基于mtd的nandflash的擦写nanderase与nandwrite
对于nand平台更新,我们有两个常用工具可用,一个是nanderase擦除的命令,一个是nandwrite写数据的命令,我们先了解一下nand的基本特性。
Nand flash只有一种操作,就是把1写为0,不能把0写为1,所以我们在写入之前,先要把所有的位置1,也就是擦除动作。Nand擦除是以block块大小为最小单位,写入是以page页为最小单位。
由于工作需求,需要封装类似nanderase与nandwrite的接口,用来更新某个分区的镜像,所以研究了下,nanderase与nandwrite的主要流程。
nanderase:
1)打开mtd设备
2)判断mtd设备是字符设备
3)获取meminfo(ioctl)
4)根据meminfo.erasersize循环擦除指定的长度(擦除前先判断是否坏块,坏块跳过)

代码实现:
int nand_erase(const char *devicename, const int offset, const int len) {
int fd;
int ret = 0;
struct stat st;
mtd_info_t meminfo;
erase_info_t erase;
//open mtd device
fd = open(devicename, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("open %s failed!\n", devicename);
return -1;
}
//check is a char device
ret = fstat(fd, &st);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("fstat %s failed!\n", devicename);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
if (!S_ISCHR(st.st_mode)) {
printf("%s: not a char device", devicename);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
//get meminfo
ret = ioctl(fd, MEMGETINFO, &meminfo);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("get MEMGETINFO failed!\n");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
erase.length = meminfo.erasesize;
for (erase.start = offset; erase.start < offset + len; erase.start += meminfo.erasesize) {
loff_t bpos = erase.start;
//check bad block
ret = ioctl(fd, MEMGETBADBLOCK, &bpos);
if (ret > 0) {
printf("mtd: not erasing bad block at 0x%08llx\n", bpos);
continue; // Don't try to erase known factory-bad blocks.
}
if (ret < 0) {
printf("MEMGETBADBLOCK error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
//erase
if (ioctl(fd, MEMERASE, &erase) < 0) {
printf("mtd: erase failure at 0x%08llx\n", bpos);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
nandwrite:
1)打开mtd设备,打开写入file文件
2)获取meminfo(ioctl)
3)如果有offset,判断offset是否是与meminfo.writesize字节对齐
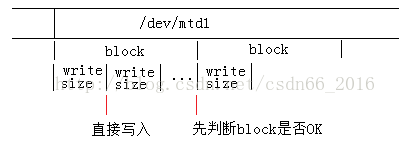
4)如果offset不是一个block的开头,判断offset所在的这个block是否是OK的,如果不是,则跳转到下一个可用的block。
5)循环从offset开始,每次从file中读取meminfo.writesize大小的数据,写入到mtd中,如果offset为block的开始位置,则先判断此block是否为OK,如果不OK,则跳转到下一个OK的block,如果offset不为block开始位置,则直接写入即可
代码实现:
static unsigned next_good_eraseblock(int fd, struct mtd_info_user *meminfo,
unsigned block_offset)
{
while (1) {
loff_t offs;
if (block_offset >= meminfo->size) {
printf("not enough space in MTD device");
return block_offset; /* let the caller exit */
}
offs = block_offset;
if (ioctl(fd, MEMGETBADBLOCK, &offs) == 0)
return block_offset;
/* ioctl returned 1 => "bad block" */
printf("Skipping bad block at 0x%08x\n", block_offset);
block_offset += meminfo->erasesize;
}
}
int nand_write(const char *device_name, const char *file_name, const int mtd_offset) {
mtd_info_t meminfo;
unsigned int blockstart;
unsigned int limit = 0;
int cnt = -1;
int size = 0;
int ret = 0;
int offset = mtd_offset;
//fopen input file
FILE *pf = fopen(file_name, "r");
if (pf==NULL) {
printf("fopen %s failed!\n", file_name);
return -1;
}
//open mtd device
int fd = open(device_name, O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("open %s failed!\n", device_name);
fclose(pf);
return -1;
}
//get meminfo
ret = ioctl(fd, MEMGETINFO, &meminfo);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("get MEMGETINFO failed!\n");
fclose(pf);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
limit = meminfo.size;
//check offset page aligned
if (offset & (meminfo.writesize - 1)) {
printf("start address is not page aligned");
fclose(pf);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
//malloc buffer for read
char *tmp = (char *)malloc(meminfo.writesize);
if (tmp == NULL) {
printf("malloc %d size buffer failed!\n", meminfo.writesize);
fclose(pf);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
//if offset in a bad block, get next good block
blockstart = offset & ~(meminfo.erasesize - 1);
if (offset != blockstart) {
unsigned int tmp;
tmp = next_good_eraseblock(fd, &meminfo, blockstart);
if (tmp != blockstart) {
offset = tmp;
}
}
while(offset < limit) {
blockstart = offset & ~(meminfo.erasesize - 1);
if (blockstart == offset) {
offset = next_good_eraseblock(fd, &meminfo, blockstart);
printf("Writing at 0x%08x\n", offset);
if (offset >= limit) {
printf("offset(%d) over limit(%d)\n", offset, limit);
fclose(pf);
close(fd);
free(tmp);
return -1;
}
}
lseek(fd, offset, SEEK_SET);
cnt = fread(tmp, 1, meminfo.writesize, pf);
if (cnt == 0) {
printf("write ok!\n");
break;
}
if (cnt < meminfo.writesize) {
/* zero pad to end of write block */
memset(tmp + cnt, 0, meminfo.writesize - cnt);
}
size = write(fd, tmp, meminfo.writesize);
if (size != meminfo.writesize) {
printf("write err, need :%d, real :%d\n", meminfo.writesize, size );
fclose(pf);
close(fd);
free(tmp);
return -1;
}
offset += meminfo.writesize;
if (cnt < meminfo.writesize) {
printf("write ok!\n");
break;
}
}
//free buf
free(tmp);
fclose(pf);
close(fd);
return 0;//test
}