AndroidR Input子系统(4)扫描/dev/input目录
上一篇文章分析了InputReader线程对Input事件的处理流程,主要分为了三大步骤:
EventHub通过INotify与Epoll监听/dev/input下的事件,在读取到事件之后放入mEventBuffer,此步骤将input_event转换为了RawEvent。- 拿到原始事件
RawEvent之后调用processEventsLocked对事件进行加工,不同事件类型有不同的加工厂(InputMapper),此步骤将RawEvent转换为了NotifyKeyArgs。 - 通过
QueuedListener的flush函数将事件发送到InputDispatcher线程。
其中最复杂的就是步骤1:通过EventHub的getEvents函数获取原始事件,这个函数中留了一个扫描设备节点的函数scanDevicesLocked没有分析,本篇文章的目的就是分析这个函数,从函数名字可以看出,这个函数的目的是扫描设备,触发时机则是首次启动设备时:
EventHub::scanDevicesLocked
//EventHub.cpp
void EventHub::scanDevicesLocked() {
status_t result = scanDirLocked(DEVICE_PATH);
if (result < 0) {
ALOGE("scan dir failed for %s", DEVICE_PATH);
}
if (isV4lScanningEnabled()) {
result = scanVideoDirLocked(VIDEO_DEVICE_PATH);
if (result != OK) {
ALOGE("scan video dir failed for %s", VIDEO_DEVICE_PATH);
}
}
if (mDevices.indexOfKey(ReservedInputDeviceId::VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID) < 0) {
createVirtualKeyboardLocked();
}
}
此函数中调用scanDirLocked扫描具体目录,路径是DEVICE_PATH = “/dev/input”;,我们首先跟进此函数:
scanDirLocked
status_t EventHub::scanDirLocked(const char* dirname) {
//dirname = "/dev/input"
char devname[PATH_MAX];
char* filename;
DIR* dir;
struct dirent* de;
//打开"/dev/input"
dir = opendir(dirname);
if (dir == nullptr) return -1;
strcpy(devname, dirname);
filename = devname + strlen(devname);
*filename++ = '/';
//循环读取"/dev/input"目录下所有节点,
while ((de = readdir(dir))) {
if (de->d_name[0] == '.' &&
(de->d_name[1] == '\0' || (de->d_name[1] == '.' && de->d_name[2] == '\0')))
continue;
//de->d_name是"/dev/input"目录下节点名称,如event0,event1
strcpy(filename, de->d_name);
//devname是filename拼接上dirname,如/dev/input/event0,/dev/input/event1
openDeviceLocked(devname);
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
这个函数很简单,就是调用openDeviceLocked循环打开"/dev/input"目录下所有设备:

EventHub::openDeviceLocked
status_t EventHub::openDeviceLocked(const char* devicePath) {
char buffer[80];
ALOGV("Opening device: %s", devicePath);
//打开/dev/input/eventX...
int fd = open(devicePath, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd < 0) {
ALOGE("could not open %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//创建InputDeviceIdentifier来描述/dev/input/下的设备节点信息
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier;
// 获取设备名称,这里的设备名称就是通过adb shell getevent看到的每个
//设备节点下的name
if (ioctl(fd, EVIOCGNAME(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {
ALOGE("Could not get device name for %s: %s", devicePath, strerror(errno));
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.name = buffer;
}
......
// Get device identifier.
struct input_id inputId;
if (ioctl(fd, EVIOCGID, &inputId)) {
ALOGE("could not get device input id for %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
close(fd);
return -1;
}
//设备节点相关信息:
//bus=0x0019, vendor=0x0000, product=0x0000, version=0x0000
identifier.bus = inputId.bustype;
identifier.product = inputId.product;
identifier.vendor = inputId.vendor;
identifier.version = inputId.version;
// 获取设备节点物理地址
if (ioctl(fd, EVIOCGPHYS(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {
...
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.location = buffer;
}
// 获取设备唯一ID
if (ioctl(fd, EVIOCGUNIQ(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {
...
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.uniqueId = buffer;
}
...
