input子系统
input子系统——kernel中input设备介绍
一、输入子系统驱动层分析
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/u013604527/article/details/53432623
在键盘驱动代码分析的笔记中,接触到了input子系统,键盘驱动,键盘驱动将检测到的所有按键都上报给了input子系统。Input子系统是所有I/O设备驱动的中间层,为上层提供了一个统一的界面。例如,在终端系统中,我们不需要去管有多少个键盘,多少个鼠标。它只要从input子系统中去取对应的事件(按键,鼠标移位等)就可以了。今天就对input子系统做一个详尽的分析。
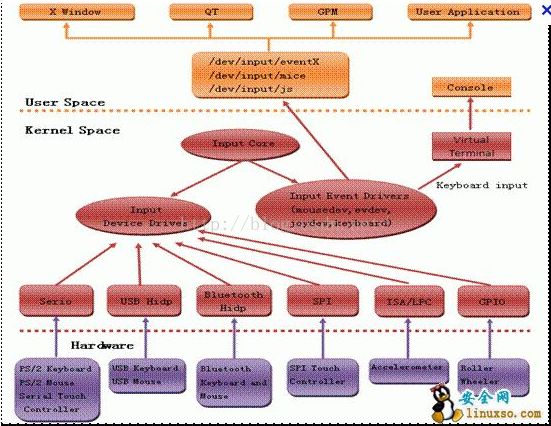
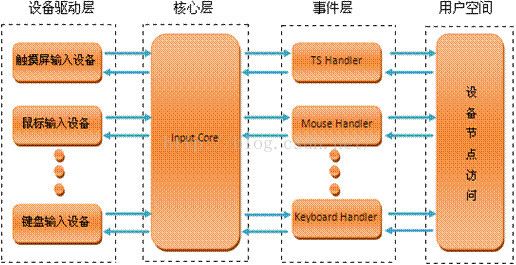
输入子系统由驱动层、输入子系统核心、事件处理层三部分组成。一个输入事件,如鼠标移动、键盘按下等通过Driver->Inputcore->Event handler->userspace的顺序到达用户控件的应用程序,具体的流程可以用下图描叙。
1、驱动层:将底层的硬件输入转化为统一事件形式,向输入核心(Input Core)汇报;6
2、输入子系统核心:承上启下,为驱动层提供输入设备注册与操作接口,如:input_register_device,通知事件处理层对事件进行处理,在/Proc下产生相应的设备信息;
3、事件处理层:主要是和用户空间交互。(Linux中在用户空间将所有的设备都当初文件来处理,由于在一般的驱动程序中都有提供fops接口,以及在/dev下生成相应的设备文件nod,这些操作在输入子系统中由事件处理层完成);
4、设备描述:
-
struct input_dev { -
const char *name; //名字 -
const char *phys; -
const char *uniq; -
struct input_id id; //输入id -
unsigned long evbit[NBITS(EV_MAX)]; // 表示能产生哪类事件 -
unsigned long keybit[NBITS(KEY_MAX)]; // 表示能产生哪些按键 -
unsigned long relbit[NBITS(REL_MAX)]; // 表示能产生哪些相对位移事件, x,y,滚轮 -
unsigned long absbit[NBITS(ABS_MAX)]; // 表示能产生哪些绝对位移事件, x,y -
unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)]; -
unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)]; -
unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)]; -
unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)]; -
... -
}
实现设备驱动核心工作是:向系统报告按键、触摸屏等输入事件event,通过input_event结构描述,不再需要关心文件操作接口。驱动报告事件经过inputCore和Eventhandler到达用户空间。
b、注册输入设备函数:int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev)
c、注销输入设备函数:void input_unregister_device(struct input_dev *dev)
d、驱动实现——初始化(事件支持):--> probe函数
set_bit()告诉input输入子系统支持哪些事件,哪些按键。例如:
-
set_bit()告诉input输入子系统支持哪些事件,哪些按键。例如: -
/* 设置按键能产生哪类事件 */ -
set_bit(EV_KEY,buttons_dev->evbit); -
set_bit(EV_REP,buttons_dev->evbit); -
/* 设置能产生这类操作的哪些事件 */ -
set_bit(KEY_L,buttons_dev->keybit); -
set_bit(KEY_S,buttons_dev->keybit); -
set_bit(KEY_ENTER,buttons_dev->keybit); -
set_bit(KEY_LEFTSHIFT,buttons_dev->keybit); -
struct input_dev中有两个成员为: -
evbit:事件类型(包括EV_RST,EV_REL,EV_MSC,EV_KEY,EV_ABS,EV_REP等) -
在input.h中有这些类的定义: -
#define EV_SYN 0x00 //同步事件 -
#define EV_KEY 0x01 //按键类,如键盘或按钮 -
#define EV_REL 0x02 //绝对结果,如鼠标设备 -
#define EV_ABS 0x03 //绝对位移类 ,如操纵杆、书写板 -
#define EV_MSC 0x04 //其他类 -
#define EV_SW 0x05 //开关事件 -
#define EV_LED 0x11 //LED或其他指示设备 -
#define EV_SND 0x12 //声音类,如蜂鸣器 -
#define EV_REP 0x14 //重复类,允许按键自重复 -
#define EV_FF 0x15 //力反馈 -
#define EV_PWR 0x16 //电源管理事件 -
#define EV_FF_STATUS 0x17 -
#define EV_MAX 0x1f -
#define EV_CNT (EV_MAX+1) -
keybit:按键类型(当事件类型为EV_KEY时包括BTN_LEFT,BTN_0,BTN_1,BTN_MIDDLE等)
e、驱动实现——报告事件:
用于报告EV_KEY,EV_REL,EV_ABS事件的函数分别为
-
void input_report_key(struct input_dev *dev,unsigned int code,int value) -
void input_report_rel(struct input_dev *dev,unsigned int code,int value) -
void input_report_abs(struct input_dev *dev,unsigned int code,int value)
f、驱动实现——报告结束:
input_sync()同步用于告诉input core子系统报告结束。
总结而言:
probe为input子系统做了三件事:
(1)首先调用input_allocate_device创建一个input_dev对象;
(2)然后设置设备input_dev的各种属性以告诉input core你将提供哪些事件;
(3)最后调用input_register_device把input_dev注册到input core;
实例分析(按键中断程序):
-
//按键初始化 -
static int __init button_init(void) -
{//申请中断 -
if(request_irq(BUTTON_IRQ,button_interrupt,0,”button”,NUll)) -
return –EBUSY; -
set_bit(EV_KEY,button_dev.evbit); //支持EV_KEY事件 -
set_bit(BTN_0,button_dev.keybit); //支持设备两个键 -
set_bit(BTN_1,button_dev.keybit); // -
input_register_device(&button_dev);//注册input设备 -
} -
/*在按键中断中报告事件*/ -
Static void button_interrupt(int irq,void *dummy,struct pt_regs *fp) -
{ -
input_report_key(&button_dev,BTN_0,inb(BUTTON_PORT0));//读取寄存器BUTTON_PORT0的值 -
input_report_key(&button_dev,BTN_1,inb(BUTTON_PORT1)); -
input_sync(&button_dev); -
}
总结:input子系统仍然是字符设备驱动程序,但是代码量减少很多,input子系统只需要完成两个工作:初始化和事件报告(这里在linux中是通过中断来实现的)。
二、input设备注册分析
1、Input设备注册的接口为:input_register_device()
/kernel/driver/input/input.c
-
int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev) -
{ -
//这个原子变量,代表总共注册的input设备,每注册一个加1,因为是静态变量,所以每次调用都不会清零的 -
static atomic_t input_no = ATOMIC_INIT(0); -
struct input_devres *devres = NULL; -
struct input_handler *handler; -
unsigned int packet_size; -
const char *path; -
int error; -
if (dev->devres_managed) { -
devres = devres_alloc(devm_input_device_unregister, -
sizeof(struct input_devres), GFP_KERNEL); -
if (!devres) -
return -ENOMEM; -
devres->input = dev; -
} -
/* Every input device generates EV_SYN/SYN_REPORT events. */ -
__set_bit(EV_SYN, dev->evbit);//EN_SYN是设备都要支持的事件类型所以要设置 -
/* KEY_RESERVED is not supposed to be transmitted to userspace. */ -
__clear_bit(KEY_RESERVED, dev->keybit); -
/* Make sure that bitmasks not mentioned in dev->evbit are clean. */ -
input_cleanse_bitmasks(dev); -
packet_size = input_estimate_events_per_packet(dev); -
if (dev->hint_events_per_packet < packet_size) -
dev->hint_events_per_packet = packet_size; -
dev->max_vals = max(dev->hint_events_per_packet, packet_size) + 2; -
dev->vals = kcalloc(dev->max_vals, sizeof(*dev->vals), GFP_KERNEL); -
if (!dev->vals) { -
error = -ENOMEM; -
goto err_devres_free; -
} -
/* -
//rep主要是处理重复按键,如果没有定义dev->rep[REP_DELAY]和dev->rep[REP_PERIOD], -
//则将其赋值为默认值。dev->rep[REP_DELAY]是指第一次按下多久算一次,这里是250ms, -
//dev->rep[REP_PERIOD]指如果按键没有被抬起,每33ms算一次。 -
*/ -
init_timer(&dev->timer);//这个内核定时器是为了重复按键而设置的 -
if (!dev->rep[REP_DELAY] && !dev->rep[REP_PERIOD]) { -
dev->timer.data = (long) dev; -
dev->timer.function = input_repeat_key; -
dev->rep[REP_DELAY] = 250; -
dev->rep[REP_PERIOD] = 33; -
//如果没有定义有关重复按键的相关值,就用内核默认的 -
} -
/*如果dev没有定义getkeycode和setkeycode,则赋默认值。他们的作用一个是获得键的扫描码,一个是设置键的扫码*/ -
if (!dev->getkeycode) -
dev->getkeycode = input_default_getkeycode; -
if (!dev->setkeycode) -
dev->setkeycode = input_default_setkeycode; -
//设置input_dev中device的名字,这个名字会在/class/input中出现 -
dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "input%ld",(unsigned long) atomic_inc_return(&input_no)-1); -
//添加input设备,注册到linux设备模型中,生成一系列的sys相关文件,udev会根据dev文件生成设备节点 -
error = device_add(&dev->dev); -
