【笔记】制作自己的MSCOCO数据集(VOC2COCO)
推荐先从这里学习从零开始制作自己的Pascal VOC数据集。
文章目录
- 1 MSCOCO数据集简介
- 1.1 概要
- 1.2 数据集格式
- 公共格式
- 特有格式-目标检测类
- 2 动手制作
- 2.1 数据集框架准备
- 2.1 制作xml格式的annotation文件
- 2.2 xml2coco
- 3 测试
- 3.1 安装cocoapi
- 3.2 实测
- 【完】
1 MSCOCO数据集简介
1.1 概要
现今最流行的公开数据集是啥?COCO,Common Objects in Context。现如今最先进的视觉检测模型都是在COCO上评测了。
相较于上一代的Pascal VOC,COCO拥有更多的图片–330K,更多的标注–1.5 million,更多的物体类别–80类,更复杂的场景,更多的小的物体,总之就是更大更复杂更具挑战性,也更具说服力。想了解更多,移步COCO官网
1.2 数据集格式
COCO一共有5种不同任务分类,分别是目标检测、关键点检测、语义分割、场景分割和图像描述。COCO数据集的标注文件以JSON格式保存,官方的注释文件有仨 captions_type.json instances_type.json person_keypoints_type.json,其中的type是 train/val/test+year,比如captions_train2017.json instances_train2017.json person_keypoints_train2017.json,其中目标检测的注释放在instances_xxx.json里。
公共格式
{
//公共格式,三个json文件开头都是他们
"info" : info, //数据集的信息,
"images" : [image],//数据集中所有图片的信息,详细见下方
"annotations" : [annotation], //数据集中注释的信息
"licenses" : [license],//这个是证书信息,跑模型时不用理会
}
info{
"year" : int, //数据集年份 2014,2015,2017。
"version" : str, //剩下信息不必理会
"description" : str,
"contributor" : str,
"url" : str,
"date_created" : datetime,
}
image{//对每一张图片
"id" : int, //可唯一标识图片的 图片id
"width" : int,//图片的 宽、高,,,,没有提到图片的depth
"height" : int,
"file_name" : str, //文件名称 ,"xxx.jpg"
"license" : int,
"flickr_url" : str,
"coco_url" : str,
"date_captured" : datetime,
}
license{
"id" : int,
"name" : str,
"url" : str,
}
特有格式-目标检测类
//注意:COCO中的每个annotation是独立的,有自己的id。比如说目标检测,一张图片中的每个object是单独存在的,都有自己的一个annotation实例。
annotation{
"id" : int, //object id
"image_id" : int,//这个object在哪个图片中
"category_id" : int, //object的类别
"segmentation" : RLE or [polygon],//分割用,
"area" : float,
"bbox" : [x,y,width,height],//划重点,bbox,以左上角为原点,是实际坐标!!
"iscrowd" : 0 or 1,
}
categories[//这个是所有类别的一个总的集合,python.list,比如COCO一共有80类,那它的大小就是80。其中的每一个类别又有如下的结构
{
"id" : int,//类别id
"name" : str, //类名
"supercategory" : str,//父 类名,通常不用管
}
]
2 动手制作
仅以目标检测为例!!!
自己制作时只需要image,annotation,categories就足够了。
2.1 数据集框架准备
找个位置,新建文件夹coco,进入coco,新建两个文件夹images,annotations,最终形成的目录结构应该是
- coco/
- images/
- annotations/
2.1 制作xml格式的annotation文件
参考【笔记】从零开始制作自己的Pascal VOC数据集的2.1小节。
2.2 xml2coco
把刚才用到的图片直接拷贝到 coco/images。
运行如下脚本:
注意:脚本文件来自脚本地址,只做了一点修改使得结果更符合强迫症患者
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2019/7/8 16:10
# @Author : lazerliu
# @File : voc2coco.py
# just for object detection
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import json
coco = dict()
coco['images'] = []
coco['type'] = 'instances'
coco['annotations'] = []
coco['categories'] = []
category_set = dict()
image_set = set()
category_item_id = 0
image_id = 0
annotation_id = 0
def addCatItem(name):
global category_item_id
category_item = dict()
category_item['supercategory'] = 'none'
category_item_id += 1
category_item['id'] = category_item_id
category_item['name'] = name
coco['categories'].append(category_item)
category_set[name] = category_item_id
return category_item_id
def addImgItem(file_name, size):
global image_id
if file_name is None:
raise Exception('Could not find filename tag in xml file.')
if size['width'] is None:
raise Exception('Could not find width tag in xml file.')
if size['height'] is None:
raise Exception('Could not find height tag in xml file.')
img_id = "%04d" % image_id
image_id += 1
image_item = dict()
image_item['id'] = int(img_id)
# image_item['id'] = image_id
image_item['file_name'] = file_name
image_item['width'] = size['width']
image_item['height'] = size['height']
coco['images'].append(image_item)
image_set.add(file_name)
return image_id
def addAnnoItem(object_name, image_id, category_id, bbox):
global annotation_id
annotation_item = dict()
annotation_item['segmentation'] = []
seg = []
# bbox[] is x,y,w,h
# left_top
seg.append(bbox[0])
seg.append(bbox[1])
# left_bottom
seg.append(bbox[0])
seg.append(bbox[1] + bbox[3])
# right_bottom
seg.append(bbox[0] + bbox[2])
seg.append(bbox[1] + bbox[3])
# right_top
seg.append(bbox[0] + bbox[2])
seg.append(bbox[1])
annotation_item['segmentation'].append(seg)
annotation_item['area'] = bbox[2] * bbox[3]
annotation_item['iscrowd'] = 0
annotation_item['ignore'] = 0
annotation_item['image_id'] = image_id
annotation_item['bbox'] = bbox
annotation_item['category_id'] = category_id
annotation_id += 1
annotation_item['id'] = annotation_id
coco['annotations'].append(annotation_item)
def parseXmlFiles(xml_path):
for f in os.listdir(xml_path):
if not f.endswith('.xml'):
continue
bndbox = dict()
size = dict()
current_image_id = None
current_category_id = None
file_name = None
size['width'] = None
size['height'] = None
size['depth'] = None
xml_file = os.path.join(xml_path, f)
# print(xml_file)
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
if root.tag != 'annotation':
raise Exception('pascal voc xml root element should be annotation, rather than {}'.format(root.tag))
# elem is , , ,
for elem in root:
current_parent = elem.tag
current_sub = None
object_name = None
if elem.tag == 'folder':
continue
if elem.tag == 'filename':
file_name = elem.text
if file_name in category_set:
raise Exception('file_name duplicated')
# add img item only after parse tag
elif current_image_id is None and file_name is not None and size['width'] is not None:
if file_name not in image_set:
current_image_id = addImgItem(file_name, size)
# print('add image with {} and {}'.format(file_name, size))
else:
raise Exception('duplicated image: {}'.format(file_name))
# subelem is , , , ,
for subelem in elem:
bndbox['xmin'] = None
bndbox['xmax'] = None
bndbox['ymin'] = None
bndbox['ymax'] = None
current_sub = subelem.tag
if current_parent == 'object' and subelem.tag == 'name':
object_name = subelem.text
if object_name not in category_set:
current_category_id = addCatItem(object_name)
else:
current_category_id = category_set[object_name]
elif current_parent == 'size':
if size[subelem.tag] is not None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at size tag.')
size[subelem.tag] = int(subelem.text)
# option is , , , , when subelem is
for option in subelem:
if current_sub == 'bndbox':
if bndbox[option.tag] is not None:
raise Exception('xml structure corrupted at bndbox tag.')
bndbox[option.tag] = int(option.text)
# only after parse the
if bndbox['xmin'] is not None:
if object_name is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
if current_image_id is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
if current_category_id is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
bbox = []
# x
bbox.append(bndbox['xmin'])
# y
bbox.append(bndbox['ymin'])
# w
bbox.append(bndbox['xmax'] - bndbox['xmin'])
# h
bbox.append(bndbox['ymax'] - bndbox['ymin'])
# print('add annotation with {},{},{},{}'.format(object_name, current_image_id, current_category_id,
# bbox))
addAnnoItem(object_name, current_image_id, current_category_id, bbox)
if __name__ == '__main__':
#修改这里的两个地址,一个是xml文件的父目录;一个是生成的json文件的绝对路径
xml_path = 'xxx/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations/'
json_file = 'xxx/coco/annotations/instances.json'
parseXmlFiles(xml_path)
json.dump(coco, open(json_file, 'w'))
至此,自制的coco数据集完成。
3 测试
测试制作的coco数据集能否被cocoapi识别。
3.1 安装cocoapi
git clone https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi.git
cd cocoapi/PythonAPI
make
3.2 实测
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2019/7/8 14:32
# @Author : lazerliu
# @File : CocoForm_Learn.py
import sys
import json
sys.path.append("/xxx/cocoapi/PythonAPI")#把cocoapi的绝对路径加上
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
ann_file = "xxx/coco/annotations/instances.json"# json文件的绝对路径
coco = COCO(annotation_file=ann_file)
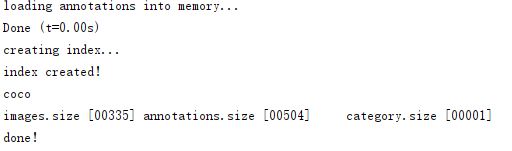
print("coco\nimages.size [%05d]\tannotations.size [%05d]\t category.size [%05d]\ndone!"
%(len(coco.imgs),len(coco.anns),len(coco.cats)))