Java-集合性能测试及结果分析
本文欢迎转载,转载前请联系作者,经允许后方可转载。转载后请注明出处,谢谢! http://blog.csdn.net/colton_null 作者:喝酒不骑马 Colton_Null from CSDN
一.引言
上篇介绍了java中集合的部分内容,本篇则针对常用集合进行性能的测试。测试方法借鉴于《Java编程思想》。具体实现代码在文末给出。
测试结果通过格式化输出方式展示。时间单位为毫秒(ms)。时间计算记录为某项测试结束时间减去开始时间并除以循环次数,就是说消除了集合数量大小不同带来的时间干扰,只展示集合中某个方法在不同大小的情况下的处理速度。
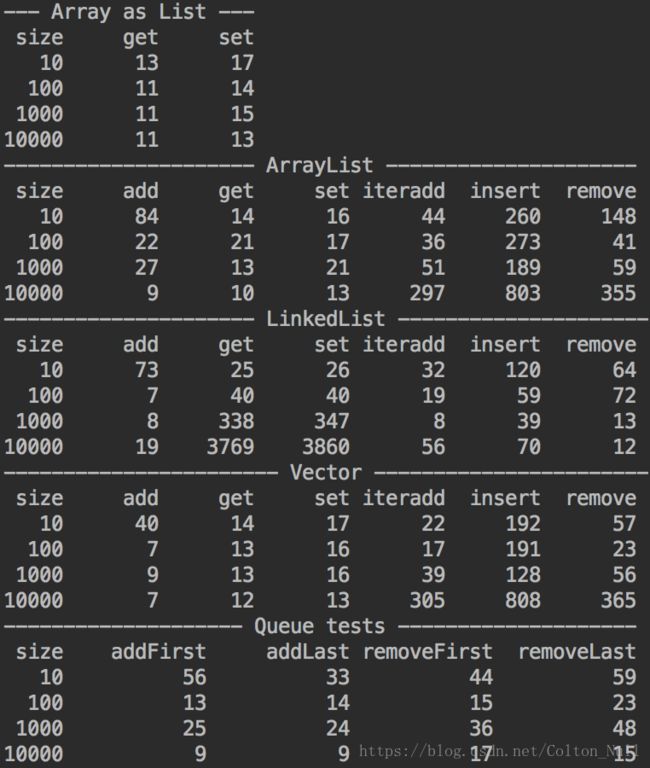
二.List集合性能测试
根据图中的结果,可以总结出以下几点:
1. 由于List和ArrayList的底层实现为数组,所以,无论List的大小如何,随机访问例如get()和set()的速度都很快且一致。
2. LinkedList的底层实现是链表,所以随机访问的性能随着列表容量增大而下降。
3. iteradd是使用迭代器插入新的元素。ArrayList在调用ListIterator的add()方法时,元素被插入到当前迭代器位置之前,所以ArrayList中所有的引用都将向后移动,这样随着ArrayList的容量增大,add()方法的开销会逐渐增加。
4. LinkedList在元素插入方面,开销几乎是一样的。因为底层由链表实现,所以每次插入只需要修改引用指针指向即可,所以add()的开销与LinkedList的大小无关。
5. insert()和remove()方法同第3点和第4点。在本次测试中,insert()和remove()都对位置5的元素进行操作,这么做是排除LinkedList对列表两端数据操作优化的影响。这一点优化可以在Queue测试时体现。
6. 在LinkedList被用作是Queue的时候,可以发现LinkedList对列表两端的数据操作,都做了优化,所以LinkedList对首尾元素的增删与列表大小无关。
7. Vector作为遗留类,这里仅供测试参考,实际使用中应避免使用它。
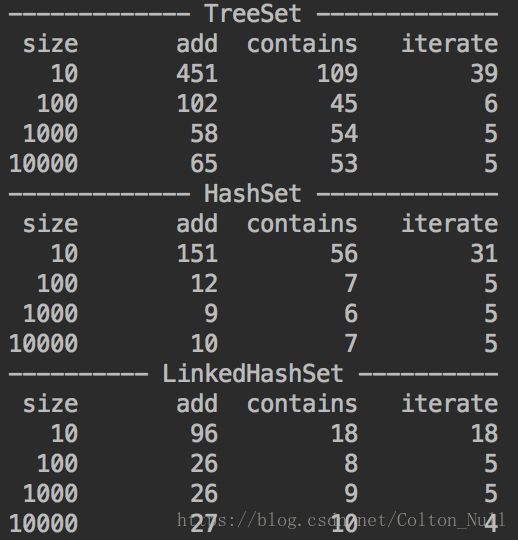
三.Set集合性能测试
- 总体情况上来看,HashSet的性能要优于TreeSet。因为TreeSet有排序的功能,它的存在就是可以维持集合内元素的排序状态。
- 因为TreeSet内部支持排序,所以在迭代功能上,有时候TreeSet会相对方便一些,所以用TreeSet迭代通常要比HashMap快。
- 对于插入操作,LinkedHashMap比HashSet开销更大一些,这是由于LinkedHashMap底层由链表维护所以有额外的开销。
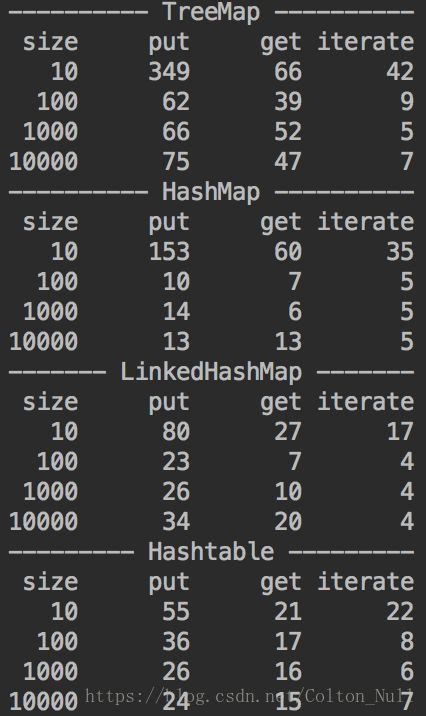
四.Map集合性能测试
- TreeMap与HashMap相比,前者通常较慢。因为TreeMap需要保证元素的顺序。
- LinkedHashMap在插入操作上,比HashMap慢一些。因为LinkedHashMap底层使用链表维护元素的插入顺序。但也正是因为这个链表,使其在迭代操作上更快。
- HashMap是日常开发的首选,如果有特殊需要,则根据不同情况选择对应的Map。
以上就是有关List、Set、Map集合的性能测试结果与分析。下面附上测试的源代码。
五.测试代码
Test.java
public abstract class Test {
// 用于记录集合类型名称
String name;
public Test(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 测试方法
abstract int test(C container, TestParam tp);
} Tester.java
import java.util.List;
public class Tester {
// 格式化输出每条记录的占位长度
public static int fieldWidth = 8;
public static TestParam[] defaultParams = TestParam.array(
10, 5000, 100, 5000, 1000, 5000, 10000, 500);
protected C container;
protected C initialize(int size) {
return container;
}
// 头部分割线
private String headline = "";
private List> tests;
// 字符格式化
private static String stringField() {
return "%" + fieldWidth + "s";
}
// 数字格式化
private static String numberField() {
return "%" + fieldWidth + "d";
}
// 针对集合长度的占位限制
private static int sizeWidth = 5;
// 集合长度格式化
private static String sizeField = "%" + sizeWidth + "s";
private TestParam[] paramList = defaultParams;
public Tester(C container, List> tests) {
this.container = container;
this.tests = tests;
if(container != null) {
headline = container.getClass().getSimpleName();
}
}
public Tester(C container, List> tests, TestParam[] paramList) {
this(container, tests);
this.paramList = paramList;
}
public void setHeadline(String newHeadline) {
headline = newHeadline;
}
public static void run(C cntnr, List> tests) {
new Tester(cntnr, tests).timedTest();
}
public static void run(C cntnr, List> tests, TestParam[] paramList) {
new Tester(cntnr, tests, paramList).timedTest();
}
/**
* 显示头部
*/
private void displayHeader() {
int width = fieldWidth * tests.size() + sizeWidth;
int dashLength = width - headline.length() - 1;
StringBuilder head = new StringBuilder(width);
for (int i = 0; i < dashLength / 2; i++) {
head.append("-");
}
head.append(" ");
head.append(headline);
head.append(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < dashLength / 2; i++) {
head.append("-");
}
System.out.println(head);
System.out.format(sizeField, "size");
for (Test test : tests) {
System.out.format(stringField(), test.name);
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 显示时间差
*/
public void timedTest() {
displayHeader();
for (TestParam param : paramList) {
System.out.format(sizeField, param.size);
for (Test test : tests) {
C container = initialize(param.size);
long start = System.nanoTime();
int reps = test.test(container, param);
long duration = System.nanoTime() - start;
long timePerRep = duration / reps;
System.out.format(numberField(), timePerRep);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} TestParam.java
public class TestParam {
public final int size;
public final int loops;
public TestParam(int size, int loops) {
this.size = size;
this.loops = loops;
}
public static TestParam[] array(int... values) {
int size = values.length / 2;
TestParam[] result = new TestParam[size];
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
result[i] = new TestParam(values[n++], values[n++]);
}
return result;
}
// public static TestParam[] array(String[] values) {
// int[] vals = new int[values.length];
// for (int i = 0; i < vals.length; i++) {
// vals[i] = Integer.decode(values[i]);
// }
// return array(vals);
// }
}List测试类
ListTest.java
import java.util.*;
public class ListTest {
static Random rand = new Random();
static int reps = 1000;
static final int REPLACE_NUM = 50;
static final int INSERT_ITEM_INDEX = 5;
static List>> tests = new ArrayList<>();
static List>> qTests = new ArrayList<>();
static {
// 测试add方法性能
tests.add(new Test>("add") {
int test(List list, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int listSize = tp.size;
for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
list.clear();
for (int j = 0; j < listSize; j++) {
list.add(j);
}
}
return loops * listSize;
}
});
// 测试get方法性能
tests.add(new Test>("get") {
int test(List list, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops * reps;
int listSize = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
list.get(rand.nextInt(listSize));
}
return loops;
}
});
// 测试set方法性能
tests.add(new Test>("set") {
int test(List list, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops * reps;
int listSize = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
list.set(rand.nextInt(listSize), REPLACE_NUM);
}
return loops;
}
});
// 测试迭代器add方法性能
tests.add(new Test>("iteradd") {
int test(List list, TestParam tp) {
final int LOOPS = 1000000;
int half = list.size() / 2;
ListIterator it = list.listIterator(half);
for (int i = 0; i < LOOPS; i++) {
it.add(REPLACE_NUM);
}
return LOOPS;
}
});
// 测试插入操作性能
tests.add(new Test>("insert") {
int test(List list, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
list.add(INSERT_ITEM_INDEX, REPLACE_NUM);
}
return loops;
}
});
// 测试删除操作性能
tests.add(new Test>("remove") {
int test(List list, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int size = tp.size;
for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
list.clear();
list.addAll(new CountingIntegerList(size));
while (list.size() > 5) {
list.remove(5);
}
}
return loops * size;
}
});
// 测试LinkedList添加首部元素性能
qTests.add(new Test>("addFirst") {
int test(LinkedList list, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int size = tp.size;
for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
list.clear();
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
list.addFirst(REPLACE_NUM);
}
}
return loops * size;
}
});
// 测试LinkedList添加尾部元素性能
qTests.add(new Test>("addLast") {
int test(LinkedList list, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int size = tp.size;
for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
list.clear();
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
list.addLast(REPLACE_NUM);
}
}
return loops * size;
}
});
// 测试LinkedList删除首部元素性能
qTests.add(new Test>("removeFirst") {
int test(LinkedList list, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int size = tp.size;
for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
list.clear();
list.addAll(new CountingIntegerList(size));
while (list.size() > 5) {
list.removeFirst();
}
}
return loops * size;
}
});
// 测试LinkedList删除尾部元素性能
qTests.add(new Test>("removeLast") {
int test(LinkedList list, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int size = tp.size;
for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
list.clear();
list.addAll(new CountingIntegerList(size));
while (list.size() > 0) {
list.removeLast();
}
}
return loops * size;
}
});
}
/**
* 测试内部类
*/
static class ListTester extends Tester> {
public ListTester(List container, List>> tests) {
super(container, tests);
}
/**
* 初始化列表
* @param size
* @return
*/
@Override
protected List initialize(int size) {
container.clear();
container.addAll(new CountingIntegerList(size));
return container;
}
/**
* 执行测试
* @param list List类型
* @param tests 要测试的功能集合
*/
public static void run(List list, List>> tests) {
new ListTester(list, tests).timedTest();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试List
Tester> arrayTest =
new Tester>(null, tests.subList(1, 3)) {
// This will be called before each test. It
// produces a non-resizeable array-backed list:
@Override
protected List initialize(int size) {
Integer[] ia = Generated.array(Integer.class,
new CountingGenerator.Integer(), size);
return Arrays.asList(ia);
}
};
arrayTest.setHeadline("Array as List");
arrayTest.timedTest();
Tester.defaultParams = TestParam.array(
10, 5000, 100, 5000, 1000, 1000, 10000, 200);
// 测试ArrayList
ListTester.run(new ArrayList<>(), tests);
// 测试LinkedList
ListTester.run(new LinkedList<>(), tests);
// 测试Vector
ListTester.run(new Vector<>(), tests);
Tester.fieldWidth = 12;
// 测试LinkedList的Queue特性
Tester> qTest = new Tester<>(new LinkedList<>(), qTests);
qTest.setHeadline("Queue tests");
qTest.timedTest();
}
}
} 测试Set类
SetTest.java
import java.util.*;
public class SetTest {
static List>> tests =
new ArrayList>>();
static {
// 测试add方法
tests.add(new Test>("add") {
int test(Set set, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int size = tp.size;
for(int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
set.clear();
for(int j = 0; j < size; j++)
set.add(j);
}
return loops * size;
}
});
// 测试contains方法
tests.add(new Test>("contains") {
int test(Set set, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int span = tp.size * 2;
for(int i = 0; i < loops; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < span; j++)
set.contains(j);
return loops * span;
}
});
// 测试迭代器性能
tests.add(new Test>("iterate") {
int test(Set set, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops * 10;
for(int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
Iterator it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
it.next();
}
return loops * set.size();
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tester.fieldWidth = 10;
// 测试TreeSet
Tester.run(new TreeSet<>(), tests);
// 测试HashSet
Tester.run(new HashSet<>(), tests);
// 测试LinkedHashSet
Tester.run(new LinkedHashSet<>(), tests);
}
} 测试Map类
MapTest.java
import java.util.*;
public class MapTest {
static List>> tests =
new ArrayList>>();
static {
// 测试put方法
tests.add(new Test>("put") {
int test(Map map, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int size = tp.size;
for(int i = 0; i < loops; i++) {
map.clear();
for(int j = 0; j < size; j++)
map.put(j, j);
}
return loops * size;
}
});
// 测试get方法
tests.add(new Test>("get") {
int test(Map map, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops;
int span = tp.size * 2;
for(int i = 0; i < loops; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < span; j++)
map.get(j);
return loops * span;
}
});
// 测试迭代器性能
tests.add(new Test>("iterate") {
int test(Map map, TestParam tp) {
int loops = tp.loops * 10;
for(int i = 0; i < loops; i ++) {