if (error) goto err_free_vals; -
path = kobject_get_path(&dev->dev.kobj, GFP_KERNEL); -
pr_info("%s as %s\n",dev->name ? dev->name : "Unspecified device", path ? -
path : "N/A"); -
kfree(path); -
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex); -
if (error) goto err_device_del; -
/* 如果input device没有定义getkeycode和setkeycode,则将其赋默认值,这两个操作函数就可以用来取键的扫描码和设置键的扫描码,然后调用device_add()将input_dev中封装的device注册到sysfs;*/ -
//将新分配的input设备连接到input_dev_list链表上 -
list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list); -
//遍历input_handler_list链表,配对input_dev和input_handler -
list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node) -
input_attach_handler(dev, handler); -
input_wakeup_procfs_readers();//与proc文件系统有关 -
mutex_unlock(&input_mutex); -
if (dev->devres_managed) { -
dev_dbg(dev->dev.parent, "%s: registering %s with devres.\n", -
__func__, dev_name(&dev->dev)); -
devres_add(dev->dev.parent, devres); -
} -
/* 这里就是重点了,将input device 挂到input_dev_list链表上.然后,对每一个挂在input_handler_list的handler调用input_attach_handler(),在这里的情况有好比设备模型中的device和driver的匹配,所有的input device都挂在input_dev_list链上。所有的handle都挂在input_handler_list上。*/ -
下面介绍详细的匹配过程:。。。。。 -
return 0; -
...... -
}
三、input_device和input_handle匹配过程
1、一般来说input_handler的注册会在input_dev之前注册,常见的input_handler有:mousedev handler(处理来自鼠标类的Input事件),joydev_handler(处理摇杆类事件),kdev_handler(出来来自键盘类事件),evdev_handler(响应绝大部分的事件,默认的input处理事件)。先看input的handler的注册函数,Handler注册的接口如下所示:
-
int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler) -
{ -
struct input_dev *dev; -
int retval; -
retval = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex); -
if (retval) -
return retval; -
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&handler->h_list); -
if (handler->fops != NULL) { -
if (input_table[handler->minor >> 5]) { //添加到全局数组中 -
//为什么会这样呢,因为每个handler都会处理最大32个input_dev,所以要以minor的32为倍数对齐,这个minor是传进来的handler的MINOR_BASE -
//每一个handler都有一个这一个MINOR_BASE,以evdev为例,EVDEV_MINOR_BASE = 64,可以看出系统总共可以注册8个handler -
retval = -EBUSY; -
goto out; -
} -
input_table[handler->minor >> 5] = handler; -
} -
//连接到input_handler_list链表中 -
list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list); -
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node) -
input_attach_handler(dev, handler); //device和handle匹配函数 -
input_wakeup_procfs_readers(); -
out: -
mutex_unlock(&input_mutex); -
return retval; -
}
handler->minor表示对应input设备节点的次设备号,以handler->minor右移五位做为索引值插入到input_table[ ]中.....之后再来分析input_talbe[ ]的作用,然后将handler挂到input_handler_list中,然后将其与挂在input_dev_list中的input device匹配,这个过程和input device的注册有相似的地方,都是注册到各自的链表,然后与另外一条链表的对象相匹配。
2、匹配是在input_attach_handler()中完成的。代码如下:
-
static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler) -
{ -
const struct input_device_id *id; -
int error; -
//这个是主要的配对函数,主要比较id中的各项 -
id = input_match_device(handler, dev); -
if (!id) return -ENODEV; -
//配对成功调用handler的connect函数,这个函数在事件处理器中定义,主要生成一个input_handle结构,并初始化,还生成一个事件处理器相关的设备结构 -
