- mysql++库的分享和介绍
会&唱歌的鱼
C++mysql项目实战mysql数据库
目录1.mysql++库的简介2.编译和安装3.mysql++常用类概述4.Mysql++用法详解5.Query支持的三种查询方式5.1直接使用Querystream输入SQL语句5.2使用TemplateQuery采用类似于printf的方式进行输入SQL语句5.3使用SSQLS,通过类似于Hibernate的方式对DataStruct进行操作来操作底层数据库6.在mysql++中使用事务7.使
- vector存储对象后在调用clear时是否会release对象所在的空间
闪闪加油干(◍>∇<◍)ノ゙
AndroidAndroid系统android
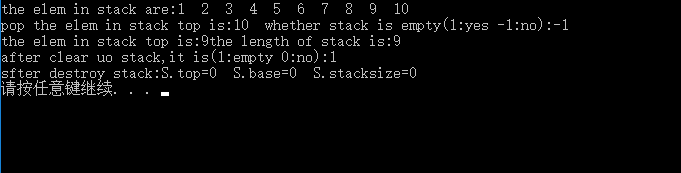
vector存储对象后,在调用clear时并不会release对象所在的空间,需要手动释放空间。classDataStructure:publicRefbase{DataStructure();virtual~DataStructure;}vectorlist;DataStructure*data=newDataStructure();list.push_back(data);DataStruct
- Redis跳表学习
吃饼青年
Redis有序集合redis跳表zskiplistzskiplistNode
参考:http://redisbook.com/preview/skiplist/datastruct.htmlRedis的跳跃表由redis.h/zskiplistNode和redis.h/zskiplist两个结构定义,其中zskiplistNode结构用于表示跳跃表节点,而zskiplist结构则用于保存跳跃表节点的相关信息,比如节点的数量,以及指向表头节点和表尾节点的指针,等等。图5-1展
- Boost中DataStruct模块的any
jian_xiong_1985
boostdatastruct的any
头文件boost/any.hpp作用将基本数据类型,自定义类类型,指针类型,转化为any,同时通过any_cast函数,将any类型,转为需要的类型,如果转化失败,则会抛出bad_any_cast异常。any类,有如下APIswap:交换,与std::swap一致。empty:判断any是否为空,如果构造一个无惨的any,则为trueclear:将有参数类型的any,清空,清空之后,empty为t
- 数据结构--ArrayList02 逆置顺序表的所有元素
说说互联网的那些事
数据结构最强面试宝典数据结构顺序表
1)题目:设置一个高效算法,将顺序表L的所有元素逆置,要求算法的空间复杂度为O(1)2)思路:头尾元素依次交换3)代码:源码中使用到的ArrrayList,是调用的是自己实现的ArrayList,自己实现的ArrayList源码地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u012441545/article/details/89667486packagecom.sam.datastruct.
- 数据结构、数据类型、抽象数据类型之间的关系
Xu Ricol
数据结构
计算机跨考选手刚刚学到了数据结构的绪论,感觉这块比较难以理解,分享一下自己的观点吧,还请大家多多指教~严蔚敏教授编写的《数据结构》中对于以上三者的定义是:1.数据结构:是相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据元素的集合。2.数据类型:是一个值的集合和定义在这个值集上的一组操作的总称。3.抽象数据类型:是指一个数学模型以及定义在该模型上的一组操作。数据结构的形式定义为:一个二元组,DataStruct
- 图的广度遍历和深度遍历实现
satadriver
数据结构和算法算法数据结构
DFT实现深度遍历,BFT实现广度遍历。genGraph函数帮助生成一个无向图,用于测试。完整工程代码:https://github.com/satadriver/dataStruct废话不说上干货。头文件:#pragmaonce#include"Element.h"#include"list.h"#pragmapack(1)typedefstruct{ELEMENT*element;intver
- 循环队列实现
satadriver
数据结构和算法算法数据结构
非常简单的循环队列实现,仅包含入队列和出队列操作,cpp代码不超过100行,在座的各位都是软件开发小能手,因此功能不再赘述。完整工程代码:https://github.com/satadriver/dataStruct废话不说,直接上源码。头文件:#pragmaonce#include"Element.h"classQueue{public:Queue();Queue(intsize);~Queu
- 链表的实现
satadriver
数据结构和算法链表数据结构