Iterator it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
it.next();
}
return loops * map.size();
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试TreeMap
Tester.run(new TreeMap<>(), tests);
// 测试HashMap
Tester.run(new HashMap<>(), tests);
// 测试LinkedHashMap
Tester.run(new LinkedHashMap<>(),tests);
// Tester.run(new IdentityHashMap<>(), tests);
// Tester.run(new WeakHashMap<>(), tests);
// 测试HashTable
Tester.run(new Hashtable<>(), tests);
}
} 其它辅助类
Generator.java
public interface Generator {
T next();
} Generated.java
public class Generated {
// Fill an existing array:
public static T[] array(T[] a, Generator gen) {
return new CollectionData(gen, a.length).toArray(a);
}
// Create a new array:
public static T[] array(Class type, Generator gen, int size) {
T[] a = (T[]) java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(type, size);
return new CollectionData(gen, size).toArray(a);
}
} CollectionData.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CollectionData<T> extends ArrayList<T> {
public CollectionData(Generator gen, int quantity) {
for (int i = 0; i < quantity; i++)
add(gen.next());
}
// A generic convenience method:
public static CollectionData list(Generator gen, int quantity) {
return new CollectionData(gen, quantity);
}
} CountingGenerator.java
public class CountingGenerator {
public static class
Boolean implements Generator<java.lang.Boolean> {
private boolean value = false;
public java.lang.Boolean next() {
value = !value; // Just flips back and forth
return value;
}
}
public static class
Byte implements Generator<java.lang.Byte> {
private byte value = 0;
public java.lang.Byte next() { return value++; }
}
static char[] chars = ("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" +
"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ").toCharArray();
public static class
Character implements Generator<java.lang.Character> {
int index = -1;
public java.lang.Character next() {
index = (index + 1) % chars.length;
return chars[index];
}
}
public static class
String implements Generator<java.lang.String> {
private int length = 7;
Generator cg = new Character();
public String() {}
public String(int length) { this.length = length; }
public java.lang.String next() {
char[] buf = new char[length];
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++)
buf[i] = cg.next();
return new java.lang.String(buf);
}
}
public static class
Short implements Generator<java.lang.Short> {
private short value = 0;
public java.lang.Short next() { return value++; }
}
public static class
Integer implements Generator<java.lang.Integer> {
private int value = 0;
public java.lang.Integer next() { return value++; }
}
public static class
Long implements Generator<java.lang.Long> {
private long value = 0;
public java.lang.Long next() { return value++; }
}
public static class
Float implements Generator<java.lang.Float> {
private float value = 0;
public java.lang.Float next() {
float result = value;
value += 1.0;
return result;
}
}
public static class
Double implements Generator<java.lang.Double> {
private double value = 0.0;
public java.lang.Double next() {
double result = value;
value += 1.0;
return result;
}
}
} CountingIntegerList.java
import java.util.AbstractList;
/**
* 可以生成任意长度的List,元素从0开始递增
*/
public class CountingIntegerList extends AbstractList<Integer> {
private int size;
public CountingIntegerList(int size) {
this.size = size < 0 ? 0 : size;
}
@Override
public Integer get(int index) {
return Integer.valueOf(index);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// List list = new CountingIntegerList(30);
// System.out.println(new CountingIntegerList(30));
// }
}站在前人的肩膀上前行,感谢以下博客及文献的支持。
《Java编程思想(第四版) 机械工业出版社》