error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id);//调用evdev_connect -
if (error && error != -ENODEV) -
pr_err("failed to attach handler %s to device %s, error: %d\n", -
handler->name, kobject_name(&dev->dev.kobj), error); -
return error; -
}
先来匹配handle->id和dev->id中的数据,如果匹配成功,则调用handler->connect()。每个handler在注册的时候都有自己的id_table,如果设备和input handler能够匹配成功的话,就会调用input handler的connect函数,在Input_match_device中会将input device的id.bus type vendor和id.version首先匹配,然后回去match的evbit等。
3、具体的数据匹配过程是在input_match_device()中完成的。代码如下:
-
static const struct input_device_id *input_match_device(struct input_handler *handler, -
struct input_dev *dev) { -
const struct input_device_id *id; -
//id->driver_info=1,表示可以配对所有 -
for (id = handler->id_table; id->flags || id->driver_info; id++) { -
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_BUS) -
if (id->bustype != dev->id.bustype) -
continue; -
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR) -
if (id->vendor != dev->id.vendor) -
continue; -
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT) -
if (id->product != dev->id.product) -
continue; -
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VERSION) -
if (id->version != dev->id.version) -
continue; -
if (!bitmap_subset(id->evbit, dev->evbit, EV_MAX)) -
continue; -
if (!bitmap_subset(id->keybit, dev->keybit, KEY_MAX)) -
continue; -
if (!bitmap_subset(id->relbit, dev->relbit, REL_MAX)) -
continue; -
if (!bitmap_subset(id->absbit, dev->absbit, ABS_MAX)) -
continue; -
if (!bitmap_subset(id->mscbit, dev->mscbit, MSC_MAX)) -
continue; -
if (!bitmap_subset(id->ledbit, dev->ledbit, LED_MAX)) -
continue; -
if (!bitmap_subset(id->sndbit, dev->sndbit, SND_MAX)) -
continue; -
if (!bitmap_subset(id->ffbit, dev->ffbit, FF_MAX)) -
continue; -
if (!bitmap_subset(id->swbit, dev->swbit, SW_MAX)) -
continue; -
if (!handler->match || handler->match(handler, dev))//没有match函数 -
return id; -
} -
return NULL; -
}
在id->flags中定义了要匹配的项,定义INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_BUS,则是要比较input device和input handler的总线类型。INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR,INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT,INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VERSION分别要求设备厂商。设备号和设备版本。
如果id->flags定义的类型匹配成功,或者是id->flags没有定义,就会进入到MATCH_BIT的匹配项了,从MATCH_BIT宏的定义可以看出,只有当iput device和input handler的id成员在evbit、keybit......swbit项相同才会匹配成功。而且匹配的顺序是从evbit,keybit到swbit.只要有一项不同,就会循环到id中的下一项进行比较。
简而言之,注册input device的过程就是为input device设置默认值,并将其挂以input_dev_list.与挂载在input_handler_list中的handler相匹配,如果匹配成功,就会调用handler的connect函数。
如果handler和device能够匹配上,就会创建一个evdev,就会调用handler的match的回调函数,它里边封装了一个handle,会把input_dev和input_handler关联到一起。
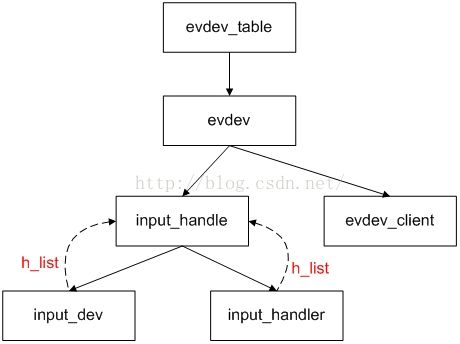
在evdev_connect,它设置设备名,初始化input_handle中各个数据成员(关键是其input_dev和input_handler),然后再调用input_register_handle把evdev中的input_handle添加到input_dev的h_lis链表中,并且把此input_handle添加到input_handler的h_list链表中。从此它们的三角关系建立完成。注:当用户每打开一次它就要创建一个evdev_client,并加入到client_list链表中,当input_dev产生事件时,evdev_event函数将把此input_event放入evdev->client_list链表中的每个evdev_client的buffer中。它们的关系如下图所示:
可以看到evdev是作为一个通用的handler去处理input_device的事件,也就是说一旦有设备注册就会去调用evdev的connect函数。
-
static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, -
const struct input_device_id *id) -
{ -
struct evdev *evdev; -
int minor; -
int dev_no; -
int error; -
minor = input_get_new_minor(EVDEV_MINOR_BASE, EVDEV_MINORS, true); -
if (minor < 0) { -
error = minor; -
pr_err("failed to reserve new minor: %d\n", error); -
return error; -
} -
evdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev), GFP_KERNEL);//分配evdev空间 -
if (!evdev) { -
error = -ENOMEM; -
goto err_free_minor; -
} -
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&evdev->client_list); -
spin_lock_init(&evdev->client_lock); -
mutex_init(&evdev->mutex); -
init_waitqueue_head(&evdev->wait); -
evdev->exist = true; -
dev_no = minor; -
/* Normalize device number if it falls into legacy range */ -
if (dev_no < EVDEV_MINOR_BASE + EVDEV_MINORS) -
dev_no -= EVDEV_MINOR_BASE; -
dev_set_name(&evdev->dev, "event%d", dev_no);//命名/dev/evdev_num -
evdev->handle.dev = input_get_device(dev); -
evdev->handle.name = dev_name(&evdev->dev); -
evdev->handle.handler = handler; -
evdev->handle.private = evdev; -
//初始化evdev->dev结构,所属类型指向input_class -
evdev->dev.devt = MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, minor); -
evdev->dev.class = &input_class; -
evdev->dev.parent = &dev->dev; -
evdev->dev.release = evdev_free; -
device_initialize(&evdev->dev); -
//注册input->handle结构 -
error = input_register_handle(&evdev->handle); -
if (error) -
goto err_free_evdev; -
//注册字符设备,添加文件操作接口file_opertions -
cdev_init(&evdev->cdev, &evdev_fops); -
evdev->cdev.kobj.parent = &evdev->dev.kobj; -
error = cdev_add(&evdev->cdev, evdev->dev.devt, 1); -
if (error) -
goto err_unregister_handle; -
//将evdev->dev注册到sysfs文件系统中 -
error = device_add(&evdev->dev); -
if (error) -
goto err_cleanup_evdev; -
return 0; -
err_cleanup_evdev: -
evdev_cleanup(evdev); -
err_unregister_handle: -
input_unregister_handle(&evdev->handle); -
err_free_evdev: -
put_device(&evdev->dev); -
err_free_minor: -
input_free_minor(minor); -
return error; -
} -
static const struct file_operations evdev_fops = { -
.owner = THIS_MODULE, -
.read = evdev_read, -
.write = evdev_write, -
.poll = evdev_poll, -
.open = evdev_open, -
.release = evdev_release, -
.unlocked_ioctl = evdev_ioctl, -
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT -
.compat_ioctl = evdev_ioctl_compat, -
#endif -
.fasync = evdev_fasync, -
.flush = evdev_flush, -
.llseek = no_llseek, -
};
这里面又有个设备注册的过程,重新创建了一个evdev设备,存在于/dev/input/eventX。这是Android上层需要直接操作的文件节点,就是在这个时候注册的,input_register_handle也是将匹配好的input设备和input handler 分别加到自己的input设备链表和handler链表,Evdev对应的设备节点一般位于/dev/input/event0 ~ /dev/input/event4,理论上可以对应32个设备节点,分别代表被handler匹配的32个input device。 可以用cat /dev/input/event0.然后移动鼠标或者键盘按键就会有数据输出(两者之间只能选一,因为一个设备文件只能关能一个输入设备),还可以往这个文件里写数据,使其产生特定的事件,。 到这里整个kernel层的从设备的初始化到创建,再到与hal层交互的的工作就已经介绍完毕。
以上文字叙述的具体流程用UML图绘制如下图所示: