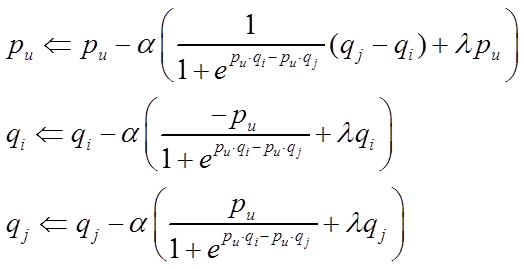实验2——建模
建模buildModle
def buildModel(self):
loss_pre = sys.float_info.max
nonzeros = self.trainMatrix.nnz
hr_prev = 0.0
sys.stderr.write("Run for BPR. \n")
for itr in xrange(self.maxIter):
start = time.time()
# Each training epoch
for s in xrange(nonzeros):
# sample a user
u = np.random.randint(self.userCount)
itemList = self.trainMatrix.getrowview(u).rows[0]
if len(itemList) == 0:
continue
# sample a positive item
i = random.choice(itemList)
# One SGD step update
self.update_ui(u, i)
# Show progress
if self.showProgress:
self._showProgress(itr, start, self.testRatings)
# Show loss
if self.showLoss:
loss_pre = self._showLoss(itr, start, loss_pre)
if self.adaptive:
if not self.showProgress:
self.evaluate(self.testRatings)
hr = np.mean(self.ndcgs)
self.lr = self.lr * 1.05 if hr > hr_prev else self.lr * 0.5
hr_prev = hr2. numpy.random.randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l')
Return random integers from low (inclusive) to high (exclusive).返回一个随机数
3. rowsLIL format row index array of the matrix
4. numpy.random.choice(a, size=None, replace=True, p=None)
Generates a random sample from a given 1-D array.从a=itemlist生成的一个随机样本
5. update_ui()函数是自己写的 One SGD step update
6. sys.float_info.max Python所能处理的浮点数的最大值
7.__init__ 构造函数,在生成对象时调用
8.python单继承
class Recommender(object):
class MFbpr(Recommender):
def update_ui(self, u, i):
# sample a negative item(uniformly random)
j = np.random.randint(self.itemCount)
while self.trainMatrix[u, j] != 0:
j = np.random.randint(self.itemCount)
# BPR update rules
y_pos = self.predict(u, i) # target value of positive instance
y_neg = self.predict(u, j) # target value of negative instance
mult = -self.partial_loss(y_pos - y_neg)
for f in xrange(self.factors):
grad_u = self.V[i, f] - self.V[j, f]
self.U[u, f] -= self.lr * (mult * grad_u + self.reg * self.U[u, f])
grad = self.U[u, f]
self.V[i, f] -= self.lr * (mult * grad + self.reg * self.V[i, f])
self.V[j, f] -= self.lr * (-mult * grad + self.reg * self.V[j, f])
9.itemCount是在Recommend.py(bpr的父类)中定义过了,见9.
self.userCount = self.trainMatrix.shape[0] 训练矩阵的第一维的长度
self.itemCount = self.trainMatrix.shape[1]
def predict(self, u, i):
return np.dot(self.U[u], self.V[i])11.计算中xuiy=rui-ruj
# Partial of the ln sigmoid function used by BPR
def partial_loss(self, x):
exp_x = np.exp(-x)
return exp_x / (1.0 + exp_x)12.
for f in xrange(self.factors):
grad_u = self.V[i, f] - self.V[j, f]
self.U[u, f] -= self.lr * (mult * grad_u + self.reg * self.U[u, f])
grad = self.U[u, f]
self.V[i, f] -= self.lr * (mult * grad + self.reg * self.V[i, f])
self.V[j, f] -= self.lr * (-mult * grad + self.reg * self.V[j, f])是模型学习公式【U即q,V即q,lr即学习速率 α,mult即lnσ(xuij),即下面公式的,reg是正则化参数】
_showProgress()函数在父类Recommend里
def _showProgress(self, itr, start, testRatings):
end_itr = time.time()
if self.userCount == len(testRatings):
# leave-1-out eval
self.evaluate(testRatings)
else:
# global split
self.evaluateOnline(testRatings, 1000)
end_eval = time.time()
sys.stderr.write(【1】使用 弃(留)一法交叉验证 离线模型evalute
即每个用户的最近的交互被用来预测,剩余数据用来训练。这种人为区分在论文中广泛使用,但是不能适用于实际场景。
并且新用户问题因每个用户有训练历史所以被忽略掉,没有解决。因此,这种protocol只能评估算法为已存在用户提供一次性建议时的能力
def evaluate(self, testRatings):
self.hits = np.array([0.0] * self.userCount)
self.ndcgs = np.array([0.0] * self.userCount)
self.precs = np.array([0.0] * self.userCount)
for rating in testRatings:
u = rating[0]
i = rating[1]
res = self.evaluate_for_user(u, i)
self.hits[u] = res[0]
self.ndcgs[u] = res[1]
self.precs[u] = res[2]其中又有个evaluate_for_user()函数
def evaluate_for_user(self, u, gtItem):
result = [0.0] * 3
map_item_score = {}
# Get the score of the test item first.
maxScore = self.predict(u, gtItem)
# Early stopping if there are topK items larger than maxScore.
countLarger = 0
for i in xrange(self.itemCount):
score = self.predict(u, i)
map_item_score[i] = score
if score > maxScore:
countLarger += 1
if countLarger > self.topK:
# early stopping
return result
# Selecting topK items (does not exclude train items).
if self.ignoreTrain:
rankList = Utils.TopKeysByValue(map_item_score, self.topK, self.trainMatrix.getrowview(u).rows[0])
else:
rankList = Utils.TopKeysByValue(map_item_score, self.topK, None)
result[0] = self.getHitRatio(rankList, gtItem)
result[1] = self.getNDCG(rankList, gtItem)
result[2] = self.getPrecision(rankList, gtItem)
return result【2】在线反馈验证 evaluateOnline
计算动态数据流才是更贴切与实际场景。
首先,将所有互动按时间先后排序。
然后,将时间中排在前90%的互动作为训练数据集,后10%作为测试数据集。
在测试阶段,模型第一次推荐一个项目排序列表给用户,从测试数据集中拿出一个测试交互(如,用户项目对),判断在排序列表上的用户反映。
然后,将测试交互放到模型中,进行增量迭代。
注意,按时间进行全局切分。
def evaluateOnline(self, testRatings, interval):
testCount = len(testRatings)
self.hits = np.array([0.0]*testCount)
self.ndcgs = np.array([0.0]*testCount)
self.precs = np.array([0.0]*testCount)
intervals = 10
counts = [0] * (intervals + 1)
hits_r = [0.0] * (intervals + 1)
ndcgs_r = [0.0] * (intervals + 1)
precs_r = [0.0] * (intervals + 1)
updateTime = 0
for i in xrange(testCount):
if i > 0 and interval > 0 and i % interval == 0:
# Check performance per interval:
sys.stderr.write("{}: =\t {}\t {}\t {}\n".format(
i, np.sum(self.hits) / i, np.sum(self.ndcgs) / i, np.sum(self.precs) / i))
# Evaluate model of the current test rating:
rating = testRatings[i]
res = self.evaluate_for_user(rating[0], rating[1])
self.hits[i] = res[0]
self.ndcgs[i] = res[1]
self.precs[i] = res[2]
# statisitcs for break down
r = len(self.trainMatrix.getrowview(rating[0]).rows[0])
r = intervals if r > intervals else r
counts[r] += 1
hits_r[r] += res[0]
ndcgs_r[r] += res[1]
precs_r[r] += res[2]
# Update the model
start = time.time()
self.updateModel(rating[0], rating[1])
updateTime += time.time() - start
sys.stderr.write("Break down the results by number of user ratings for the test pair.\n")
sys.stderr.write("#Rating\t Percentage\t HR\t NDCG\t MAP\n")
for i in xrange(intervals+1):
if counts[i] == 0:
continue
sys.stderr.write("{}\t {}%%\t {}\t {}\t {} \n".format(
i, float(counts[i])/testCount*100,
hits_r[i] / counts[i], ndcgs_r[i] / counts[i], precs_r[i] / counts[i]))
sys.stderr.write("Avg model update time per instance: {}\n".format(float(updateTime)/testCount)) 使用用户实际上购买的 ground-truth(GT)项目来评价排序列表
采用 Hit Ration(HR)——度量ground-truth(GT)项目是否出现在排序列表上。
def getHitRatio(self, rankList, gtItem):
for item in rankList:
if item == gtItem:
return 1
return 0Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG).——统计命中的次数
并截取了这两个列表的前100个。top-100
def getNDCG(self, rankList, gtItem):
for i, item in enumerate(rankList):
if item == gtItem:
return np.log(2) / np.log(i+2)
return 0 def getPrecision(self, rankList, gtItem):
for i, item in enumerate(rankList):
if item == gtItem:
return 1.0 / (i+1)
return 0