Android 显示Intent和隐示Intent
Intent 是 Android 程序中各组件之间进行交互的一种重要方式,它不仅可以指明当前组件想要执行的动作,还可以在不同组件之间传递数据。Intent 一般可被用于启动活动、启动服务、以及发送广播等场景,由于服务、广播等概念你暂时还未涉及,那么本章我们的目光无疑就锁定在了启动活动上面。
Intent 有多个构造函数的重载,其中一个是 Intent(Context packageContext, Class cls)。这个构造函数接收两个参数,第一个参数 Context 要求提供一个启动活动的上下文,第二个参数 Class 则是指定想要启动的目标活动,通过这个构造函数就可以构建出 Intent 的“意图”。然后我们应该怎么使用这个 Intent 呢?Activity 类中提供了一个 startActivity()方法,这个方法是专门用于启动活动的,它接收一个 Intent 参数,这里我们将构建好的 Intent 传入 startActivity()
方法就可以启动目标活动了。
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.chenxiaoyang.intent.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/app_name"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="转到SecondActivity"/>
LinearLayout>
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private Button mButton; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); //实例化Button mButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn); //响应按钮btn事件 mButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { //显示方式声明Intent,直接启动SecondActivity Intent it = new Intent(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class); //启动Activity startActivity(it); } }); } }
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/activity_second" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context="com.example.chenxiaoyang.intent.SecondActivity"> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center" android:text="@string/app_name_second" android:textSize="30dp"/> <Button android:id="@+id/secondBtn" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="返回"/> LinearLayout>
public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private Button mButtonSecond; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_second); //实例化Button mButtonSecond = (Button) findViewById(R.id.secondBtn); //响应按钮secondBtn事件 mButtonSecond.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { //显示方式声明Intent,直接启动MainActivity Intent intent = new Intent(SecondActivity.this, MainActivity.class); //启动Activity startActivity(intent); } }); } }
<intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/> intent-filter>
activity> <activity android:name=".SecondActivity"> activity>
什么叫做合适的活动呢?简单来说就是可以响应我们这个隐式 Intent 的活动,那么目前SecondActivity 可以响应什么样的隐式 Intent 呢?额,现在好像还什么都响应不了,不过很快就会有了。
新建一个SecondActivity类,通过在
<activity android:name=".SecondActivity"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="com.example.activitytest.ACTION_START"/> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/> intent-filter> activity>
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.chenxiaoyang.initent.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/app_name"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="转到SecondActivity"/>
LinearLayout>
修改 MainActivity 中按钮的点击事件,代码如下所示:
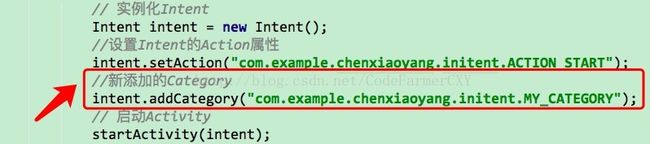
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private Button mButton; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); //实例化button mButton= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn); // 响应按钮Button事件 mButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // 实例化Intent Intent intent = new Intent(); //设置Intent的Action属性 intent.setAction("com.example.chenxiaoyang.initent.ACTION_START"); // 启动Activity startActivity(intent); } }); }
可以看到,我们使用了 Intent 的另一个构造函数,直接将 action 的字符串传了进去,表明我们想要启动能够响应 com.example.chenxiaoyang.initent.ACTION_START 这个 action 的活动。那前面不是说要
修改MainActivity中按钮的点击事件,代码如下所示:
//新添加的Category intent.addCategory("com.example.chenxiaoyang.initent.MY_CATEGORY");
错误信息中提醒我们,没有任何一个活动可以响应我们的 Intent,为什么呢?这是因为我们刚刚在 Intent 中新增了一个 category,而 SecondActivity 的
<category android:name="com.example.chenxiaoyang.initent.MY_CATEGORY"/>
使用隐式 Intent,我们不仅可以启动自己程序内的活动,还可以启动其他程序的活动,这使得 Android 多个应用程序之间的功能共享成为了可能。比如说你的应用程序中需要展示一个网页,这时你没有必要自己去实现一个浏览器,而是只需要调用系统的浏览器来打开这个网页就行了。
这里我们首先指定了 Intent 的 action 是 Intent.ACTION_VIEW,这是一个 Android 系统内置的动作,其常量值为 android.intent.action.VIEW。然后通过 Uri.parse()方法,将一个网址字符串解析成一个 Uri 对象,再调用 Intent 的 setData()方法将这个 Uri 对象传递进去。
重新运行程序,在 FirstActivity 界面点击按钮就可以看到打开了系统浏览器
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_second"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.chenxiaoyang.initent.SecondActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/app_name_second"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/secondBtn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="跳转网页"/>
LinearLayout>
SecondActivity
public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private Button mButtonSecond; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_second); //实例化Button mButtonSecond= (Button) findViewById(R.id.secondBtn); // 响应按钮Button事件 mButtonSecond.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { //实例化Intent Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW); //指定Intent跳转网页 intent.setData(Uri.parse("http://www.baidu.com")); // 启动Activity startActivity(intent); } }); } }
上述的代码中,可能你会对 setData()部分感觉到陌生,它接收一个 Uri 对象,主要用于指定当前 Intent 正在操作的数据,而这些数据通常都是以字符串的形式传入到 Uri.parse()方法中解析产生的。