一、引言
Jenkins 2.0的到来,pipline进入了视野,jenkins2.0的核心特性. 也是最适合持续交付的feature。
简单的来说,就是把Jenkins1.0版本中,Project中的相关配置信息,如SVN/Git的配置,Parameter的配置等都变成Code,即Pipeline as Code。
随着pipeline交付流水线在团队中的推广,使用pipeline脚本的job也迅速增加。
优势:
通过写代码的形式配置Project,且Jenkins中内置了常用的steps。
实现了构建步骤代码化、构建过程视图化。
二、语法简介
Pipeline最基本的部分是“step”。基本上,step告诉Jenkins 要做什么,并且作为Declarative Pipeline和Scripted Pipeline语法的基本构建块。
Pipeline支持两种语法:Declarative Pipeline(在Pipeline 2.5中引入,结构化方式)和Scripted Pipeline,两者都支持建立连续输送的Pipeline。
选择Declarative Pipeline还是Scripted Pipeline
最开始的Pipeline plugin,支持的只有一种脚本类型,就是Scripted Pipeline;
Declarative Pipeline为Pipeline plugin在2.5版本之后新增的一种脚本类型,与原先的Scripted Pipeline一样,都可以用来编写脚本。
相关资料:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/43484979/jenkins-scripted-pipeline-or-declarative-pipeline
http://jenkins-ci.361315.n4.nabble.com/Declarative-pipelines-vs-scripted-td4891792.html
从检索的资料来看,Declarative Pipeline 是后续Open Blue Ocean所支持的类型。相对而言,Declarative Pipeline比较简单,Declarative Pipeline中,也是可以内嵌Scripted Pipeline代码的。
为与BlueOcean脚本编辑器兼容,通常建议使用Declarative Pipeline的方式进行编写,从jenkins社区的动向来看,很明显这种语法结构也会是未来的趋势。
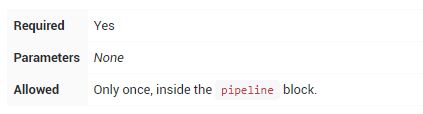
三、Declarative Pipeline
Declarative Pipeline是Jenkins Pipeline 的一个相对较新的补充, 它在Pipeline子系统之上提出了一种更为简化和有意义的语法。
所有有效的Declarative Pipeline必须包含在一个pipeline块内,例如:
pipeline { /* insert Declarative Pipeline here */ }
Declarative Pipeline中的基本语句和表达式遵循与Groovy语法相同的规则 ,但有以下例外:
a.Pipeline的顶层必须是块,具体来说是:pipeline { }
b.没有分号作为语句分隔符。每个声明必须在自己的一行
c.块只能包含Sections, Directives, Steps或赋值语句。
d.属性引用语句被视为无参方法调用。所以例如,输入被视为input()
1.Sections(章节)
Declarative Pipeline里的Sections通常包含一个或多个Directives或 Steps
agent
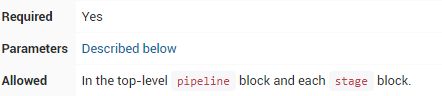
agent部分指定整个Pipeline或特定阶段将在Jenkins环境中执行的位置,具体取决于该agent 部分的放置位置。该部分必须在pipeline块内的顶层定义 ,但stage级使用是可选的。
为了支持Pipeline可能拥有的各种用例,该agent部分支持几种不同类型的参数。这些参数可以应用于pipeline块的顶层,也可以应用在每个stage指令内。
参数
any
在任何可用的agent 上执行Pipeline或stage。例如:agent any
none
当在pipeline块的顶层使用none时,将不会为整个Pipeline运行分配全局agent ,每个stage部分将需要包含其自己的agent部分。
label
使用提供的label标签,在Jenkins环境中可用的代理上执行Pipeline或stage。例如:agent { label 'my-defined-label' }
node
agent { node { label 'labelName' } },等同于 agent { label 'labelName' },但node允许其他选项(如customWorkspace)。
docker
定义此参数时,执行Pipeline或stage时会动态供应一个docker节点去接受Docker-based的Pipelines。 docker还可以接受一个args,直接传递给docker run调用。例如:agent { docker 'maven:3-alpine' }或
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
docker
agent {
docker {
image
'maven:3-alpine'
label
'my-defined-label'
args
'-v /tmp:/tmp'
}
}
|
dockerfile
使用从Dockerfile源存储库中包含的容器来构建执行Pipeline或stage 。为了使用此选项,Jenkinsfile必须从Multibranch Pipeline或“Pipeline from SCM"加载。
默认是在Dockerfile源库的根目录:agent { dockerfile true }。如果Dockerfile需在另一个目录中建立,请使用以下dir选项:agent { dockerfile { dir 'someSubDir' } }。您可以通过docker build ...使用additionalBuildArgs选项,如agent { dockerfile { additionalBuildArgs '--build-arg foo=bar' } }。
