Dlib模型人脸特征检测原理及demo
目录
- 序
- Dlib模型
- Dlib人脸特征检测原理
- (1)提取特征点
- (2)获取特征数据集写入csv
- (3)计算特征数据集的欧氏距离作对比
- 正文
- 一、构建自己的数据集
- 二、特征检测
- 三、人脸识别
- 四、扩展
序
Dlib模型
- 安装dlib
下载地址:https://pypi.org/simple/dlib/
安装教程参考前一文:基于dlib库人脸特征提取【构建自己的人脸识别数据集】
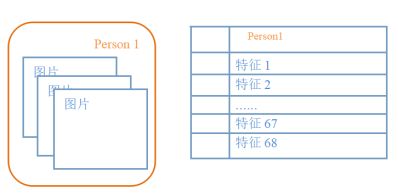
dlib人脸检测模块有5个特征点以及68个特征点的数据集
Dlib人脸特征检测原理
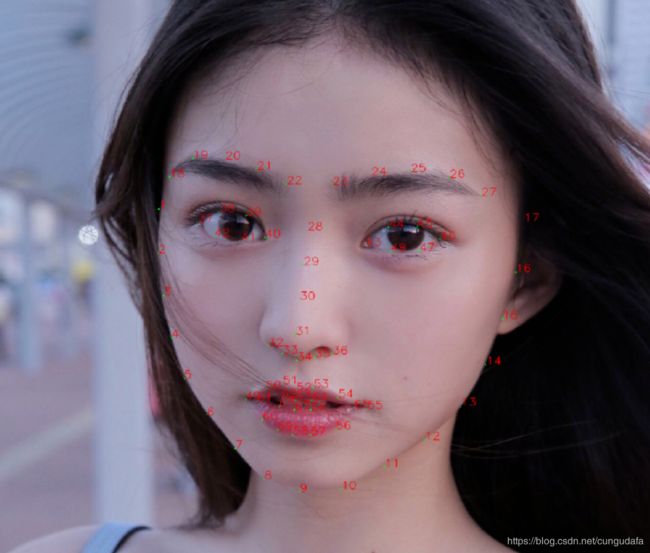
(1)提取特征点
参考链接:python+OpenCv+dlib实现人脸68个关键点检测并标注
(2)获取特征数据集写入csv
根据数据集,模型----训练----》68个特征数据
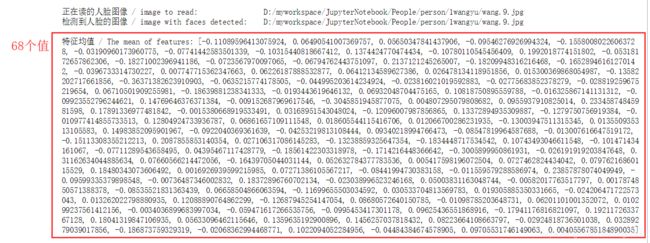
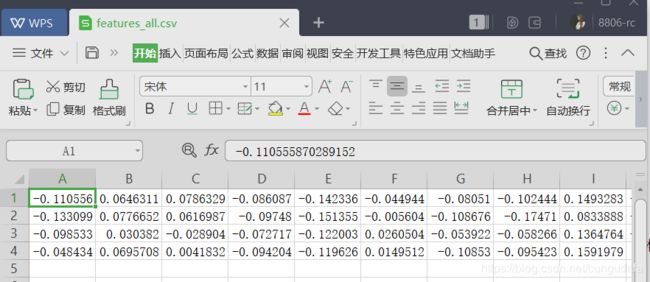
写入csv:
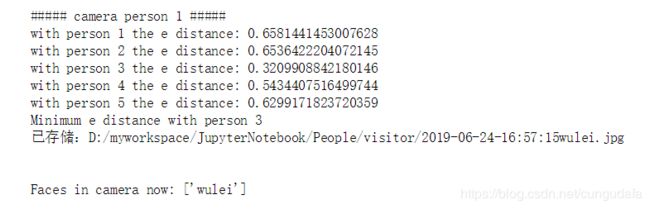
(3)计算特征数据集的欧氏距离作对比
图中为我的运行效果:选取最接近(欧氏距离最小)的值,标注为person 1

图像处理部分运用了python3.7和opencv3.4.1,需要具备这方面的知识。
正文
环境:python3.7+anaconda3+jupyternotebook
一、构建自己的数据集
1录入数据集源码-》
参考我前一篇文章:基于dlib库人脸特征提取【构建自己的人脸识别数据集】
二、特征检测
2获取特征点并保存数据源码:get_features.py
# 从人脸图像文件中提取人脸特征存入 CSV
# Features extraction from images and save into features_all.csv
# return_128d_features() 获取某张图像的128D特征
# compute_the_mean() 计算128D特征均值
from cv2 import cv2 as cv2
import os
import dlib
from skimage import io
import csv
import numpy as np
# 要读取人脸图像文件的路径
path_images_from_camera = "D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/person/"
# Dlib 正向人脸检测器
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# Dlib 人脸预测器
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor("D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/model/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat")
# Dlib 人脸识别模型
# Face recognition model, the object maps human faces into 128D vectors
face_rec = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1("D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/model/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat")
# 返回单张图像的 128D 特征
def return_128d_features(path_img):
img_rd = io.imread(path_img)
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rd, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
faces = detector(img_gray, 1)
print("%-40s %-20s" % ("检测到人脸的图像 / image with faces detected:", path_img), '\n')
# 因为有可能截下来的人脸再去检测,检测不出来人脸了
# 所以要确保是 检测到人脸的人脸图像 拿去算特征
if len(faces) != 0:
shape = predictor(img_gray, faces[0])
face_descriptor = face_rec.compute_face_descriptor(img_gray, shape)
else:
face_descriptor = 0
print("no face")
return face_descriptor
# 将文件夹中照片特征提取出来, 写入 CSV
def return_features_mean_personX(path_faces_personX):
features_list_personX = []
photos_list = os.listdir(path_faces_personX)
if photos_list:
for i in range(len(photos_list)):
# 调用return_128d_features()得到128d特征
print("%-40s %-20s" % ("正在读的人脸图像 / image to read:", path_faces_personX + "/" + photos_list[i]))
features_128d = return_128d_features(path_faces_personX + "/" + photos_list[i])
