数(从1 到 n 中X出现的次数)。
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n)
{ // 1到n 中,1出现的次数
if(n<0)
return 0;
int high,low,curr,temp,i=1;
high = n;
int total = 0;
while(high!=0){
high = n/(int)pow(10,i);
temp = n%(int)pow(10,i);
curr = temp/(int)pow(10,i-1);
low = temp%(int)pow(10,i-1);
if(curr == 1)
total = total + high*(int)pow(10,i-1)+low+1;
else if(curr > 1)
total = total + (high+1)*(int)pow(10,i-1);
else
total = total + high*(int)pow(10,i-1);
i++;
}
return total;
}
};
26. 找出数组中最小的K个元素
输入n个整数,找出其中最小的K个数。
例如输入4,5,1,6,2,7,3,8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1,2,3,4。
【思路】:最小堆+priority_queue结构
class Solution {
public:
vector GetLeastNumbers_Solution(vector input, int k) {
// 必须要遍历一遍,才知道某个数是否最小(冒泡排序):n*k
// 快排:n*logn
// 最小(大)堆: n*logk
priority_queue Q; // 自带优先级的队列(时刻保持按序排列,且队首元素最大(默认))
vector res;
if(input.size() < k || k <= 0) return res;
auto beg = input.begin(), end = input.end();
while(beg!=end){
if(Q.size() < k) Q.push(*beg);
else if(*beg < Q.top()){
Q.pop(); Q.push(*beg);
}
++beg;
}
while(!Q.empty()){
res.push_back(Q.top());
Q.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
25. 统计数组中元素的出现次数
数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。
例如输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。如果不存在则输出0。
【思路】:很容易想到使用Map
class Solution {
public:
int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector numbers) {
auto beg = numbers.begin(), end = numbers.end();
if (beg == end)
return 0;
map Num;
int count = 0; int len = numbers.size()/2;
while(beg!=end){
count = ++Num[*beg];
if (count>len)
return *beg;
++beg;
}
return 0;
}
};
24. 返回二叉树的所有路径
输入一棵二叉树的根节点和一个整数,打印出符合要求的所有路径。
路径定义为:从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。要求是,组成路径的所有节点的和,等于给定整数。
(注意: 在返回值的list中,数组长度大的数组靠前)
【思路1】:首先返回所有路径,然后进行下一步处理。
【思路2】:再先序遍历基础上作修改。path.pop()还未想明白。
class Solution:
# 返回二维列表,内部每个列表表示找到的路径
def FindPath(self, root, expectNumber):
# write code here
if root is None:
return []
result = []
def DeepthFirstTravel(root, path, currentSum): # 考虑一个小的节点,所有可能都处理到
currentSum = currentSum+root.val # 这就是递归(统一的形式)
path.append(root)
isLeaf = root.left==None and root.right==None
if currentSum==expectNumber and isLeaf:
onePath = []
for node in path:
onePath.append(node.val)
result.append(onePath)
if currentSum23. 判断是否是二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则输出Yes,否则输出No。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
【注】:代码中,有几处,将多行语句放在了同一行
class Solution:
def VerifySquenceOfBST(self, sequence):
# write code here 二叉搜索树
length = len(sequence) # 1. 递归基的处理
if length == 0: return False
if length == 1: return True
root = sequence[-1]; i = 0
while True:
if sequence[i]22. 二叉树的镜像
操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
【注】:其中有一句Python小技巧作为初始思路的改进
class Solution:
# 返回镜像树的根节点
def Mirror(self, root):
# write code here
if not root: # 1.处理递归基
return root
# treenode1 = root.left
# root.left = self.Mirror(root.right) # 2.左子树。被改变之前,保存一下
# root.right = self.Mirror(treenode1) # 3.右子树。否则,这样两边相同了!
# Python小技巧
root.left, root.right = self.Mirror(root.right), self.Mirror(root.left)
return root
21. 层次遍历(广度优先遍历)
从上往下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同层节点从左至右打印。
【思路】:这里借助两个list——queue保存当前访问层的节点;queue1保存下一访问层的节点。
实际上,可以借助一个队列实现,待改进。
class Solution:
# 返回从上到下每个节点值列表,例:[1,2,3]
def PrintFromTopToBottom(self, root):
# write code here
result = []
if not root:
return result
queue = [root]
while queue:
queue1 = []
for i in queue:
if i.left:
queue1.append(i.left)
if i.right:
queue1.append(i.right)
result.append(i.val)
queue = queue1
return result
20. 判断B是否是A的子结构
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。
(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
【注】:此处,我是把子结构按成子树来理解的,暂不知二者有什么区别。
class Solution:
def HasSubtree(self, pRoot1, pRoot2):
# write code here
result = False
if pRoot1 != None and pRoot2 != None:
if pRoot1.val == pRoot2.val:
result = self.doesTree1HasTree2(pRoot1, pRoot2)
if not result:
result = self.HasSubtree(pRoot1.left, pRoot2)
if not result:
result = self.HasSubtree(pRoot1.right, pRoot2)
return result
def doesTree1HasTree2(self, pRoot1, pRoot2): # 判断(有相同根节点的)树是否相同
if pRoot2 is None:
return True
if pRoot1 is None:
return False
if pRoot1.val != pRoot2.val: # 必不可少,用来包括根节点在内的所有值
return False
return self.doesTree1HasTree2(pRoot1.left, pRoot2.left) and self.doesTree1HasTree2(pRoot1.right, pRoot2.right)
【额外补充】:
该链接中给出了 二叉树的Python实现
该链接中给出了 二叉树的Python实现及它的7种遍历方法
19. 重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回构造的TreeNode根节点(对于递归而言,认清函数的功能非常重要!)
def reConstructBinaryTree(self, pre, tin):
# write code here
if not pre or not tin: # 1.递归基处理:如果pre为空 或 tin为空
return None
root = TreeNode(pre.pop(0))
index = tin.index(root.val)
root.left = self.reConstructBinaryTree(pre, tin[:index]) # 2. 左子树的根为left
root.right = self.reConstructBinaryTree(pre, tin[index+1:]) # 3. 右子树的根为right
return root
【体悟】: 对于递归而言,站在函数功能的角度去思考很重要!
18. 输入一个字符串,按字典序打印所有排列
从此处起,换成python 2啦~
第一次见到该题目是在 图森的面试题里。该问题经典解决思路有不少,但都不是我当时的想法,直到翻到了下面一篇文章(不谋而合!!):
字典序全排列算法研究
核心思路以例子说明(截图援引上文):
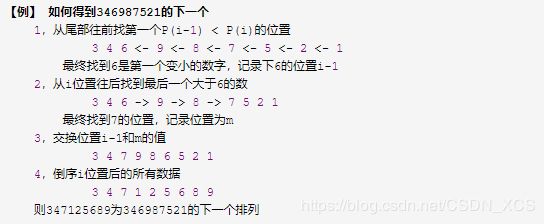
代码实现:
【版本一】:自己写的,思路很清晰。(do while循环不是很舒服)
vector Permutation(string str) {
auto beg = str.begin(), end = str.end();
vector result;
if (beg == end) // 表明str 为空
return result;
sort(str.begin(), str.end()); // 以下处理不为空的情况
result.push_back(str);
string str_revorder = str;
reverse(str_revorder.begin(), str_revorder.end());
if (str == str_revorder) // 表明str 只有一个元素
return result;
while (str != str_revorder) { // 表明str 至少有两个元素
auto iter1 = --str.end(); // 尽量不要改变 beg和end 的值。
auto iter2 = iter1; auto iter = iter1;
do {
--iter;
if (*iter < *iter1)
break;
iter1 = iter;
} while (iter != beg);
iter1 = iter;
do{
if (*iter2 > *iter1)
break;
--iter2;
} while (iter2 != iter1 && iter2 != beg);
swap(*iter1, *iter2);
sort((iter1 + 1), end);
//cout << str << endl;
result.push_back(str);
}
return result;
}
【版本二】:利用反向迭代器
class Solution {
public:
vector Permutation(string str) {
auto beg = str.begin(), end = str.end();
vector result;
if (beg == end) // 表明str 为空
return result;
sort(str.begin(), str.end()); // 以下处理不为空的情况
result.push_back(str);
auto rbeg = str.rbegin(), rend = str.rend(); // 反向迭代器
while (true) { // 表明str 至少有两个元素
auto iter = rbeg, iter1 = rbeg, iter2 = rbeg;
++iter;
while (iter != rend) {
if (*iter < *iter1)
break;
iter1 = iter;
++iter;
}
iter1 = iter;
if (iter1 == rend)
break;
while (iter2 != iter1) {
if (*iter2 > *iter1)
break;
++iter2;
}
swap(*iter1, *iter2);
sort(rbeg, iter1, greater()); // 必须加上greater
//cout << str << endl;
result.push_back(str);
}
return result;
}
};
版本3. 最终优化版
class Solution {
public:
vector Permutation(string str) {
vector res;
if(str.size()==1) res.push_back(str);
if(str.size()<=1) return res;
sort(str.begin(),str.end());
res.push_back(str);
while(true){
string::reverse_iterator iter, iter1, iter2;
for(iter = str.rbegin(), iter1 = iter+1; iter1!=str.rend(); iter1++,iter++){
if(*iter1<*iter) break;
}
if(iter1==str.rend()) break;
for(iter2 = str.rbegin(); iter2!=iter1; iter2++){
if(*iter1<*iter2) break;
}
swap(*iter1,*iter2);
sort(str.rbegin(), iter1, greater());
res.push_back(str);
}
return res;
}
};
另有递归算法:http://www.cnblogs.com/cxjchen/p/3932949.html
17. 判断序列是否有可能是栈的弹出序列
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。
例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)
【思路】:空间换时间
【体悟】:while本质是 多次if和goto的组合
class Solution {
public:
bool IsPopOrder(vector pushV,vector popV) {
// 本题的意思是,压入 弹出有可能交叉进行
// 借助一个 辅助栈实现,判断 栈顶元素是否和给出的弹出序列相应元素相等?
// 相等,则弹出,并且将新栈顶与序列下一个元素比较
// 不相等,则继续压入栈,
// 直到所有序列结束,给出判断结果
stack dataStack;
auto beg1 = pushV.begin(), end1 = pushV.end();
auto beg2 = popV.begin(), end2 = popV.end();
while(beg1!=end1){
dataStack.push(*beg1);
beg1++;
while(!dataStack.empty() && dataStack.top()==*beg2){
dataStack.pop();
beg2++;
}
}
// return dataStack.empty(); //含义等价于下面两句
if(dataStack.empty())
return true;
else
return false;
}
};
16. 栈的最小值
实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数
(时间复杂度应为O(1))。
【思路】:空间换时间
class Solution {
public:
stack dataStack, minStack;
void push(int value) {
dataStack.push(value);
// 保证minStack的顶部,一直存放最小值
if(minStack.empty())
minStack.push(value);
else{
int min = minStack.top();
value<=min? minStack.push(value): minStack.push(min);
}
}
void pop() {
dataStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
int top() {
return dataStack.top();
}
int min() {
return minStack.top();
}
};
#15. 绕圈形式输出矩阵
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,
例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.
【思路】:用 四个变量框定了输出矩阵的大小,
四个 for 循环依次 完成行列输出;
class Solution {
public:
vector printMatrix(vector > matrix) {
int rows = matrix.size(), cols = matrix[0].size();
vector res;
if(rows == 0||cols == 0) return res;
int top = 0, left = 0, right = cols-1, bottom = rows-1;
while(top<=bottom && left<=right){
// left to right
for(int i=left; i<=right; i++) res.push_back(matrix[top][i]);
top++;
// top to bottom
for(int i=top; i<=bottom; i++) res.push_back(matrix[i][right]);
right--;
// right to left
for(int i=right; i>=left && top<=bottom; i--) res.push_back(matrix[bottom][i]);
bottom--;
// bottom to top
for(int i=bottom; i>=top && left<=right; i--) res.push_back(matrix[i][left]);
left++;
}
return res;
}
};
14. 合并有序链表
【思路3】:迭代方法!!
减而治之
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2)
{ //3ms 356k
ListNode *node = nullptr;
if(pHead1 == nullptr) return pHead2;
if(pHead2 == nullptr) return pHead1;
if(pHead1->val<=pHead2->val){
node = pHead1;
node->next = Merge(pHead1->next,pHead2);
}
else{
node = pHead2;
node->next = Merge(pHead1,pHead2->next);
}
return node;
}
};
【思路2】:创建一个新的链表3,(运行错误:请检查是否存在数组、列表等越界非法访问,内存非法访问等情况)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2)
{
// 思路:把元素插入到 新建的链表3中去
ListNode *head3 = nullptr, *p =nullptr, *head1 = pHead1, *head2 = pHead2;
if(!head1)
return head2;
if(!head2)
return head1;
if(head2->val <= head1->val){
ListNode list3(head2->val);
head2 = head2->next;
*head3 = list3;
}
else{
ListNode list3(head1->val);
head1 = head1->next;
*head3 = list3;
}
p = head3;
while(head1&&head2){
//判断应该插入 哪个链表的元素
if(head2->val <= head1->val){
ListNode list3(head2->val);
*(p->next) = list3;
head2 = head2->next;
}
else{
ListNode list3(head1->val);
*(p->next) = list3;
head1 = head1->next;
}
p = p->next;
}
if(head1==nullptr)
p->next = head2;
if(head2==nullptr)
p->next = head1;
return head3;
}
};
【思路1】:把第二个链表插入到第一个中去。
觉得没有问题,但就是通过不了!
【注意:】
定义 ListNode *p
给 p 和 p->next 赋值是不同的!!
要想改变 节点中 next成员的值,必须 是给p->next 赋值!
正确的代码–思路更加清晰!
【注意:】p指针在带插入节点之前一个位置,才能够 用p->next修改。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2)
{
// 思路:通过一个 ListNode指针 遍历,将顺序连接
ListNode *head1 = pHead1, *head2 = pHead2;
if(!head1)
return head2;
if(!head2)
return head1;
// 以较小的作为头节点
ListNode *head3 = nullptr, *p = nullptr;
if(head1->val <= head2->val){
head3 = head1;
head1 = head1->next;
}
else{
head3 = head2;
head2 = head2->next;
}
p = head3; //【此处不能写成 p=head->next】
//遍历
while(head1&&head2){
if(head1->val <= head2->val){
//【p = pHead1; 体会括号里的句子为什么实现不了相同的效果!!】
p->next = head1;
head1 = head1->next;
}
else{
p->next = head2;
head2 = head2->next;
}
p = p->next;
}
if(head1 == nullptr)
p->next = head2;
if(head2 == nullptr)
p->next = head1;
return head3;
}
};
13. 反向输出链表
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
【思路】:改变指向,需要定义一个保存指向改变之前的值。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
ListNode* head = pHead, *behind = nullptr, *res = nullptr;
if(head == nullptr)
return nullptr;
while(head != nullptr){
res = head->next;
head->next = behind;
behind = head;
head = res;
}
return behind;
}
};
12. 输出链表倒数第k个元素
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
【思路2】:把k这个量,用两个同时运动的指针体现出来。
说是考察的:代码的鲁棒性,一个好的解决思路自带鲁棒性。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, unsigned int k) {
// 设置两个指针frontP和behindP,先让frontP走k-1步,
//当它走到指针尾部时,behindP即为所求。
ListNode* frontP = pListHead, *behindP = pListHead;//注意后面一个变量的*号
while(k){
if (frontP == nullptr)
return nullptr;
frontP = frontP->next;
k--;
}
while(frontP!=nullptr){
frontP = frontP->next;
behindP = behindP->next;
}
return behindP;
}
};
【思路1】:求总长度,计算倒数第k个,返回。(自己的想法)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, unsigned int k) {
ListNode* head = pListHead;
// 记录总长度
int count = 0;
while(head != nullptr){
head = head->next;
count++;
}
// 鲁棒性
if((count-int(k))<0)//注意这里的强制类型转换!否则,unsigned int不可能<0
return nullptr;
// 寻找目标指针
head = pListHead;
while(count-k){
head = head->next;
count--;
}
return head;
}
};
11. 将数组元素按要求排放
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
【思路2】:插排,(节约空间、纯c语言版,之后再了解)
【思路1】:空间换时间;
原来数组放奇数,新建一个数组放偶数,再进行一些删除、拼接操作。
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector &array) {
// 空间换时间 3ms 476k
vector evenArray;
int oddNum = 0;
for(auto beg=array.begin(), end=array.end(); beg!=end; beg++){
if(*beg%2){//为真时,奇数
array[oddNum] = *beg;
oddNum++;
}
else
evenArray.push_back(*beg);
}
array.erase(array.begin()+oddNum,array.end());
array.insert(array.end(),evenArray.begin(),evenArray.end());
}
};
10. 求幂
给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。
【注意】:int型,有正、有负、有零。
【思路?】:还想使用递归方法解决,但是还没能实现,说是内存超出限制。
把 指数的符号 放到底数上,好思路!了解到了,快速幂!