参数
any
在任何可用的agent 上执行Pipeline或stage。例如:agent any
none
当在pipeline块的顶层使用none时,将不会为整个Pipeline运行分配全局agent ,每个stage部分将需要包含其自己的agent部分。
label
使用提供的label标签,在Jenkins环境中可用的代理上执行Pipeline或stage。例如:agent { label 'my-defined-label' }
node
agent { node { label 'labelName' } },等同于 agent { label 'labelName' },但node允许其他选项(如customWorkspace)。
docker
定义此参数时,执行Pipeline或stage时会动态供应一个docker节点去接受Docker-based的Pipelines。 docker还可以接受一个args,直接传递给docker run调用。例如:agent { docker 'maven:3-alpine' }或
docker
agent {
docker {
image 'maven:3-alpine'
label 'my-defined-label'
args '-v /tmp:/tmp'
}}
dockerfile
使用从Dockerfile源存储库中包含的容器来构建执行Pipeline或stage 。为了使用此选项,Jenkinsfile必须从Multibranch Pipeline或“Pipeline from SCM"加载。
默认是在Dockerfile源库的根目录:agent { dockerfile true }。如果Dockerfile需在另一个目录中建立,请使用以下dir选项:agent { dockerfile { dir 'someSubDir' } }。您可以通过docker build ...使用additionalBuildArgs选项,如agent { dockerfile { additionalBuildArgs '--build-arg foo=bar' } }。
常用选项
这些是可以应用于两个或多个agent的选项。除非明确定义,否则不需要。
label
一个字符串。标记在哪里运行pipeline或stage
此选项适用于node,docker和dockerfile,并且 node是必需的。
customWorkspace
一个字符串。自定义运行的工作空间内。它可以是相对路径,在这种情况下,自定义工作区将位于节点上的工作空间根目录下,也可以是绝对路径。例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
agent {
node {
label
'my-defined-label'
customWorkspace
'/some/other/path'
}
}
|
reuseNode
一个布尔值,默认为false。如果为true,则在同一工作空间中。
此选项适用于docker和dockerfile,并且仅在 individual stage中使用agent才有效。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
pipeline {
//Execute all the steps defined in this Pipeline within a newly created container of the given name and tag (maven:3-alpine).
agent { docker
'maven:3-alpine'
}
stages {
stage(
'Example Build'
) {
steps {
sh
'mvn -B clean verify'
}
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
pipeline {
agent none
stages {
stage(
'Example Build'
) {
agent { docker
'maven:3-alpine'
}
steps {
echo
'Hello, Maven'
sh
'mvn --version'
}
}
stage(
'Example Test'
) {
agent { docker
'openjdk:8-jre'
}
steps {
echo
'Hello, JDK'
sh
'java -version'
}
}
}
}
|
post
定义Pipeline或stage运行结束时的操作。post-condition块支持post部件:always,changed,failure,success,unstable,和aborted。这些块允许在Pipeline或stage运行结束时执行步骤,具体取决于Pipeline的状态。
conditions项:
always
运行,无论Pipeline运行的完成状态如何。
changed
只有当前Pipeline运行的状态与先前完成的Pipeline的状态不同时,才能运行。
failure
仅当当前Pipeline处于“失败”状态时才运行,通常在Web UI中用红色指示表示。
success
仅当当前Pipeline具有“成功”状态时才运行,通常在具有蓝色或绿色指示的Web UI中表示。
unstable
只有当前Pipeline具有“不稳定”状态,通常由测试失败,代码违例等引起,才能运行。通常在具有×××指示的Web UI中表示。
aborted
只有当前Pipeline处于“中止”状态时,才会运行,通常是由于Pipeline被手动中止。通常在具有灰色指示的Web UI中表示。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage(
'Example'
) {
steps {
echo
'Hello World'
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo
'I will always say Hello again!'