//为设备节点创建Device对象,Device是定义在EventHub的结构体,其中
//定义了很多描述该设备节点详细信息的变量,deviceId以累加的方式计数
int32_t deviceId = mNextDeviceId++;
Device* device = new Device(fd, deviceId, devicePath, identifier);
......
//为设备节点加载配置文件,后面分析
loadConfigurationLocked(device);
......
if (haveKeyboardKeys || haveGamepadButtons) {
//输入设备类型是键盘或者button
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD;
}
if (test_bit(BTN_MOUSE, device->keyBitmask) && test_bit(REL_X, device->relBitmask) &&
test_bit(REL_Y, device->relBitmask)) {
//输入设备类型是鼠标或者轨迹球
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR;
}
//省略一些类型判断...
.......
// 如果输入设备类型是触摸屏(包括单点和多点触控)
if ((device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH)) {
// 加载虚拟键盘表,路径为"/sys/board_properties/virtualkeys."
//拼接上identifier.getCanonicalName()
bool success = loadVirtualKeyMapLocked(device);
if (success) {
//如果存在,则将输入设备类型改为INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD;
}
}
//如果输入设备类型为KEYBOARD或者游戏操纵杆
status_t keyMapStatus = NAME_NOT_FOUND;
if (device->classes & (INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK)) {
//加载键盘表,后面分析
keyMapStatus = loadKeyMapLocked(device);
}
// Configure the keyboard, gamepad or virtual keyboard.
if (device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD) {
...
...
//输入设备具有DPAD按键,DPAD类似游戏手柄上的上下左右按键,
//AKEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER就是DPAD包围的中间按键
if (hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_UP) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER)) {
//源码注释中对INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD的描述:
//输入设备是方向盘(表示键盘,具有DPAD键)
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(GAMEPAD_KEYCODES) / sizeof(GAMEPAD_KEYCODES[0]); i++) {
if (hasKeycodeLocked(device, GAMEPAD_KEYCODES[i])) {
//输入设备是戏键盘
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD;
break;
}
}
}
//省略一些输入设备类型的判断...
......
//调用addDeviceLocked将每一个输入设备添加到mDevices这个map中
addDeviceLocked(device);
return OK;
}
这个函数我们大致看完了,它主要为每个输入设备节点创建了两个结构体来描述,InputDeviceIdentifier和Device,每个输入设备节点信息都被一一解析出来,填充到这两个结构体中,我们来看几个有代表性的信息:
- identifier.name就是如下每个设备节点的对应的name:
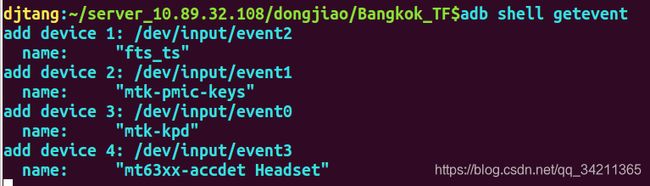
- keyLayoutFile就是”kl“表,就是定义每个输入设备节点key的文件,例如通用表:Generic.kl,路径为’/system/usr/keylayout/Generic.kl’,每一个输入设备节点都对应有一张,定义了按键的名称和扫描码
- device->classes代表的是输入设备的类型,它的值是定义在
EventHub.h中的枚举值:
/*
* Input device classes.
*/
enum {
/* The input device is a keyboard or has buttons. */
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD = 0x00000001,
/* The input device is an alpha-numeric keyboard (not just a dial pad). */
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY = 0x00000002,
/* The input device is a touchscreen or a touchpad (either single-touch or multi-touch). */
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH = 0x00000004,
/* The input device is a cursor device such as a trackball or mouse. */
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR = 0x00000008,
/* The input device is a multi-touch touchscreen. */
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT = 0x00000010,
/* The input device is a directional pad (implies keyboard, has DPAD keys). */
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD = 0x00000020,
....
...
}
我们这里只列出了几个代表性信息,更多信息可以通过adb shell dumpsys input来查看,dump出来的类似如下:
Event Hub State:
BuiltInKeyboardId: -2
Devices:
-1: Virtual
Classes: 0x40000023
Path: <virtual>
Enabled: true
Descriptor: a718a782d34bc767f4689c232d64d527998ea7fd
Location:
ControllerNumber: 0
UniqueId: <virtual>
Identifier: bus=0x0000, vendor=0x0000, product=0x0000, version=0x0000
KeyLayoutFile: /system/usr/keylayout/Generic.kl
KeyCharacterMapFile: /system/usr/keychars/Virtual.kcm
ConfigurationFile:
HaveKeyboardLayoutOverlay: false
1: msm8998-tasha-snd-card Button Jack
Classes: 0x00000001
Path: /dev/input/event6
Enabled: true
Descriptor: 2a5b482f07b4af57a2804c724ce7f8287c9aa808
Location: ALSA
ControllerNumber: 0
UniqueId:
Identifier: bus=0x0000, vendor=0x0000, product=0x0000, version=0x0000
KeyLayoutFile: /system/usr/keylayout/Generic.kl
KeyCharacterMapFile: /system/usr/keychars/Generic.kcm
ConfigurationFile:
HaveKeyboardLayoutOverlay: false
.......
openDeviceLocked中留了两个比较重要的函数没有具体进去分析,loadConfigurationLocked和loadKeyMapLocked,接下来我们就具体来看看这两个函数,
EventHub::loadConfigurationLocked
void EventHub::loadConfigurationLocked(Device* device) {
device->configurationFile = getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByDeviceIdentifier(
device->identifier, INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION);
if (device->configurationFile.empty()) {
ALOGD("No input device configuration file found for device '%s'.",
device->identifier.name.c_str());
} else {
status_t status = PropertyMap::load(String8(device->configurationFile.c_str()),
&device->configuration);
if (status) {
ALOGE("Error loading input device configuration file for device '%s'. "
"Using default configuration.",
device->identifier.name.c_str());
}
}
}
这个函数主要是通过getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByDeviceIdentifier函数加载输入设备节点的配置文件,如果有则通过PropertyMap::load加载到device->configuration,没有就算了,getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByDeviceIdentifier接收两个参数,一个描述当前输入设备节点的InputDeviceIdentifier结构体,另一个是配置文件类型INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION,配置文件类型是定义在InputDevice.h的枚举值,代表了三种后缀文件:
/* Types of input device configuration files. */
enum InputDeviceConfigurationFileType {
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION = 0, /* .idc file */
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_LAYOUT = 1, /* .kl file */
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_CHARACTER_MAP = 2, /* .kcm file */
};
接着看getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByDeviceIdentifier函数:
getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByDeviceIdentifier
std::string getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByDeviceIdentifier(
const InputDeviceIdentifier& deviceIdentifier,
InputDeviceConfigurationFileType type) {
if (deviceIdentifier.vendor !=0 && deviceIdentifier.product != 0) {
if (deviceIdentifier.version != 0) {
// Try vendor product version.
std::string versionPath = getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(
StringPrintf("Vendor_%04x_Product_%04x_Version_%04x",
deviceIdentifier.vendor, deviceIdentifier.product,
deviceIdentifier.version),
type);
...
}
// Try vendor product.
std::string productPath = getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(
StringPrintf("Vendor_%04x_Product_%04x",
deviceIdentifier.vendor, deviceIdentifier.product),
type);
....
}
// Try device name.
return getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(deviceIdentifier.getCanonicalName(), type);
}
这个函数不管怎么样都会调用getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName函数,
getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName
std::string getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(
const std::string& name, InputDeviceConfigurationFileType type) {
// Search system repository.
std::string path;
// 定义了三个路径数组,"/odm", "/vendor","/system"
const char *rootsForPartition[] {"/odm", "/vendor", getenv("ANDROID_ROOT")};
for (size_t i = 0; i < size(rootsForPartition); i++) {
if (rootsForPartition[i] == nullptr) {
continue;
}
path = rootsForPartition[i];
//"/odm", "/vendor","/system"拼接上"/usr/"
path += "/usr/";
//path 继续拼接name和type
appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath(path, name, type);
if (!access(path.c_str(), R_OK)) {
return path;
}
}
path = "";
char *androidData = getenv("ANDROID_DATA");
if (androidData != nullptr) {
path += androidData;
}
path += "/system/devices/";
appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath(path, name, type);
if (!access(path.c_str(), R_OK)) {
return path;
}
// Not found.
return "";
}
此函数作用是拼接一些路径,然后从这些路径中查找对应配置文件,appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath函数定义了拼接规则:
static void appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath(std::string& path,
const std::string& name, InputDeviceConfigurationFileType type) {
path += CONFIGURATION_FILE_DIR[type];
path += name;
path += CONFIGURATION_FILE_EXTENSION[type];
}
在for循环里面path已经拼接为了"/odm/usr/", “/vendor/usr/”,"/system/usr/",这个函数继续拼接,CONFIGURATION_FILE_DIR和CONFIGURATION_FILE_EXTENSION分别定义为如下:
static const char* CONFIGURATION_FILE_DIR[] = {
"idc/",
"keylayout/",
"keychars/",
};
static const char* CONFIGURATION_FILE_EXTENSION[] = {
".idc",
".kl",
".kcm",
};
前面我们已经看了传递的type为INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION = 0,所以这里path拼接的路径就是"/odm/usr/", “/vendor/usr/”,"/system/usr/“加上"idc/”,加上文件名称再加上后缀".idc",所以getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName函数的作用就是首先去寻找"/odm/usr/idc/", “/vendor/usr/idc/”,"/system/usr/idc/“目录下是否存在指定名称的后缀为"idc"的配置文件,如果没找到则去"/data/system/devices/idc"目录下找,这里并不会真正的将这些路径下的文件加载出来,仅仅是判断路径是否可访问,这也是loadConfigurationLocked这个函数的主要作用。
接下来我们回到openDeviceLocked中再看看另一个函数loadKeyMapLocked,这个函数其实和loadConfigurationLocked函数作用类似,loadConfigurationLocked查找的是后缀为".idc"的文件,loadKeyMapLocked查找的则是后缀为".kl"和".kcm"的文件:
EventHub::loadKeyMapLocked
status_t EventHub::loadKeyMapLocked(Device* device) {
return device->keyMap.load(device->identifier, device->configuration);
}
Device的成员变量keyMap指向KeyMap,定义在Keyboard.h中,调用其load函数:
KeyMap::load
//Keyboard.h
status_t KeyMap::load(const InputDeviceIdentifier& deviceIdentifier,
const PropertyMap* deviceConfiguration) {
// Use the configured key layout if available.
if (deviceConfiguration) {
String8 keyLayoutName;
if (deviceConfiguration->tryGetProperty(String8("keyboard.layout"),
keyLayoutName)) {
status_t status = loadKeyLayout(deviceIdentifier, keyLayoutName.c_str());
if (status == NAME_NOT_FOUND) {
ALOGE("Configuration for keyboard device '%s' requested keyboard layout '%s' but "
"it was not found.",
deviceIdentifier.name.c_str(), keyLayoutName.string());
}
}
String8 keyCharacterMapName;
if (deviceConfiguration->tryGetProperty(String8("keyboard.characterMap"),
keyCharacterMapName)) {
status_t status = loadKeyCharacterMap(deviceIdentifier, keyCharacterMapName.c_str());
if (status == NAME_NOT_FOUND) {
ALOGE("Configuration for keyboard device '%s' requested keyboard character "
"map '%s' but it was not found.",
deviceIdentifier.name.c_str(), keyCharacterMapName.string());
}
}
if (isComplete()) {
return OK;
}
}
// Try searching by device identifier.
if (probeKeyMap(deviceIdentifier, "")) {
return OK;
}
// Fall back on the Generic key map.
// TODO Apply some additional heuristics here to figure out what kind of
// generic key map to use (US English, etc.) for typical external keyboards.
if (probeKeyMap(deviceIdentifier, "Generic")) {
return OK;
}
// Try the Virtual key map as a last resort.
if (probeKeyMap(deviceIdentifier, "Virtual")) {
return OK;
}
// Give up!
ALOGE("Could not determine key map for device '%s' and no default key maps were found!",
deviceIdentifier.name.c_str());
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
此函数大致可以分为两部分:
- 查找后缀名为".kl"的按键值映射文件,对应函数
loadKeyLayout。 - 查找后缀名为".kcm"的按键字符映射文件,对应函数
loadKeyCharacterMap。
我们接下来就分别看看loadKeyLayout和loadKeyCharacterMap函数:
KeyMap::loadKeyLayout
status_t KeyMap::loadKeyLayout(const InputDeviceIdentifier& deviceIdentifier,
const std::string& name) {
std::string path(getPath(deviceIdentifier, name,
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_LAYOUT));
if (path.empty()) {
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
status_t status = KeyLayoutMap::load(path, &keyLayoutMap);
if (status) {
return status;
}
keyLayoutFile = path;
return OK;
}
此函数接收的name是从属性值"keyboard.layout"获取的,如果有的话。INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_LAYOUT是定义在InputDevice.h中的三个枚举值之一,我们在前面分析loadConfigurationLocked时见过,只不过那时用的是INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION指代".idc"的文件,这里使用的是指代后缀为".kl"的文件,等下loadKeyCharacterMap函数中就会用最后一个指代".kcm"的文件。
/* Types of input device configuration files. */
enum InputDeviceConfigurationFileType {
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION = 0, /* .idc file */
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_LAYOUT = 1, /* .kl file */
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_CHARACTER_MAP = 2, /* .kcm file */
};
接着来看构造".kl"文件路径的函数getPath:
std::string KeyMap::getPath(const InputDeviceIdentifier& deviceIdentifier,
const std::string& name, InputDeviceConfigurationFileType type) {
return name.empty()
? getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByDeviceIdentifier(deviceIdentifier, type)
: getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(name, type);
}
getPath中调用的两个函数就是我们在loadConfigurationLocked中已经分析过的,最终其实都会调到getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName函数中去,区别就是传递的文件name不同,getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName这个函数我们再来看一下吧:
std::string getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(
const std::string& name, InputDeviceConfigurationFileType type) {
// Search system repository.
std::string path;
// 定义了三个路径数组,"/odm", "/vendor","/system"
const char *rootsForPartition[] {"/odm", "/vendor", getenv("ANDROID_ROOT")};
for (size_t i = 0; i < size(rootsForPartition); i++) {
if (rootsForPartition[i] == nullptr) {
continue;
}
path = rootsForPartition[i];
//"/odm", "/vendor","/system"拼接上"/usr/"
path += "/usr/";
//path 继续拼接name和type
appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath(path, name, type);
if (!access(path.c_str(), R_OK)) {
return path;
}
}
path = "";
char *androidData = getenv("ANDROID_DATA");
if (androidData != nullptr) {
path += androidData;
}
path += "/system/devices/";
appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath(path, name, type);
if (!access(path.c_str(), R_OK)) {
return path;
}
// Not found.
return "";
}
我们前面已经总结过此函数的作用:
getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName函数的作用就是首先去寻找"/odm/usr/idc/", “/vendor/usr/idc/”,"/system/usr/idc/“目录下是否存在指定名称的后缀为".idc"的配置文件,如果没找到则去"/data/system/devices/idc"目录下找,这是针对type为INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION的总结,而对于type为INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_LAYOUT只需要更换"idc"目录为"keylayout"目录,后缀".idc"改为".kl"即可,所以这里的KeyMap::getPath函数的作用总结为首先去寻找"/odm/usr/keylayout/", “/vendor/usr/keylayout/”,"/system/usr/keylayout/“目录下是否存在指定名称的后缀为".kl"的文件,如果没找到则去"/data/system/devices/keylayout"目录下找,这里并不会真正的将这些路径下的文件加载出来,仅仅是判断路径是否可访问。
static const char* CONFIGURATION_FILE_DIR[] = {
"idc/",
"keylayout/",
"keychars/",
};
static const char* CONFIGURATION_FILE_EXTENSION[] = {
".idc",
".kl",
".kcm",
};
而对于loadKeyCharacterMap函数,作用和loadKeyLayout类似,loadKeyCharacterMap中使用的type就是INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_CHARACTER_MAP 了,它也会通过KeyMap::getPath函数去寻找"/odm/usr/keychars/", “/vendor/usr/keychars/”,"/system/usr/keychars/“目录下是否存在指定名称的后缀为".kcm"的文件,如果没找到则去"/data/system/devices/keychars"目录下找。
找到".kl"文件的具体路径之后接下来就会通过KeyLayoutMap::load函数对此"kl"文件进行解析,主要是解析扫描码,这部分比较复杂,我们下一篇文章单独来看"kl"文件的解析。
loadKeyLayout函数的最后就将".kl"文件的路径保存到了keyLayoutFile中,我们可以通过adb shell dumpsys input查看详细信息,如下是我自己手机dump出来的信息:
Event Hub State:
BuiltInKeyboardId: -2
Devices:
-1: Virtual
...
KeyLayoutFile: /system/usr/keylayout/Generic.kl
KeyCharacterMapFile: /system/usr/keychars/Virtual.kcm
ConfigurationFile:
...
1: msm8998-tasha-snd-card Button Jack
...
KeyLayoutFile: /system/usr/keylayout/Generic.kl
KeyCharacterMapFile: /system/usr/keychars/Generic.kcm
ConfigurationFile:
...
2: msm8998-tasha-snd-card Headset Jack
...
KeyLayoutFile:
KeyCharacterMapFile:
ConfigurationFile:
...
3: gf_input
...
KeyLayoutFile: /system/usr/keylayout/gf_input.kl
KeyCharacterMapFile: /system/usr/keychars/Generic.kcm
ConfigurationFile: /system/usr/idc/gf_input.idc
...
4: qpnp_pon
...
KeyLayoutFile: /system/usr/keylayout/Generic.kl
KeyCharacterMapFile: /system/usr/keychars/Generic.kcm
ConfigurationFile:
...
5: hbtp_vm
...
KeyLayoutFile:
KeyCharacterMapFile:
ConfigurationFile:
...
6: gpio-keys
...
KeyLayoutFile: /system/usr/keylayout/Generic.kl
KeyCharacterMapFile: /system/usr/keychars/Generic.kcm
ConfigurationFile:
...
7: synaptics,s3320
...
KeyLayoutFile: /system/usr/keylayout/Generic.kl
KeyCharacterMapFile: /system/usr/keychars/Generic.kcm
ConfigurationFile:
...
可以看到我手机有7个输入设备节点,KeyLayoutFile代表".kl"文件的路径,KeyCharacterMapFile代表".kcm"文件的路径,ConfigurationFile代表".idc"文件的路径。
KeyMap::load函数中我们会发现".kl"文件的名称首先是从"keyboard.layout"属性值中读取的,".kcm"名称首先是从"keyboard.characterMap"属性值中读取的,而对于没有提供"keyboard.layout"和"keyboard.characterMap"的输入设备节点那加载的是那张".kl"表或者".kcm"表呢?
我们接着看KeyMap::load函数后半部分:
status_t KeyMap::load(const InputDeviceIdentifier& deviceIdentifier,
const PropertyMap* deviceConfiguration) {
......
if (probeKeyMap(deviceIdentifier, "")) {
return OK;
}
if (probeKeyMap(deviceIdentifier, "Generic")) {
return OK;
}
if (probeKeyMap(deviceIdentifier, "Virtual")) {
return OK;
}
// Give up!
ALOGE("Could not determine key map for device '%s' and no default key maps were found!",
deviceIdentifier.name.c_str());
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
对于前半部分没有找到"keyboard.layout"和"keyboard.characterMap"属性值对应的".kl"和".kcm"的情况,系统还提供了三次寻找机会:
probeKeyMap
bool KeyMap::probeKeyMap(const InputDeviceIdentifier& deviceIdentifier,
const std::string& keyMapName) {
if (!haveKeyLayout()) {
loadKeyLayout(deviceIdentifier, keyMapName);
}
if (!haveKeyCharacterMap()) {
loadKeyCharacterMap(deviceIdentifier, keyMapName);
}
return isComplete();
}
这函数就很简单了,就是拿着系统写死的".kl"和".kcm"表名称去"/odm/usr/keylayout/", “/vendor/usr/keylayout/”,"/system/usr/keylayout/“查找".kl"表,去"/odm/usr/keychars/", “/vendor/usr/keychars/”,"/system/usr/keychars/“查找".kcm"表,通常默认找到的就是"Generic"对应的通用表,比如我上面dump出我自己手机的大部分输入设备节点使用的都是通用".kl"和".kcm"表。
到此EventHub::openDeviceLocked函数剩下的两个函数loadConfigurationLocked和loadKeyMapLocked就分析完了,
这两个函数的作用都类似,一句话总结:
就是首先去寻找"/odm/usr/*/", “/vendor/usr/*/”,"/system/usr/*/“目录下是否存在指定名称的后缀为".idc"或者".kl"或者".kcm"的文件,如果没找到则去"/data/system/devices/*“目录下找,这里并不会真正的将这些路径下的文件加载出来,仅仅是判断路径是否可访问。对于”.kl"或者".kcm"的文件,系统还提供了默认的通用表"Generic"。
这里我们还剩了一个坑,就是KeyLayoutMap::load函数,这个函数会解析查找到的".kl"或者".kcm"表,后面单独分析。
接着我们需要回到最开始的EventHub的scanDevicesLocked函数:
void EventHub::scanDevicesLocked() {
status_t result = scanDirLocked(DEVICE_PATH);
if (result < 0) {
ALOGE("scan dir failed for %s", DEVICE_PATH);
}
if (isV4lScanningEnabled()) {
result = scanVideoDirLocked(VIDEO_DEVICE_PATH);
if (result != OK) {
ALOGE("scan video dir failed for %s", VIDEO_DEVICE_PATH);
}
}
if (mDevices.indexOfKey(ReservedInputDeviceId::VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID) < 0) {
createVirtualKeyboardLocked();
}
}
scanDirLocked是已经分析完了的,isV4lScanningEnabled由属性值"ro.input.video_enabled"决定,默认值为true,scanVideoDirLocked会扫描"/dev"目录,这个函数和scanDirLocked类似的,都是扫描对应目录,不需要再去细看,最后从mDevices查找设备ID为ReservedInputDeviceId::VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID的Devices,VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID定义在InputDevice.h中,值为-1,我们在分析openDeviceLocked函数时知道,为每一个输入设备节点创建Devices时,设备ID是从mNextDeviceId++的,mNextDeviceId初始值为1,即设备ID从1开始,所以mDevices此时是没有设备ID为-1的Devices的,所以需要调用createVirtualKeyboardLocked函数创建设备ID为-1的虚拟设备:
EventHub::createVirtualKeyboardLocked
void EventHub::createVirtualKeyboardLocked() {
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier;
identifier.name = "Virtual";
identifier.uniqueId = "" ;
assignDescriptorLocked(identifier);
Device* device =
new Device(-1, ReservedInputDeviceId::VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID, "" , identifier);
device->classes = INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY |
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL;
loadKeyMapLocked(device);
addDeviceLocked(device);
}
这个函数也比较简单,都是我们已经分析过的,这里为设备ID为-1创建Device,然后加载".kl"和".kcm"表,最后添加到mDevices中,所以我们前面dump出的自己手机的input信息会有一个设备ID为-1的虚拟设备:
Event Hub State:
BuiltInKeyboardId: -2
Devices:
-1: Virtual
...
KeyLayoutFile: /system/usr/keylayout/Generic.kl
KeyCharacterMapFile: /system/usr/keychars/Virtual.kcm
ConfigurationFile:
...
...
到此我们就分析完了扫描/dev/input目录的全部过程,整个过程就是为每一个输入设备节点创建InputDeviceIdentifier和Device结构体,并将输入设备节点的信息填充进去,其中比较重要的就是获取".kl"和".kcm"表并解析。
下一篇文章我们就来分析".kl"和".kcm"表的具体解析规则。