递归实现的过程,比想象的复杂些,仔细体会过程。
体会递归程序的架构!
class Solution {
public:
double Power(double base, int exponent) {
int n = abs(exponent); // 3ms 376k
double result = 0.0;
if (n == 0)
return 1.0;
if (n == 1)
return base;
result = Power(base, n >> 1);
result *= result;
if ((n & 1) == 1) // 如果指数n为奇数,则要再乘一次底数base
result *= base;
if (exponent < 0) // 如果指数为负数,则应该求result的倒数
result = 1 / result;
return result;
}
};
【思路1】:调用函数 和 循环实现(缺点是一步一步乘,时间复杂度是 o ( n ) o(n) o(n))
class Solution {
public:
double Power(double base, int exponent) {
//return pow(base,exponent); //2ms 480k--函数
if(exponent == 0) //2ms 476k--循环
return 1;
double result = 1;
for(int num = abs(exponent); num != 0; num--){
result *= base;
}
if(exponent>0)
return result;
else
return 1/result;
}
};
9. 位操作
输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
【补充概念】:补码的计算方法
-5对应正数5(00000101)→所有位取反(11111010)→加1(11111011)
所以-5的补码是11111011。
在计算机系统中,数值一律用补码来表示和存储。 (计算机里只有加法器,没有减法器)
原因:补码,可以将符号位和数值域统一处理;同时,加法和减法也可以统一处理。
[X+Y]补 = [X]补 + [Y]补
[X-Y]补 = [X]补 - [Y]补 = [X]补 + [-Y]补
【X*Y】补=【X】补×【Y】补
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
//问题1?当int型进行为操作的时候,会自动转换成 二进制形式吗?
//问题2?当进行右移位操作的时候,最左端添加的元素是什么?
//问题3?int型就是32位吗?
int count = 0;
if(n<0){
n = n&0x7fffffff;
count++;
}
while(n!=0){
count += n&1;
n = n>>1;
}
return count;
}
};
- 答3:int型的长度是由 计算机和编译器决定,在32位机上,int型是32位的(4个字节)。
而类型 _int8,_int16,_int32,_int64长度是确定的,分别长1,2,3,4个字节。 - 答2:移位运算符:最重要的一点,虽然数字存贮在计算机内存中是以2进制的补码形式,但是运用移位运算符时是对源码进行的。(这也是为什么要首先保证为正数)
<<移位运算符:高位舍弃,低位补0(负数与正数的运算是一样的)
>>移位运算符:符号位随着运算数的移动,当为正数的时候最高位补0,为负数的时候符号位补1,最高位的补位取决于编译器,较多的补1 - 答1:自动转换成二进制的形式–所有的类型在计算机内,都是以二进制形式存放的,都可以进行移位操作。
8. 小矩形覆盖大矩形
我们可以用21的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个21的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
【思路】:本质上仍然是,斐波那契数列,代码完全相同。
7. 变态青蛙跳台阶问题
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
【思路3】:这地方有猫腻啊!仔细观察发现
F ( n ) = F ( n − 1 ) + F ( n − 2 ) + ⋯ + F ( 1 ) F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)+\cdots+F(1) F(n)=F(n−1)+F(n−2)+⋯+F(1)
同时,也有 F ( n − 1 ) = F ( n − 2 ) + ⋯ + F ( 1 ) F(n-1)=F(n-2)+\cdots+F(1) F(n−1)=F(n−2)+⋯+F(1)
于是, F ( n ) = 2 1 F ( n − 1 ) = 2 2 F ( n − 2 ) = ⋯ = 2 n − 1 F ( n − ( n − 1 ) ) = 2 n − 1 F(n)=2^1F(n-1)=2^2F(n-2)=\cdots\\=2^{n-1}F(n-(n-1))=2^{n-1} F(n)=21F(n−1)=22F(n−2)=⋯=2n−1F(n−(n−1))=2n−1
内存操作,或调用函数均可实现。
【注】:自己使用数学函数时,记得包含头文件#include
class Solution {
public:
int jumpFloorII(int number) {
return pow(2,number-1); //3ms 376k
//return 1<<--number; //4ms 596k
}
};
【思路2】:然鹅!!运行结果会告诉你,算法复杂度太高!
因为 for 循环里嵌套了一层 while 循环 用来求vector的和,所以,这里需要改进!!
使用 标准库自带的 容器可以通用的 函数速度更快,通过了!
#include %自己使用时需要包含,leetcode自动包含
sum = accumulate(&floor[1],&floor[count],0);
【思路1】:显然和青蛙跳问题有联系!
不难写出: F ( n ) = F ( n − 1 ) + F ( n − 2 ) + ⋯ + F ( 1 ) F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)+\cdots+F(1) F(n)=F(n−1)+F(n−2)+⋯+F(1)
且初值为: F ( 1 ) = 1 , F ( 2 ) = 2 F(1)=1,F(2)=2 F(1)=1,F(2)=2,程序和青蛙跳编写思路相同,有:
class Solution {
public:
int jumpFloorII(int number) {
vector floor{0,1,2};
if(number<=2)
return number;
else{
for(int stageNum=3; stageNum<=number; stageNum++){
int count = stageNum, sum = 0;
sum = accumulate(&floor[1],&floor[count],0);
% while(count>=1) sum += floor[count];
floor.push_back(sum+1);
}
}
return floor[number];
}
};
6. 青蛙跳台阶问题
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
【思路1】:有一种直观的解法是 求子集的个数,但是 这种解法的复杂度为 o ( 2 n ) o(2^n) o(2n);
发现其中的规律:
假设现在6个台阶,
我们可以从5跳到6,这样有多少种方案跳到5就有多少种方案跳到6;
其他的,都不能跳到6了,
所以最后就是f(6) = f(5) + f(4);
进一步归纳,就是 F ( n ) = F ( n − 1 ) + F ( n − 2 ) F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2) F(n)=F(n−1)+F(n−2)
不难给出初值, F ( 1 ) = 1 , F ( 2 ) = 2 F(1)=1,F(2)=2 F(1)=1,F(2)=2
这里的代码,试着给出了每一级台阶 n n n,青蛙可以选择的跳法,并保存在数组里。
class Solution {
public:
int jumpFloor(int number) {
vector floor{0,1,2};
if(number <= 2)
return number;
else{
//return jumpFloor(number-1)+jumpFloor(number-2);
for(int stageNum = 3; stageNum<=number; stageNum++){
floor.push_back(floor[stageNum-1]+floor[stageNum-2]);
}
}
return floor[number];
}
};
5. 求斐波那契(qi)数列第n项
大家都知道斐波那契数列,现在要求输入一个整数n,请你输出斐波那契数列的第n项(从0开始,第0项为0)。n<=39
【思路2】:利用递归求解
一个需要解决的问题是,复杂度太高!重复计算造成的!
Fibonacci(4) = Fibonacci(3) + Fibonacci(2);
= Fibonacci(2) + Fibonacci(1) + Fibonacci(1) + Fibonacci(0);
= Fibonacci(1) + Fibonacci(0) + Fibonacci(1) + Fibonacci(1) + Fibonacci(0);
因此!!应把递推公式稍作修改!!
【思路1】:正向循环(迭代)求解,直到求解到给定的第n项;
此处,如果将每次计算所得的 Fn 用数组保存,就得到了 Fibonacci数列。
class Solution {
public:
int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0)
return 0;
else if(n == 1)
return 1;
else{
int front = 0, now = 1, sum = now;
for(int count = 2; count<=n; count++){
sum = now+front;
front = now;
now = sum;
}
return now+front;
}
}
};
(意大利人:Fibonacci)
以递归形式定义:
F 0 = 0 , F 1 = 1 F n = F n − 1 + F n − 2 F_0 = 0,\quad F_1 = 1\\ F_n = F_{n-1}+F_{n-2} F0=0,F1=1Fn=Fn−1+Fn−2

且,n越大,前后两项的比值越接近黄金比例:1:1.618
4. 寻找特殊向量里面的最小值
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。 输入一个非减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。 例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。 NOTE:给出的所有元素都大于0,若数组大小为0,请返回0。
【思路2】:寻找分解点,分界点之后的那个值就是最小值;如果找不到分界点,有两种情况,1.这个向量在单增(但这种不合输入的旋转数组的要求);2.这个向量所有元素相等!(正解)此时第一个元素即最小值。
(24ms,74k)
class Solution {
public:
int minNumberInRotateArray(vector rotateArray) {
auto beg = rotateArray.begin(), end = rotateArray.end();
if(beg < end){
int front = *beg++;
for(; beg < end; beg++){
if(front > *beg)
return *beg;
}
return rotateArray.front();
}
else
return 0;
}
};
【思路1】:按一般向量处理,不考虑特殊性。求最小值
class Solution {
public:
int minNumberInRotateArray(vector rotateArray) {
auto beg = rotateArray.begin(), end = rotateArray.end();
if(beg < end){
int min = *beg++;
for(; beg < end; beg++){
min = (min >= *beg)?*beg:min;
}
return min;
}
else
return 0;
}
};
3.反向输出链表的元素到vector中 2018-8-4
输入一个链表,按链表值从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList。
【另一种思路】:
vector有很多已经存在的操作,比如反向。
因此,首先将元素顺序存入vector,再利用vector已有的性质完成处理。
class Solution {
public:
vector printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
vector ArrayList;
ListNode* p=head;
while(p!=nullptr){
ArrayList.push_back(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
return vector(ArrayList.rbegin(),ArrayList.rend());
}
};
【解题思路】:
首先,从前向后得到链表的长度;
然后,将链表元素顺序取出,并在vector中从后向前存放。
class Solution {
public:
vector printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
//链表是一个单向链表,无法反向输出
//思路,求得长度,顺序输出,在vector后面向前存放。
ListNode* p=head;
int len=0;
for(;p!=nullptr;len++){
p = p->next;
}
p = head;
vector ArrayList(len,0);
for(int ii=len-1;ii>=0;ii--){
ArrayList[ii]= p->val;
p = p->next;
}
return ArrayList;
}
};
2.字符串替换某些元素 2018-8-3
请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”。
例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy。
【解题思路】:
首先,从前向后查找待替换元素的个数,计算替换后字符串的长度;
然后,从后向前完成替换。
class Solution {
public:
void replaceSpace(char *str,int length) {
//难点在于 空格占一个字节,而%20占3个字节,
//即,替换后 字符串长度会多出 2*空格个数 个字节
//问题在于,可以直接将 这个字符串长度增加吗? 安全吗?
int count = 0, length2 = 0;
for(int i=0;i=0;ii--){
if(str[ii]!=' ')
str[length2] = str[ii];
else{
str[length2--] = '0';
str[length2--] = '2';
str[length2] = '%';
}
length2--;
}
}
};
1. 二维数组查找特定元素 2018-8-2
在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
class Solution {
public:
bool Find(int target, vector > array) {
//array是一个二维数组
int rows = array.size();
int cols = array[0].size();
int i = rows-1, j = 0;//左下角元素坐标
while(i>=0 && j array[i][j])
j++;
else
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
【悟】:代码很简洁也很直接,想法如下图:

【注意】:**一定不要超出索引范围!**记得 .size-1
自己写了一个类似与一维数组二分法的二维数组的二分法,但是未通过。。。。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool Find(int target, vector > array) {
auto rows = array.size()-1;
auto cols = array[0].size()-1;
int beg = 0, end = rows, mid = beg+(end-beg)/2;
int targetrow=0;
while(beg!=end){
if(array[mid][0]>target)
end = mid;
else if (array[mid][cols]target){
end = mid;
}
else if(array[targetrow][mid]> array = {{1, 2, 3, 4},
{5, 6, 7, 8},
{9, 10, 11, 12},
{13, 14, 15, 16},
{17,18,19,20}};
int target = 23;
bool b = Find(target,array);
cout< 面试(技术面试(算法面试))
探讨解决问题的方案!
对于问题的细节、应用环境,可以和面试官沟通。暗示了你在思考问题。答案正确的条件,会使答案不正确的情况。
对一组数据进行排序
?这组数据有什么样的特征?
- 是否大量重复?三路快排
- 是否近乎有序?插入排序
- 是否取值有限?计数排序
- 有额外的要求?稳定性?
- 数据存储状况?内存条件?
“正确”的深层次含义:
- 见解;优化;规范;容错性
如果不能给出问题的答案,可以指出解决问题的方向,你的思考。
不要简单地,极端地用对、错去看待问题。