(防坑笔记)hadoop3.0 (四)MapReduce的输入输出解析及常用数据切分方式(附带压缩)
防坑留言:
主要是对MapReduce的输入与输出进行 分析,并且能够自定义方法,同时了解其他数据切分方式
MapReduce的输入输出
输入处理类:
上图的类中为输入处理类(仅以这个为例)
InputFormat
|
FileInputFormat
|
TextInputFormat
实现的InputFormat 是仅有2种方法
------getSplits() 用于将文件切分成为InputSplit小文件
InputSplit:可以进入链接查看细节:chlaws大佬的源码分析
--------createRecordReader( )用于创建Mapper可读的RecordReader实现类
TextInputFormat 是 默认的处理类,处理文本文件
内部就实现了RecordReader()方法,值得一提的是内部又再次将编码格式确定为Utf-8
其他输入处理类
①CombineFileInputFormat
相对于大量的小文件来说,hadoop更合适处理少量的大文件。
CombineFileInputFormat可以缓解这个问题,它是针对小文件而设计的。
②KeyValueTextInputFormat
当输入数据的每一行是两列,并用tab分离的形式的时候,KeyValueTextInputformat处理这种格式的文件非常适合。
③NLineInputformat
NLineInputformat可以控制在每个split中数据的行数。
④SequenceFileInputformat
当输入文件格式是sequencefile的时候,要使用SequenceFileInputformat作为输入。
自定义输入处理类
继承InputFormat抽象类 ,并实现的两个抽象方法即可,可借鉴源码
输出处理类
OutputFormat
|
FileOutputFormat
|
TextOutputFormat 。。。。
与输入类相差无几,简单说明调FileOutputFormat 的实现类
①TextOutputformat
默认的输出格式,key和value中间值用tab隔开的。
②SequenceFileOutputformat
将key和value以sequencefile格式输出。
③ SequenceFileAsOutputFormat
将key和value以原始二进制的格式输出。
④ MapFileOutputFormat
将key和value写入MapFile中。由于MapFile中的key是有序的,所以写入的时候必须保证记录是按key值顺序写入的。
⑤ MultipleOutputFormat
默认情况下一个reducer会产生一个输出,但是有些时候我们想一个reducer产生多个输出,MultipleOutputFormat和MultipleOutputs可以实现这个功能。
常用切分方式
1、自定义排序编程
主要是利用NullWritable 这个类的特性来进行排序,让值为空,相当于仅排列key,因为都实现了WritableComparable
下列例子中的FlowBean 可以任意自定义,仅做例子
public static class SortMapper extends Mapper{
@Override
protected void map(
LongWritable key,
Text value,
Mapper.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String[] fields = StringUtils.split(line,"\t");
String phoneNB = fields[0];
long up_flow = Long.parseLong(fields[1]);
long d_flow = Long.parseLong(fields[2]);
context.write(new FlowBean(phoneNB, up_flow, d_flow), NullWritable.get());
}
}
public static class SortReducer extends Reducer{
@Override
protected void reduce(FlowBean key, Iterable values,
Reducer.Context content)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String phoneNB = key.getPhoneNB();
content.write(new Text(phoneNB), key);
}
}
} 上述代码仅比较key
2、Partitioner方式
相当于自定义一个规则类,也可以说是分组逻辑吧,所有类实现 Partitioner 接口,是K/V结构,可以存入相应数值,第一位是自定义的值,第二位是Reducer的节点。
如果你Debug的话你会发现,在mapper类中会出现所有的值,然后到Reduce节点的时候,会根据你的分组数进入Reduce节点相应次数,显然, 有相同key的键/值对会送到同一个Reducer节点中进行归并
给一个广泛的例子说明一下,内部含注释,这边主要是判断如果不是135开头的,就分到1节点,是的就0节点
KpiPartitioner.java
public class KpiPartitioner extends Partitioner {
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, KpiWritable value, int numPartitions) {
// 实现不同的长度不同的号码分配到不同的reduce task中,返回的数值从0开始算节点数
String substring = key.toString().substring(0, 3);
if (substring.equals("135")) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
}
FlowSumArea.java
/**
* 对流量原始日志进行流量统计,将不同省份的用户统计结果输出到不同文件
* 需要自定义改造两个机制:
* 1、改造分区的逻辑,自定义一个partitioner
* 2、自定义reduer task的并发任务数
*
*/
public class FlowSumArea extends Configured implements Tool{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
try {
int res = ToolRunner.run(conf, new FlowSumArea(), args);