分两种方式实现,一种是双向链表,一种是双向循环链表。循环双向链表和双向链表的编码实现,差别很小,但是循环链表在效率上胜出很多,综合考虑,循环链表是首选。完整工程代码:https://github.com/satadriver/dataStruct头文件:#pragmaonce#include"Element.h"#pragmapack(1)typedefstruct_LIST{_LIST*prev
- 【数据结构学习笔记】一、数据结构介绍及算法分析(新手入门进阶指南)
大家好我叫张同学
数据结构+算法做题笔记数据结构算法leetcode
文章目录一、数据结构和算法介绍1.什么是数据结构?2.什么是算法?3.数据结构和算法的重要性4.如何学好数据结构和算法5.数据结构和算法书籍及资料推荐6.经常遇到不会做的题目二、算法分析1、算法效率时间复杂度1.时间复杂度的概念:2.大O的渐进表示法空间复杂度1.空间复杂度的概念:2.大O渐进法表示法:数据结构学习的心理准备:一、数据结构和算法介绍1.什么是数据结构?数据结构(DataStruct
- java 字典
hatlonely
java字典数据结构总览datastruct.pngMapMap描述的是一种映射关系,一个key对应一个value,可以添加,删除,修改和获取key/value,util提供了多种MapHashMap:hash表实现的map,插入删除查找性能都是O(1),key没有顺序TreeMap:红黑树实现的map,插入删除查找都是O(lgn),key按从大到小顺序排列Hashtable:hash实现,线程安
- Go重写Redis中间件 - Go实现内存数据库
找不着工作不改名
Go数据库redis中间件
GO实现内存数据库前面我们实现了一个简单的回发Redis,这里我们要实现一个真正的Redis内核实现底层Dict数据结构新建一个datastruct文件夹,放一些我们要用的数据结构,比如Redis的核心起始就是一个map,再新建一个包实现这个map或者叫字典,字典的底层使用的就是mapdict.go写一个Dict接口定义一些map要实现的功能,注意ForEach方法的入参是一个方法,把这个方法施加
- Redis原理 - 数据结构的底层实现
CoderMast编程桅杆
Redisredis缓存数据库
原文首更地址,阅读效果更佳!Redis原理-数据结构的底层实现|CoderMast编程桅杆https://www.codermast.com/database/redis/redis-datastruct-underlying-implementation.html动态字符串SDS#基本概念Redis中保存的Key是字符串,Value往往是字符串或者字符串的集合。可见字符串是Redis中最常见的一
- idea提交代码到远程仓库gitee
一束光亮
软件安装等记录intellij-ideagiteegit
第一步:在gitee中建立一个仓库,这里我建立了一个名为datastructure的仓库第二步:复制仓库链接,在本地一个DataStruct空的文件夹里面,右键单击选择GitClone,这里的意思是将远程仓库克隆到本地,建立一个本地仓库datastructure,点击OK即可。第三步:接下来会提示输入username,password,这里的用户名密码是gitee里面的用户名,密码,输入即可。需要
- GO实现Redis:GO实现内存数据库(3)
随和的小氵
redisgo数据库redisgolang
实现Redis的database层(核心层:处理命令并返回)https://github.com/csgopher/go-redis本文涉及以下文件:dict:定义字典的一些方法sync_dict:实现dictdb:分数据库command:定义指令ping,keys,string:指令的具体处理逻辑database:单机版数据库datastruct/dict/dict.gotypeConsumer
- 基于Golang实现内存数据库的示例详解
GO实现内存数据库实现Redis的database层(核心层:处理命令并返回)https://github.com/csgopher/go-redis本文涉及以下文件:dict:定义字典的一些方法sync_dict:实现dictdb:分数据库command:定义指令ping,keys,string:指令的具体处理逻辑database:单机版数据库datastruct/dict/dict.gotyp
- DataStruct数据结构2021下半年期末考总结分析
CHessheep
数据结构算法c++
引言在我还记得的时候写一下吧,之前也有学长写过,他们写得挺好的,我也是参照他们的思路来大致写一下吧,希望能够给后来人带来帮助。2022.4.8更新,加了笔试的内容在最下面1.上机前复习考前复习的话,你要想拿高分肯定是所有老师给的OJ平台上都要做的,不能说很熟练吧,但至少你得做过,有过这么一个思路吧,不然考试你哪里够时间做其次重点的话就是书上既有讲,老师也在OJ上布置了,这些题目一定要着重注意,例如