}
}
}
|
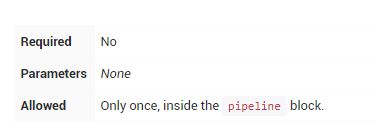
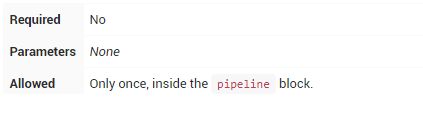
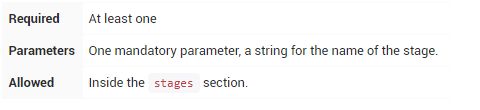
stages
包含一个或多个stage的序列,Pipeline的大部分工作在此执行。建议stages至少包含至少一个stage指令,用于连接各个交付过程,如构建,测试和部署等。
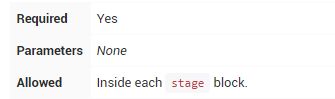
steps
steps包含一个或多个在stage块中执行的step序列。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage(
'Example'
) {
steps {
echo
'Hello World'
}
}
}
}
|
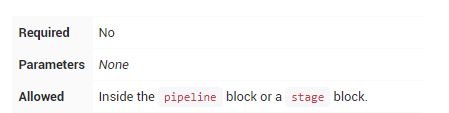
2.Directives (指令)
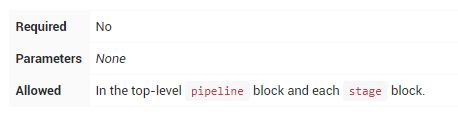
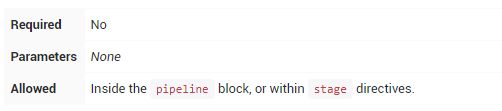
environment
environment指令指定一系列键值对,这些键值对将被定义为所有step或stage-specific step的环境变量,具体取决于environment指令在Pipeline中的位置。
该指令支持一种特殊的方法credentials(),可以通过其在Jenkins环境中的标识符来访问预定义的凭据。
对于类型为“Secret Text”的凭据,该 credentials()方法将确保指定的环境变量包含Secret Text内容;对于“标准用户名和密码”类型的凭证,指定的环境变量将被设置为username:password。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
CC =
'clang'
}
stages {
stage(
'Example'
) {
environment {
AN_ACCESS_KEY = credentials(
'my-prefined-secret-text'
)
}
steps {
sh
'printenv'
}
}
}
}
|
options
options指令允许在Pipeline本身内配置Pipeline专用选项。Pipeline本身提供了许多选项,例如buildDiscarder,但它们也可能由插件提供,例如 timestamps。
可用选项
buildDiscarder
pipeline保持构建的最大个数。例如:options { buildDiscarder(logRotator(numToKeepStr: '1')) }
disableConcurrentBuilds
不允许并行执行Pipeline,可用于防止同时访问共享资源等。例如:options { disableConcurrentBuilds() }
skipDefaultCheckout
默认跳过来自源代码控制的代码。例如:options { skipDefaultCheckout() }
skipStagesAfterUnstable
一旦构建状态进入了“Unstable”状态,就跳过此stage。例如:options { skipStagesAfterUnstable() }
timeout
设置Pipeline运行的超时时间。例如:options { timeout(time: 1, unit: 'HOURS') }
retry
失败后,重试整个Pipeline的次数。例如:options { retry(3) }
timestamps
预定义由Pipeline生成的所有控制台输出时间。例如:options { timestamps() }
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
pipeline {
agent any
options {
timeout(time: 1, unit:
'HOURS'
)
}
stages {
stage(
'Example'
) {
steps {
echo
'Hello World'
}
}
}
}
|
parameters
parameters指令提供用户在触发Pipeline时的参数列表。这些参数值通过该params对象可用于Pipeline步骤,具体用法如下
可用参数
string
A parameter of a string type, for example: parameters { string(name: 'DEPLOY_ENV', defaultValue: 'staging', description: '') }
booleanParam
A boolean parameter, for example: parameters { booleanParam(name: 'DEBUG_BUILD', defaultValue: true, description: '') }
目前只支持[booleanParam, choice, credentials, file, text, password, run, string]这几种参数类型,其他高级参数化类型还需等待社区支持。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
pipeline {
agent any
parameters {
string
(name:
'PERSON'
, defaultValue:
'Mr Jenkins'
, description:
'Who should I say hello to?'
)
}
stages {
stage(
'Example'
) {
steps {
echo
"Hello ${params.PERSON}"
}
}
}
}
|
triggers
triggers指令定义了Pipeline自动化触发的方式。对于与源代码集成的Pipeline,如GitHub或BitBucket,triggers可能不需要基于webhook的集成也已经存在。目前只有两个可用的触发器:cron和pollSCM。
cron
接受一个cron风格的字符串来定义Pipeline触发的常规间隔,例如: triggers { cron('H 4/* 0 0 1-5') }
pollSCM
接受一个cron风格的字符串来定义Jenkins检查SCM源更改的常规间隔。如果存在新的更改,则Pipeline将被重新触发。例如:triggers { pollSCM('H 4/* 0 0 1-5') }
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
pipeline {
agent any
triggers {
cron(
'H 4/* 0 0 1-5'
)
}
stages {
stage(
'Example'
) {
steps {
echo
'Hello World'
}
}
}
}
|
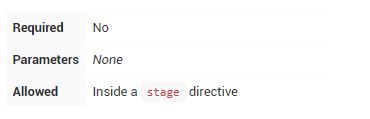
stage
stage指令在stages部分中,应包含stop部分,可选agent部分或其他特定于stage的指令。实际上,Pipeline完成的所有实际工作都将包含在一个或多个stage指令中。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage(
'Example'
) {
steps {
echo
'Hello World'
}
}
}
}
|
tools
通过tools可自动安装工具,并放置环境变量到PATH。如果agent none,这将被忽略。
Supported Tools(Global Tool Configuration)
maven
jdk
gradle
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
//工具名称必须在Jenkins 管理Jenkins → 全局工具配置中预配置。
maven
'apache-maven-3.0.1'
}
stages {
stage(
'Example'
) {
steps {
sh
'mvn --version'
}
}
}
}
|
when
when指令允许Pipeline根据给定的条件确定是否执行该阶段。该when指令必须至少包含一个条件。如果when指令包含多个条件,则所有子条件必须为stage执行返回true。这与子条件嵌套在一个allOf条件中相同(见下面的例子)。
更复杂的条件结构可使用嵌套条件建:not,allOf或anyOf。嵌套条件可以嵌套到任意深度。
内置条件
branch
当正在构建的分支与给出的分支模式匹配时执行,例如:when { branch 'master' }。请注意,这仅适用于多分支Pipeline。
environment
当指定的环境变量设置为给定值时执行,例如: when { environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' }
expression
当指定的Groovy表达式求值为true时执行,例如: when { expression { return params.DEBUG_BUILD } }
not
当嵌套条件为false时执行。必须包含一个条件。例如:when { not { branch 'master' } }
allOf
当所有嵌套条件都为真时执行。必须至少包含一个条件。例如:when { allOf { branch 'master'; environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' } }
anyOf
当至少一个嵌套条件为真时执行。必须至少包含一个条件。例如:when { anyOf { branch 'master'; branch 'staging' } }
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage(
'Example Build'
) {
steps {
echo
'Hello World'
}
}
stage(
'Example Deploy'
) {
when {
allOf {
branch
'production'
environment name:
'DEPLOY_TO'
, value:
'production'
}
}
steps {
echo
'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
|
3.Parallel(并行)
Declarative Pipeline近期新增了对并行嵌套stage的支持,对耗时长,相互不存在依赖的stage可以使用此方式提升运行效率。除了parallel stage,单个parallel里的多个step也可以使用并行的方式运行。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage(
'Non-Parallel Stage'
) {
steps {
echo
'This stage will be executed first.'
}
}
stage(
'Parallel Stage'
) {
when {
branch
'master'
}
parallel {
stage(
'Branch A'
) {
agent {
label
"for-branch-a"
}
steps {
echo
"On Branch A"
}
}
stage(
'Branch B'
) {
agent {
label
"for-branch-b"
}
steps {
echo
"On Branch B"
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
4.Steps(步骤)
Declarative Pipeline可以使用 Pipeline Steps reference中的所有可用步骤 ,并附加以下仅在Declarative Pipeline中支持的步骤。
script
script步骤需要一个script Pipeline,并在Declarative Pipeline中执行。对于大多数用例,script在Declarative Pipeline中的步骤不是必须的,但它可以提供一个有用的加强。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage(
'Example'
) {
steps {
echo
'Hello World'
script {
def browsers = [
'chrome'
,
'firefox'
]
for
(
int
i = 0; i < browsers.size(); ++i) {
echo
"Testing the ${browsers[i]} browser"
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
四、Scripted Pipeline
Groovy脚本不一定适合所有使用者,因此jenkins创建了Declarative pipeline,为编写Jenkins管道提供了一种更简单、更有主见的语法。但是不可否认,由于脚本化的pipeline是基于groovy的一种DSL语言,所以与Declarative pipeline相比为jenkins用户提供了更巨大的灵活性和可扩展性。
1.流程控制
pipeline脚本同其它脚本语言一样,从上至下顺序执行,它的流程控制取决于Groovy表达式,如if/else条件语句,举例如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
Jenkinsfile (Scripted Pipeline)
node {
stage(
'Example'
) {
if
(env.BRANCH_NAME ==
'master'
) {
echo
'I only execute on the master branch'
}
else
{
echo
'I execute elsewhere'
}
}
}
|
pipeline脚本流程控制的另一种方式是Groovy的异常处理机制。当任何一个步骤因各种原因而出现异常时,都必须在Groovy中使用try/catch/finally语句块进行处理,举例如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
Jenkinsfile (Scripted Pipeline)
node {
stage(
'Example'
) {
try
{
sh
'exit 1'
}
catch
(exc) {
echo
'Something failed, I should sound the klaxons!'
throw
}
}
}
|
2.Steps
pipeline最核心和基本的部分就是“step”,从根本上来说,steps作为Declarative pipeline和Scripted pipeline语法的最基本的语句构建块来告诉jenkins应该执行什么操作。
Scripted pipeline没有专门将steps作为它的语法的一部分来介绍,但是在Pipeline Steps reference这篇文档中对pipeline及其插件涉及的steps做了很详细的介绍。如有需要可参考jenkins官网对该部分的介绍Pipeline Steps reference
3.Differences from plain Groovy
由于pipeline的一些个性化需求,比如在重新启动jenkins后要求pipeline脚本仍然可以运行,那么pipeline脚本必须将相关数据做序列化,然而这一点 Groovy并不能完美的支持,例如collection.each { item -> /* perform operation */ }
4.Declarative pipeline和Scripted pipeline的比较
共同点:
两者都是pipeline代码的持久实现,都能够使用pipeline内置的插件或者插件提供的steps,两者都可以利用共享库扩展。
区别:
两者不同之处在于语法和灵活性。Declarative pipeline对用户来说,语法更严格,有固定的组织结构,更容易生成代码段,使其成为用户更理想的选择。但是Scripted pipeline更加灵活,因为Groovy本身只能对结构和语法进行限制,对于更复杂的pipeline来说,用户可以根据自己的业务进行灵活的实现和扩展。