在vue2项目中,组件间相互传值或者后台获取的数据需要供多个组件使用的情况很多的情况下(后台获取数据存入vuex,组件之间共享数据),那么就需要用vuex来管理这些。
整个的流程是在组件的created中提交dispatch,然后通过action调用一个封装好的axios,然后再触发mutation来提交状态改变state中的数据,然后在组件的计算属性中获取state的数据并渲染在页面上
首先新需要在项目中安装vuex:
运行命令:npm install vuex --save-dev
在项目的入口js文件main.js中:import store from './store/index'
并将store挂载到vue上:
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
template: '
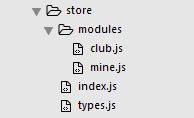
然后看下整个store的目录结构,modules文件夹用来将不同功能也面的状态分成模块,index.js文件夹是store的入口文件,types文件夹是定义常量mutation的。文件夹整个vuex的目录结构如下:
这里我新建了文件夹fetch用来编写所有的axios处理(这里是把axios封装了)并且在fetch文件夹下新建api.js文件:
import axios from 'axios'
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded';
axios.defaults.baseURL = '后台接口公共前缀';
export function fetch(url, params) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
axios.post(url, params)
.then(response => {
resolve(response.data);
})
.catch((error) => {
reject(error);
})
})
}
export default {
// 获取我的页面的后台数据
mineBaseMsgApi() {
// alert('进入api.js')
return fetch('/api/getBoardList');
},
commonApi(url, params) {
return fetch(url, params)
}
}
在store的入口文件index.js中:
// 组装模块并导出 store 的文件
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import mine from './modules/mine';
import club from './modules/club';
Vue.use(Vuex);
// 导出需要的模块
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
club,
mine
}
});
一般在项目中,我们跟在交互的时候,无非是存数据和取数据。首先我们来看存数据:
1:在你需要请求后台数据并想使用vuex的组件中的created分发第一个dispatch:
created() {
// 保存ID到vuex,在购买页面使用
this.$store.dispatch('storeMovieID',this.$route.params.ID)――(“action名”,data);
api.commonApi('url','params')
.then(res => {
this.backMsg = res.data;
console.log(this.backMsg);
console.log('调用封装后的axios成功');
})
},
2:然后在store/modules下的对应模块js文件中,这里我使用的club.js文件中编写state、action和mutation(一般为了方便,我们会习惯的把action里面的名字以驼峰式命名,而mutation里面的命名,我们会采用全大写+下划线的命名方式)actions 用来触发mutations,action可以进行异步操作 ,在action里可以用commit提交mutations
const actions = {
// 保存ID storeMovieID为上面的"action名"
storeMovieID({ commit }, res) {
//此处是触发mutation的 STORE_MOVIE_ID为"mutation名"
commit(types.STORE_MOVIE_ID, res);
},
}
3:我们需要在type.js里面定义常量:
// ID 变量名(大写)=‘常量名(大写)' export const STORE_MOVIE_ID = 'STORE_MOVIE_ID';
4:通过mutation修改state中的数据:
//mutation名常量定义 并且需要在type.js文件下定义常量
const mutations = {
// 修改ID 中括号代表常量 [types.常量名]
[types.STORE_MOVIE_ID]( state, res) {
state.movieID = res; //state.数据名 = data
},
}
5:定义state数据:(数据名:初始值)
const state = { //采用 数据名:初始值的格式
contextPathSrc: '后台接口公共部分',
movieID: '',
}
最后所有的club.js完整内容如下:(当然getters是在取数据的时候用的,下面会讲)
import api from './../../fetch/api';
import * as types from './../types.js';
// state 是vuex 保存数据的,就相当于vue里的data
const state = {
contextPathSrc: '后台接口公共部分',
movieID: '',
}
const actions = {
// 保存ID storeMovieID为上面的"action名"
storeMovieID({ commit }, res) {
//此处是触发mutation的 STORE_MOVIE_ID为"mutation名"
commit(types.STORE_MOVIE_ID, res);
},
}
const getters = {
// 图片公共 src 的获取 getter函数:state=> state.数据名
getContextPathSrc: state => state.contextPathSrc,
// 获取ID
movieID: state => {
if(state.movieID == ''){
return localStorage.getItem('STORE_MOVIE_ID');
}else{
return state.movieID;
}
},
}
//mutation名常量定义 并且需要在type.js文件下定义常量 mutations 用来向state提交数据的,只能进行同步操作
const mutations = {
// 修改ID 中括号代表常量 我们可使用ES2015风格的计算属性命名功能来使用一个常量[types.STORE_MOVIE_ID]作为函数名
[types.STORE_MOVIE_ID]( state, res) {
state.movieID = res;
},
}
export default {
state,
actions,
getters,
mutations
}
下边我们要说的是取数据并且渲染到页面中,或者在页面函数中使用的方法:
1:组建中你需要导入如下:
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
在组件的计算属性中,如下:
computed: {
...mapGetters([//...函数名 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
'getContextPathSrc'
])
},
这里的getContextPathSrc函数,在页面中可直接使用,如果在函数中使用,需要this.getContextPathSrc
2:最后在store中写getters函数:
const getters = {
// 图片公共 src 的获取 getter函数:state=> state.数据名
getContextPathSrc: state => state.contextPathSrc,
}
最后在页面渲染就可以了。。这样就完成了交互。可能有人会留意到上面的getters里的movieID函数有个if判断,最后
return localStorage.getItem('STORE_MOVIE_ID')
有人会好奇为啥用localStorage……这个我们也不想用,只是如果你的页面如果用户强制刷新一下的话,会有个很奇怪的事发生,就是数据全部取不到,后来是没办法才加的。
最后,希望这些讲解,对于初学者来说有帮助……别被vuex的官网整的云里雾里(ps:我初学时也云里雾里整不明白偷笑)。好了,下班啦,更多的内容,会慢慢跟大家分享。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。