回调函数(callback Function)
一、概念介绍
从上面的代码,可知道, JndiTemplate 持有了 JNDI 的上下问对象,默认提供了一些访问jndi的方法,但如果用户想使用jndi的上下文做些定制化的事情就需要通过“回调接口”的回调机制来实现,因为用户没有对jndi上下文的引用,JndiTemplate 也没有对外开放,所以可以通过回调方式来使用jndi上下,这样就可以在不改变JndiTemplate代码的情况下,实现扩展,JndiTemplate持有了jndi上下文的引用可以通过回调接口,在用户调用execue时候,获取到用户的实现的回调接口,调用接口定义的方法,这样就进入了用户的方法栈(用户调用JndiTemplate,JndiTemplate又反过来调用用户定义的逻辑,这就是回调机制),用户的逻辑返回的结果被JndiTemplate拿到后再转给用户,这样用户就能使用到 jndi的上下做些自己的事情了,当然 JndiTemplate 既然是工具类,自然已经实现了很多方便方法,这样方法也都是通过回调实现的,一饱眼福吧:
回调函数(callback Function),顾名思义,就是为被调用方所反过来调用的函数,比如说客户程序Client调用了服务端Server中的某个函数serverMethod,在执行过程中Server又反过来调用Client中的某个函数clientMethod(出于扩展机制的考虑),那么这个被Server调用的函数clientMethod就叫做回调函数,那么既然是为被调用方反过来调用的方法那么被调用方法如何得知这个方法的定义呢 ?那么就需要调用方和调用方就需要事先有个约定,这个约定就是“回调接口”,双方安装回调接口规范编写程序,就可以是实现回调逻辑,
回调的作用:通常是Server端不知道如何处理或处理逻辑依赖Client端逻辑,就通过回调的方式进入到Client的方法栈,回调也可以通常也用来实现Server端的扩展机制,如Server端开发回调接口,不同的回调接口实现以完成不同的业务需求,在spring框架中使用了很多的回调设计,如spring的hibernate集成(在hibernate中执行以获取响应结果),如spring提供的jndi工具 JndiTemplate , 也是利用回调实现,源码片段如下:
/**
* Callback interface to be implemented by classes that need to perform an
* operation (such as a lookup) in a JNDI context. This callback approach
* is valuable in simplifying error handling, which is performed by the
* JndiTemplate class. This is a similar to JdbcTemplate's approach.
*/
public interface JndiCallback {
/**
* Do something with the given JNDI context.
* Implementations don't need to worry about error handling
* or cleanup, as the JndiTemplate class will handle this.
*/
Object doInContext(Context ctx) throws NamingException;
}
/**
* Execute the given JNDI context callback implementation.
* org.springframework.jndi.JndiTemplate 的源代码
*/
public Object execute(JndiCallback contextCallback) throws NamingException {
Context ctx = createInitialContext();
try {
return contextCallback.doInContext(ctx);
}
finally {
try {
ctx.close();
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
logger.warn("Could not close JNDI InitialContext", ex);
}
}
}从上面的代码,可知道, JndiTemplate 持有了 JNDI 的上下问对象,默认提供了一些访问jndi的方法,但如果用户想使用jndi的上下文做些定制化的事情就需要通过“回调接口”的回调机制来实现,因为用户没有对jndi上下文的引用,JndiTemplate 也没有对外开放,所以可以通过回调方式来使用jndi上下,这样就可以在不改变JndiTemplate代码的情况下,实现扩展,JndiTemplate持有了jndi上下文的引用可以通过回调接口,在用户调用execue时候,获取到用户的实现的回调接口,调用接口定义的方法,这样就进入了用户的方法栈(用户调用JndiTemplate,JndiTemplate又反过来调用用户定义的逻辑,这就是回调机制),用户的逻辑返回的结果被JndiTemplate拿到后再转给用户,这样用户就能使用到 jndi的上下做些自己的事情了,当然 JndiTemplate 既然是工具类,自然已经实现了很多方便方法,这样方法也都是通过回调实现的,一饱眼福吧:
public Object lookup(final String name) throws NamingException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking up JNDI object with name [" + name + "]");
}
return execute(new JndiCallback() {
public Object doInContext(Context ctx) throws NamingException {
Object located = ctx.lookup(name);
if (located == null) {
throw new NameNotFoundException(
"JNDI object with [" + name + "] not found: JNDI implementation returned null");
}
return located;
}
});
}public void bind(final String name, final Object object) throws NamingException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Binding JNDI object with name [" + name + "]");
}
execute(new JndiCallback() {
public Object doInContext(Context ctx) throws NamingException {
ctx.bind(name, object);
return null;
}
});
}public void rebind(final String name, final Object object) throws NamingException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Rebinding JNDI object with name [" + name + "]");
}
execute(new JndiCallback() {
public Object doInContext(Context ctx) throws NamingException {
ctx.rebind(name, object);
return null;
}
});
}public void unbind(final String name) throws NamingException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unbinding JNDI object with name [" + name + "]");
}
execute(new JndiCallback() {
public Object doInContext(Context ctx) throws NamingException {
ctx.unbind(name);
return null;
}
});
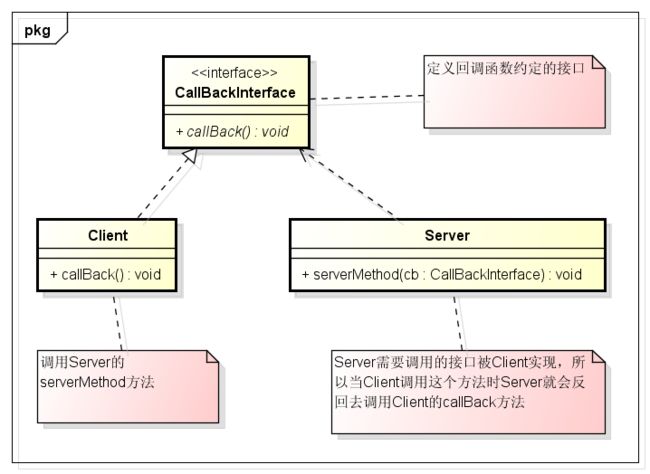
}二、原理图
三、示例代码
class AppContext {
String data;
public AppContext(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
Object process() {
return "process:" + data;
}
}
interface CallBackInterface {
Object doInContext(AppContext context);
}
class ServerPoint {
AppContext appContext = new AppContext("ServerData");
Object execute(CallBackInterface callBack) {
return callBack.doInContext(appContext);
}
}
public class CallbackTest {
static ServerPoint serverPoint = new ServerPoint();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object executeData = serverPoint.execute(new CallBackInterface() {
public Object doInContext(AppContext context) {
String process = (String) context.process();
System.out.println("客户端使用使用服务器资源AppContext处理数据");
return process;
}
});
System.out.println(executeData);
}
}
结果:
客户端使用使用服务器资源AppContext处理数据
process:ServerData