System.exit(res);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 输入文件目录
public static final String INPUT_PATH = "hdfs://192.168.88.129:9000/ha.txt";
// 输出文件目录
public static final String OUTPUT_PATH = "hdfs://192.168.88.129:9000/out";
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 首先删除输出目录已生成的文件
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(new URI(INPUT_PATH), getConf());
Path outPath = new Path(OUTPUT_PATH);
if (fs.exists(outPath)) {
fs.delete(outPath, true);
}
// 定义一个作业
Job job = new Job(getConf(), "MyKpiJob");
// 分区需要设置为打包运行 //笔记(三)的完整代码的类
job.setJarByClass(MyKpiJob.class);
// 设置输入目录
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(INPUT_PATH));
// 设置自定义Mapper类
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
// 指定的类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(KpiWritable.class);
// 设置Partitioner
job.setPartitionerClass(KpiPartitioner.class);
//设置节点数,这里的数目与partitioner的返回数目要一致
job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
// 设置Combiner
job.setCombinerClass(MyReducer.class);
// 设置自定义Reducer类
job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
// 指定的类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(KpiWritable.class);
// 设置输出目录
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(OUTPUT_PATH));
// 提交作业
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
return 0;
}
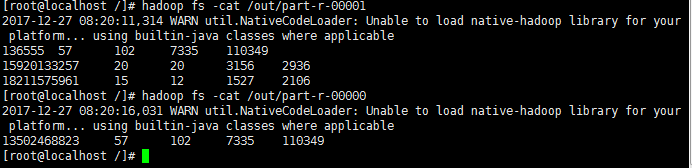
} 引用的代码是防坑笔记(三)的完整代码,将main方法去掉,因为设置打包运行是本类,原有的run方法会被覆盖忽略。效果如下
3、combiner算法
每一个map可能会产生大量的输出,combiner的作用就是在map端对输出先做一次合并,以减少传输到reducer的数据量。
combiner最基本是实现本地key的归并,combiner具有类似本地的reduce功能。
如果不用combiner,那么,所有的结果都是reduce完成,效率会相对低下。使用combiner,先完成的map会在本地聚合,提升速度。
注意:Combiner的输出是Reducer的输入,如果Combiner是可插拔的,添加Combiner绝不能改变最终的计算结果。所以Combiner只应该用于那种Reduce的输入key/value与输出key/value类型完全一致,且不影响最终结果的场景。比如累加,最大值等。
压缩简答
不建议如下操作,因为不行通
public class FlowSumArea extends Configured implements Tool{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long f = System.currentTimeMillis();
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// conf.setBoolean("mapred.compress.map.output", true); //这种不行
// conf.setClass("mapred.map.output.compression.codec", GzipCodec.class, CompressionCodec.class);
try {
int res = ToolRunner.run(conf, new FlowSumArea(), args);
System.exit(res);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(e-f);
}
这样改:在末尾添加,
// 设置输出目录
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(OUTPUT_PATH));
// 提交作业
FileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true); //job使用压缩
FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, GzipCodec.class); //设置压缩格式
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
return 0;注释掉之前的
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long f = System.currentTimeMillis();
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// conf.setBoolean("mapred.compress.map.output", true);
// conf.setClass("mapred.map.output.compression.codec", GzipCodec.class, CompressionCodec.class);
前四章的源代码已上传github https://github.com/lg625740749/hadoop_mapReducer