- 一起学习PHP中的DS数据结构扩展(一)
php
在之前学习SPL相关的文章中,我们已经学习过SPL中的一些数据结构相关的数据结构对象,非常强大也非常好用,最主要的是SPL已经集成在PHP源码中不需要我们再单独地安装别的什么扩展。但是,今天我们要学习的这个DataStruct扩展库的内容则更加地丰富,不过相对应的,这套扩展是需要我们自己手动再进行安装的。如果大家对于数据结构的需求不高的话,使用SPL中的相关对象就够用了,但是如果需要更加丰富的数据
- Python 字典基础回顾
speculatecat
关键词python、dict、datastruct、python字典、pythoncollections、dafultdict、CounterPython中字典是一种基本的数据结构,它将键与值联系起来,形成的键值对形式,让我们可以通过键快速找到对应的值。在这篇文章的以下内容,可以了解到以下内容:Python字典的基础用法Python字典的创建Python字典的赋值Python字典的查找Python
- 数据结构_串
arkulo
github地址:https://github.com/arkulo56/thought/blob/master/software/dataStruct/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84_%E4%B8%B2.md定义特殊的线性表,每个元素都是字符元素可以是零个或多个常用操作查找子串、串的相似度、截取、反转、最长公共子串、分词、回文顺序实现字符串的操作一般都不
- std::map在内存中的结构(1)
爱钓鱼的饭桶骑士
最近有幸拜读到了某大神的二叉树文章,以前用惯了C#的我对这种数据结构产生了浓厚的兴趣。为了搞清map在内存中的结构,作为萌新的我在vs中创建了c++控制台程序(控制台程序Release编译后代码干净,便于在OD中查看汇编代码!)。代码如下:```cpp#include#includestd::mapdataStruct;intmain(){dataStruct.insert(std::map::v
- 求两个线性表的并集(C语言通过动态顺序表实现)(DataStruct)(g)
Skilled_Beginner
这篇博客是关于求两个线性表的并集实现的详细代码,使用C语言实现是使用到的功能都在线性表的动态实现里面,并且有完整的测试和截图main.cppSqList.cppSqList.h小结main.cpp#include"SqList.h"voidUnionList(SqList*La,SqList*Lb){intLa_len=ListLength(La);intLb_len=ListLength(Lb)
- java编程:斐波那契数列经典案例:兔子问题
如来神(RuLaiGod)
Java-数据结构
题目:古典问题:有一对兔子,从出生后第3个月起每个月都生一对兔子,小兔子长到第三个月后每个月又生一对兔子,假如兔子都不死,问每个月的兔子总数为多少?packagecom.java.recursion;/***@描述三种方法实现斐波那契数列*@项目名称Java_DataStruct*@包名com.java.recursion*@类名Fibonacci*@authorchenlin*@date2011
- 算法笔记十三、斐波那契数列查找算法代码
努力的阳光蓝孩
【算法分析】
packagecom.hao.firstdemo.datastruct.search;importjava.util.Arrays;/***@authorhaoxiansheng*@data2020/5/922:40*/publicclassFibonacciSearch{publicstaticintmaxSize=20;publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){in
- 数据结构之栈的应用:括号匹配问题
js93105
教学日志
上课的代码我修改了下,类名也不是Client了,注意下,另外将字符串修改为从键盘输入,而且加了个辅助函数判定匹配问题。当然需要用到顺序栈,栈的接口代码,该部分代码参见百度云课程资源http://yun.baidu.com/share/link?shareid=3770451811&uk=1583175585packagemystudy.datastruct;importjava.util.Scan
- java使用数组实现线性表功能(增、删、查、改)
fcytxdy
数据结构
packagecom.fcy.dataStruct;importjava.util.Arrays;publicclassSequenceList{privateintDEFAULT_SIZE=16;//保存数组的长度privateintcapacity;//定义一个数组用于保存顺序线性表的元素privateObject[]elementData;//保存顺序线性表中元素的当前个数privatein
- C#基础之在partial类中添加Attributes
Brent姜
在我们的服务器、客户端程序中,借助EntityModel.xml进行通讯规约,大部分代码实现了自动生成。客户端代码中,会为某些Entity添加某些属性,这些属性不影响C/S共同使用的数据结构,所以基本的DataStruct.cs必须根据EntityModel.xml生成。但是我们UI所需要的一些属性,例如LogDescription(这个attribute为每个field字段定义格式化日志输出的l
- java实现赫夫曼编码封装
七月的尾巴←_←
算法数据结构
packagecom.coderman.datastruct.tree;importorg.junit.Test;importjava.util.*;/***哈夫曼编码*@Authorzhangyukang*@Date2020/6/410:54*@Version1.0**/publicclassHuffmanCodingTest{//模拟要传输的数据//privatestaticStringdat
- Redis设计与实现读书笔记——双链表
低调小一
Redis
前言首先,贴一下参考链接:http://www.redisbook.com/en/latest/internal-datastruct/adlist.html,另外真赞文章的作者,一个90后的小伙真不错,基本功扎实,而且非常乐于助人概述链表是Redis的核心数据结构之一,它不仅大量应用在Redis自身内部的实现中,而且它也是Redis的List的结构的底层实现之一这里分析的是Redis源码里adl
- 二叉树的二叉链表存储(java实现)
fcytxdy
数据结构
packagecom.fcy.dataStruct;/***二叉树的二叉链表存储的是数据域、左子节点和右子节点*/classTwoLinkBinTree{publicstaticclassTreeNode{//数据域Objectdata;//左子节点TreeNodeleft;//右子节点TreeNoderight;publicTreeNode(){}publicTreeNode(Objectdat
- 关于旗正规则引擎下载页面需要弹窗保存到本地目录的问题
何必如此
jsp超链接文件下载窗口
生成下载页面是需要选择“录入提交页面”,生成之后默认的下载页面<a>标签超链接为:<a href="<%=root_stimage%>stimage/image.jsp?filename=<%=strfile234%>&attachname=<%=java.net.URLEncoder.encode(file234filesourc
- 【Spark九十八】Standalone Cluster Mode下的资源调度源代码分析
bit1129
cluster
在分析源代码之前,首先对Standalone Cluster Mode的资源调度有一个基本的认识:
首先,运行一个Application需要Driver进程和一组Executor进程。在Standalone Cluster Mode下,Driver和Executor都是在Master的监护下给Worker发消息创建(Driver进程和Executor进程都需要分配内存和CPU,这就需要Maste
- linux上独立安装部署spark
daizj
linux安装spark1.4部署
下面讲一下linux上安装spark,以 Standalone Mode 安装
1)首先安装JDK
下载JDK:jdk-7u79-linux-x64.tar.gz ,版本是1.7以上都行,解压 tar -zxvf jdk-7u79-linux-x64.tar.gz
然后配置 ~/.bashrc&nb
- Java 字节码之解析一
周凡杨
java字节码javap
一: Java 字节代码的组织形式
类文件 {
OxCAFEBABE ,小版本号,大版本号,常量池大小,常量池数组,访问控制标记,当前类信息,父类信息,实现的接口个数,实现的接口信息数组,域个数,域信息数组,方法个数,方法信息数组,属性个数,属性信息数组
}
&nbs
- java各种小工具代码
g21121
java
1.数组转换成List
import java.util.Arrays;
Arrays.asList(Object[] obj); 2.判断一个String型是否有值
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
if (StringUtils.hasText(str)) 3.判断一个List是否有值
import org.spring
- 加快FineReport报表设计的几个心得体会
老A不折腾
finereport
一、从远程服务器大批量取数进行表样设计时,最好按“列顺序”取一个“空的SQL语句”,这样可提高设计速度。否则每次设计时模板均要从远程读取数据,速度相当慢!!
二、找一个富文本编辑软件(如NOTEPAD+)编辑SQL语句,这样会很好地检查语法。有时候带参数较多检查语法复杂时,结合FineReport中生成的日志,再找一个第三方数据库访问软件(如PL/SQL)进行数据检索,可以很快定位语法错误。
- mysql linux启动与停止
墙头上一根草
如何启动/停止/重启MySQL一、启动方式1、使用 service 启动:service mysqld start2、使用 mysqld 脚本启动:/etc/inint.d/mysqld start3、使用 safe_mysqld 启动:safe_mysqld&二、停止1、使用 service 启动:service mysqld stop2、使用 mysqld 脚本启动:/etc/inin
- Spring中事务管理浅谈
aijuans
spring事务管理
Spring中事务管理浅谈
By Tony Jiang@2012-1-20 Spring中对事务的声明式管理
拿一个XML举例
[html]
view plain
copy
print
?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>&nb
- php中隐形字符65279(utf-8的BOM头)问题
alxw4616
php中隐形字符65279(utf-8的BOM头)问题
今天遇到一个问题. php输出JSON 前端在解析时发生问题:parsererror.
调试:
1.仔细对比字符串发现字符串拼写正确.怀疑是 非打印字符的问题.
2.逐一将字符串还原为unicode编码. 发现在字符串头的位置出现了一个 65279的非打印字符.
- 调用对象是否需要传递对象(初学者一定要注意这个问题)
百合不是茶
对象的传递与调用技巧
类和对象的简单的复习,在做项目的过程中有时候不知道怎样来调用类创建的对象,简单的几个类可以看清楚,一般在项目中创建十几个类往往就不知道怎么来看
为了以后能够看清楚,现在来回顾一下类和对象的创建,对象的调用和传递(前面写过一篇)
类和对象的基础概念:
JAVA中万事万物都是类 类有字段(属性),方法,嵌套类和嵌套接
- JDK1.5 AtomicLong实例
bijian1013
javathreadjava多线程AtomicLong
JDK1.5 AtomicLong实例
类 AtomicLong
可以用原子方式更新的 long 值。有关原子变量属性的描述,请参阅 java.util.concurrent.atomic 包规范。AtomicLong 可用在应用程序中(如以原子方式增加的序列号),并且不能用于替换 Long。但是,此类确实扩展了 Number,允许那些处理基于数字类的工具和实用工具进行统一访问。
- 自定义的RPC的Java实现
bijian1013
javarpc
网上看到纯java实现的RPC,很不错。
RPC的全名Remote Process Call,即远程过程调用。使用RPC,可以像使用本地的程序一样使用远程服务器上的程序。下面是一个简单的RPC 调用实例,从中可以看到RPC如何
- 【RPC框架Hessian一】Hessian RPC Hello World
bit1129
Hello world
什么是Hessian
The Hessian binary web service protocol makes web services usable without requiring a large framework, and without learning yet another alphabet soup of protocols. Because it is a binary p
- 【Spark九十五】Spark Shell操作Spark SQL
bit1129
shell
在Spark Shell上,通过创建HiveContext可以直接进行Hive操作
1. 操作Hive中已存在的表
[hadoop@hadoop bin]$ ./spark-shell
Spark assembly has been built with Hive, including Datanucleus jars on classpath
Welcom
- F5 往header加入客户端的ip
ronin47
when HTTP_RESPONSE {if {[HTTP::is_redirect]}{ HTTP::header replace Location [string map {:port/ /} [HTTP::header value Location]]HTTP::header replace Lo
- java-61-在数组中,数字减去它右边(注意是右边)的数字得到一个数对之差. 求所有数对之差的最大值。例如在数组{2, 4, 1, 16, 7, 5,
bylijinnan
java
思路来自:
http://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/2541117420116135376632/
写了个java版的
public class GreatestLeftRightDiff {
/**
* Q61.在数组中,数字减去它右边(注意是右边)的数字得到一个数对之差。
* 求所有数对之差的最大值。例如在数组
- mongoDB 索引
开窍的石头
mongoDB索引
在这一节中我们讲讲在mongo中如何创建索引
得到当前查询的索引信息
db.user.find(_id:12).explain();
cursor: basicCoursor 指的是没有索引
&
- [硬件和系统]迎峰度夏
comsci
系统
从这几天的气温来看,今年夏天的高温天气可能会维持在一个比较长的时间内
所以,从现在开始准备渡过炎热的夏天。。。。
每间房屋要有一个落地电风扇,一个空调(空调的功率和房间的面积有密切的关系)
坐的,躺的地方要有凉垫,床上要有凉席
电脑的机箱
- 基于ThinkPHP开发的公司官网
cuiyadll
行业系统
后端基于ThinkPHP,前端基于jQuery和BootstrapCo.MZ 企业系统
轻量级企业网站管理系统
运行环境:PHP5.3+, MySQL5.0
系统预览
系统下载:http://www.tecmz.com
预览地址:http://co.tecmz.com
各种设备自适应
响应式的网站设计能够对用户产生友好度,并且对于
- Transaction and redelivery in JMS (JMS的事务和失败消息重发机制)
darrenzhu
jms事务承认MQacknowledge
JMS Message Delivery Reliability and Acknowledgement Patterns
http://wso2.com/library/articles/2013/01/jms-message-delivery-reliability-acknowledgement-patterns/
Transaction and redelivery in
- Centos添加硬盘完全教程
dcj3sjt126com
linuxcentoshardware
Linux的硬盘识别:
sda 表示第1块SCSI硬盘
hda 表示第1块IDE硬盘
scd0 表示第1个USB光驱
一般使用“fdisk -l”命
- yii2 restful web服务路由
dcj3sjt126com
PHPyii2
路由
随着资源和控制器类准备,您可以使用URL如 http://localhost/index.php?r=user/create访问资源,类似于你可以用正常的Web应用程序做法。
在实践中,你通常要用美观的URL并采取有优势的HTTP动词。 例如,请求POST /users意味着访问user/create动作。 这可以很容易地通过配置urlManager应用程序组件来完成 如下所示
- MongoDB查询(4)——游标和分页[八]
eksliang
mongodbMongoDB游标MongoDB深分页
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2177567 一、游标
数据库使用游标返回find的执行结果。客户端对游标的实现通常能够对最终结果进行有效控制,从shell中定义一个游标非常简单,就是将查询结果分配给一个变量(用var声明的变量就是局部变量),便创建了一个游标,如下所示:
> var
- Activity的四种启动模式和onNewIntent()
gundumw100
android
Android中Activity启动模式详解
在Android中每个界面都是一个Activity,切换界面操作其实是多个不同Activity之间的实例化操作。在Android中Activity的启动模式决定了Activity的启动运行方式。
Android总Activity的启动模式分为四种:
Activity启动模式设置:
<acti
- 攻城狮送女友的CSS3生日蛋糕
ini
htmlWebhtml5csscss3
在线预览:http://keleyi.com/keleyi/phtml/html5/29.htm
代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>攻城狮送女友的CSS3生日蛋糕-柯乐义<
- 读源码学Servlet(1)GenericServlet 源码分析
jzinfo
tomcatWebservlet网络应用网络协议
Servlet API的核心就是javax.servlet.Servlet接口,所有的Servlet 类(抽象的或者自己写的)都必须实现这个接口。在Servlet接口中定义了5个方法,其中有3个方法是由Servlet 容器在Servlet的生命周期的不同阶段来调用的特定方法。
先看javax.servlet.servlet接口源码:
package
- JAVA进阶:VO(DTO)与PO(DAO)之间的转换
snoopy7713
javaVOHibernatepo
PO即 Persistence Object VO即 Value Object
VO和PO的主要区别在于: VO是独立的Java Object。 PO是由Hibernate纳入其实体容器(Entity Map)的对象,它代表了与数据库中某条记录对应的Hibernate实体,PO的变化在事务提交时将反应到实际数据库中。
实际上,这个VO被用作Data Transfer
- mongodb group by date 聚合查询日期 统计每天数据(信息量)
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境mongodb纵观千象
/* 1 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("557ac1e2153c43c320393d9d"),
"msgType" : "text",
"sendTime" : ISODate("2015-06-12T11:26:26.000Z")
- java之18天 常用的类(一)
Luob.
MathDateSystemRuntimeRundom
System类
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* System:
* out:标准输出,默认是控制台
* in:标准输入,默认是键盘
*
* 描述系统的一些信息
* 获取系统的属性信息:Properties getProperties();
*
*
*
*/
public class Sy
- maven
wuai
maven
1、安装maven:解压缩、添加M2_HOME、添加环境变量path
2、创建maven_home文件夹,创建项目mvn_ch01,在其下面建立src、pom.xml,在src下面简历main、test、main下面建立java文件夹
3、编写类,在java文件夹下面依照类的包逐层创建文件夹,将此类放入最后一级文件夹
4、进入mvn_ch01
4.1、mvn compile ,执行后会在