# print(features_128d)
# 遇到没有检测出人脸的图片跳过
if features_128d == 0:
i += 1
else:
features_list_personX.append(features_128d)
else:
print("文件夹内图像文件为空 / Warning: No images in " + path_faces_personX + '/', '\n')
# 计算 128D 特征的均值
# N x 128D -> 1 x 128D
if features_list_personX:
features_mean_personX = np.array(features_list_personX).mean(axis=0)
else:
features_mean_personX = '0'
return features_mean_personX
# 读取某人所有的人脸图像的数据
people = os.listdir(path_images_from_camera)
people.sort()
with open("D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/feature/features2_all.csv", "w", newline="") as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
for person in people:
print("##### " + person + " #####")
# Get the mean/average features of face/personX, it will be a list with a length of 128D
features_mean_personX = return_features_mean_personX(path_images_from_camera + person)
writer.writerow(features_mean_personX)
print("特征均值 / The mean of features:", list(features_mean_personX))
print('\n')
print("所有录入人脸数据存入 / Save all the features of faces registered into: D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/feature/features_all2.csv")
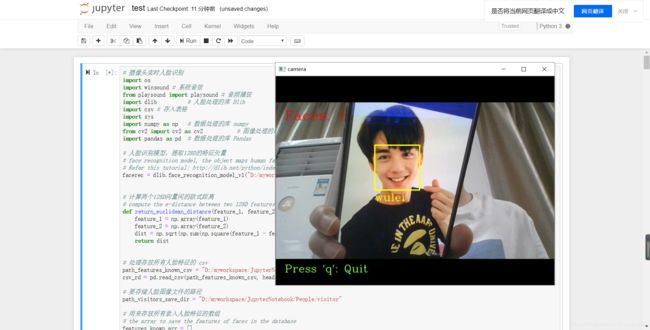
三、人脸识别
# 摄像头实时人脸识别
import os
import winsound # 系统音效
from playsound import playsound # 音频播放
import dlib # 人脸处理的库 Dlib
import csv # 存入表格
import time
import sys
import numpy as np # 数据处理的库 numpy
from cv2 import cv2 as cv2 # 图像处理的库 OpenCv
import pandas as pd # 数据处理的库 Pandas
# 人脸识别模型,提取128D的特征矢量
# face recognition model, the object maps human faces into 128D vectors
# Refer this tutorial: http://dlib.net/python/index.html#dlib.face_recognition_model_v1
facerec = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1("D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/model/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat")
# 计算两个128D向量间的欧式距离
# compute the e-distance between two 128D features
def return_euclidean_distance(feature_1, feature_2):
feature_1 = np.array(feature_1)
feature_2 = np.array(feature_2)
dist = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(feature_1 - feature_2)))
return dist
# 处理存放所有人脸特征的 csv
path_features_known_csv = "D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/feature/features2_all.csv"
csv_rd = pd.read_csv(path_features_known_csv, header=None)
# 用来存放所有录入人脸特征的数组
# the array to save the features of faces in the database
features_known_arr = []
# 读取已知人脸数据
# print known faces
for i in range(csv_rd.shape[0]):
features_someone_arr = []
for j in range(0, len(csv_rd.ix[i, :])):
features_someone_arr.append(csv_rd.ix[i, :][j])
features_known_arr.append(features_someone_arr)
print("Faces in Database:", len(features_known_arr))
# Dlib 检测器和预测器
# The detector and predictor will be used
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/model/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
# 创建 cv2 摄像头对象
# cv2.VideoCapture(0) to use the default camera of PC,
# and you can use local video name by use cv2.VideoCapture(filename)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# cap.set(propId, value)
# 设置视频参数,propId 设置的视频参数,value 设置的参数值
cap.set(3, 480)
# cap.isOpened() 返回 true/false 检查初始化是否成功
# when the camera is open
while cap.isOpened():
flag, img_rd = cap.read()
kk = cv2.waitKey(1)
# 取灰度
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rd, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# 人脸数 faces
faces = detector(img_gray, 0)
# 待会要写的字体 font to write later
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX
# 存储当前摄像头中捕获到的所有人脸的坐标/名字
# the list to save the positions and names of current faces captured
pos_namelist = []
name_namelist = []
# 按下 q 键退出
# press 'q' to exit
if kk == ord('q'):
break
else:
# 检测到人脸 when face detected
if len(faces) != 0:
# 获取当前捕获到的图像的所有人脸的特征,存储到 features_cap_arr
# get the features captured and save into features_cap_arr
features_cap_arr = []
for i in range(len(faces)):
shape = predictor(img_rd, faces[i])
features_cap_arr.append(facerec.compute_face_descriptor(img_rd, shape))
# 遍历捕获到的图像中所有的人脸
# traversal all the faces in the database
for k in range(len(faces)):
print("##### camera person", k+1, "#####")
# 让人名跟随在矩形框的下方
# 确定人名的位置坐标
# 先默认所有人不认识,是 unknown
# set the default names of faces with "unknown"
name_namelist.append("unknown")
# 每个捕获人脸的名字坐标 the positions of faces captured
pos_namelist.append(tuple([faces[k].left(), int(faces[k].bottom() + (faces[k].bottom() - faces[k].top())/4)]))
# 对于某张人脸,遍历所有存储的人脸特征
# for every faces detected, compare the faces in the database
e_distance_list = []
for i in range(len(features_known_arr)):
# 如果 person_X 数据不为空
if str(features_known_arr[i][0]) != '0.0':
print("with person", str(i + 1), "the e distance: ", end='')
e_distance_tmp = return_euclidean_distance(features_cap_arr[k], features_known_arr[i])
print(e_distance_tmp)
e_distance_list.append(e_distance_tmp)
else:
# 空数据 person_X
e_distance_list.append(999999999)
# 找出最接近的一个人脸数据是第几个
# Find the one with minimum e distance
similar_person_num = e_distance_list.index(min(e_distance_list))
print("Minimum e distance with person", int(similar_person_num)+1)
# 计算人脸识别特征与数据集特征的欧氏距离
# 距离小于0.4则标出为可识别人物
if min(e_distance_list) < 0.4:
# 这里可以修改摄像头中标出的人名
# Here you can modify the names shown on the camera
# 1、遍历文件夹目录
folder_name = 'D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/person'
# 最接近的人脸
sum=similar_person_num+1
key_id=1 # 从第一个人脸数据文件夹进行对比
# 获取文件夹中的文件名:1wang、2zhou、3...
file_names = os.listdir(folder_name)
for name in file_names:
# print(name+'->'+str(key_id))
if sum ==key_id:
#winsound.Beep(300,500)# 响铃:300频率,500持续时间
name_namelist[k] = name[1:]#人名删去第一个数字(用于视频输出标识)
key_id += 1
# 播放欢迎光临音效
#playsound('D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/music/welcome.wav')
# print("May be person "+str(int(similar_person_num)+1))
# -----------筛选出人脸并保存到visitor文件夹------------
for i, d in enumerate(faces):
x1 = d.top() if d.top() > 0 else 0
y1 = d.bottom() if d.bottom() > 0 else 0
x2 = d.left() if d.left() > 0 else 0
y2 = d.right() if d.right() > 0 else 0
face = img_rd[x1:y1,x2:y2]
size = 64
face = cv2.resize(face, (size,size))
# 要存储visitor人脸图像文件的路径
path_visitors_save_dir = "D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/visitor/known"
# 存储格式:2019-06-24-14-33-40wang.jpg
now_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
save_name = str(now_time)+str(name_namelist[k])+'.jpg'
# print(save_name)
# 本次图片保存的完整url
save_path = path_visitors_save_dir+'/'+ save_name
# 遍历visitor文件夹所有文件名
visitor_names = os.listdir(path_visitors_save_dir)
visitor_name=''
for name in visitor_names:
# 名字切片到分钟数:2019-06-26-11-33-00wangyu.jpg
visitor_name=(name[0:16]+'-00'+name[19:])
# print(visitor_name)
visitor_save=(save_name[0:16]+'-00'+save_name[19:])
# print(visitor_save)
# 一分钟之内重复的人名不保存
if visitor_save!=visitor_name:
cv2.imwrite(save_path, face)
print('新存储:'+path_visitors_save_dir+'/'+str(now_time)+str(name_namelist[k])+'.jpg')
else:
print('重复,未保存!')
else:
# 播放无法识别音效
#playsound('D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/music/sorry.wav')
print("Unknown person")
# -----保存图片-------
# -----------筛选出人脸并保存到visitor文件夹------------
for i, d in enumerate(faces):
x1 = d.top() if d.top() > 0 else 0
y1 = d.bottom() if d.bottom() > 0 else 0
x2 = d.left() if d.left() > 0 else 0
y2 = d.right() if d.right() > 0 else 0
face = img_rd[x1:y1,x2:y2]
size = 64
face = cv2.resize(face, (size,size))
# 要存储visitor-》unknown人脸图像文件的路径
path_visitors_save_dir = "D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/visitor/unknown"
# 存储格式:2019-06-24-14-33-40unknown.jpg
now_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
# print(save_name)
# 本次图片保存的完整url
save_path = path_visitors_save_dir+'/'+ str(now_time)+'unknown.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(save_path, face)
print('新存储:'+path_visitors_save_dir+'/'+str(now_time)+'unknown.jpg')
# 矩形框
# draw rectangle
for kk, d in enumerate(faces):
# 绘制矩形框
cv2.rectangle(img_rd, tuple([d.left(), d.top()]), tuple([d.right(), d.bottom()]), (0, 255, 255), 2)
print('\n')
# 在人脸框下面写人脸名字
# write names under rectangle
for i in range(len(faces)):
cv2.putText(img_rd, name_namelist[i], pos_namelist[i], font, 0.8, (0, 255, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
print("Faces in camera now:", name_namelist, "\n")
#cv2.putText(img_rd, "Press 'q': Quit", (20, 450), font, 0.8, (84, 255, 159), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_rd, "Face Recognition", (20, 40), font, 1, (0, 0, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_rd, "Visitors: " + str(len(faces)), (20, 100), font, 1, (0, 0, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
# 窗口显示 show with opencv
cv2.imshow("camera", img_rd)
# 释放摄像头 release camera
cap.release()
# 删除建立的窗口 delete all the windows
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
四、扩展
这次项目实践了解了dlib人脸识别原理,复习了opencv使用原理,我们的项目要求:
假定该系统完成后将工作于学生宿舍门口,摄像头安装于门的猫眼处、或者门侧边墙上:
- 对本宿舍的学生进行人脸识别(身份验证),
- 通过验证就播放语音“欢迎光临!”(模拟开门),否则播放“抱歉,无法验证您的身份!”,
- 同时用数据库记录来访者的身份、人脸图片和访问时间等信息。
实现过程:
- 在前文的基础上,增加数据集为全寝室人脸识别;
- python语音播放参考前文:Python读取wav音频文件
- 记录来访者,以时间和检测名命名的图片存储到文件visitor
附:
1、更多人脸识别运用github参考:https://github.com/cungudafa/cungudafa.github.io
2、人脸识别源码参考:https://github.com/ageitgey/face_recognition#face-recognition
3、基于人工智能数据集经典案例(猫狗数据集)参考:
https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-with-python-notebooks/blob/master/5.2-using-convnets-with-small-datasets.ipynb
https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-with-python-notebooks/blob/master/5.4-visualizing-what-convnets-learn.ipynb