DES算法实践(python版本)
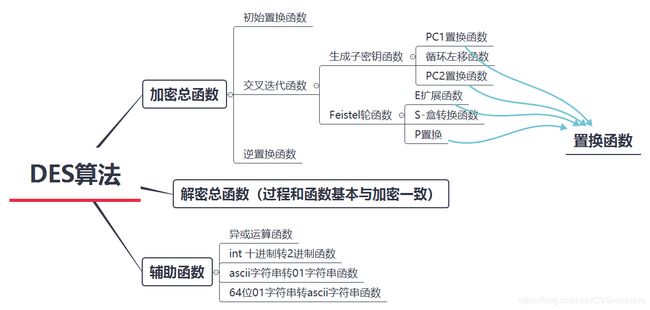
一、 DES算法原理概述
预备知识
-
64位为一个分组,当成明文输入DES算法模型,输出同样长度64位的密文。
-
对称加密,加密密钥也是解密密钥,密钥定义了加密过程。
-
密钥构成:64位,每8位的最后一位用于奇偶校验,所以实际密钥长度为56位。
-
基本过程是换位和置换(根据置换矩阵)
算法核心概要
-
总体结构
-
Feistel轮函数
-
子密钥生成
-
解密过程
信息空间处理:
-
原始明文消息的处理:最后的分组不足64位时,填充的字节为缺失的字节数目。
-
明文分组结构:$M = m_1m_2…m_{64} , m_i ∈ {0, 1},i= 1…64 $
-
密文分组结构: $C = c_1c_2…c_{64} , c_i ∈ {0, 1},i= 1…64 $
-
密钥结构:$K = k_1k_2…k_{64} , k_i ∈ {0, 1},i= 1…64 $
加密过程:
64位原始密文M经IP初始置换得到 I P ( M ) IP(M) IP(M)
I P ( M ) IP(M) IP(M)经过16次迭代 T 1 , T 2 . . . T 16 T_1, T_2... T_{16} T1,T2...T16 得到 T 1 6 T 1 5... T 1 I P ( M ) T_16T_15...T_1IP(M) T16T15...T1IP(M)
然后在经过 I P − 1 IP^{-1} IP−1 逆变换得到密文。
解密过程:
加密逆向进行分析。和加密不同的是,子密钥调度过程为逆序,其他一致。
初始置换:
给定一个固定的初始置换IP矩阵来重排明文块M中的二进制位。得到二进制串 M 0 = I P ( M ) = L 0 R 0 M_0 = IP (M) = L_0R_0 M0=IP(M)=L0R0
表: IP置换表(8 * 8)(row * col 下同)
迭代T
-
迭代规则:交叉迭代。 L i = R i − 1 R i = L i − 1 ⨁ f ( R i − 1 , K i ) L_i = R_{i-1} \,\, R_i = L_{i-1} \bigoplus f(R_{i - 1}, K_i) Li=Ri−1Ri=Li−1⨁f(Ri−1,Ki). K i K_i Ki为子密钥,长度为 K i , f K_i\,, f Ki,f为 f i e s t e l fiestel fiestel 轮函数。
-
16次迭代后产生 L 16 R 16 L_{16}R_{16} L16R16
-
左右交换输出$R_{16}L_{16}
逆置换 P − 1 P^{-1} P−1 C = I P − 1 ( R 16 L 16 ) C = IP^{-1}(R_{16}L_{16}) C=IP−1(R16L16)
表: 逆置换表(8 * 8)
轮函数 f ( R i − 1 , K i ) f(R_{i-1}, K_i) f(Ri−1,Ki)
密码函数f(R, K)接受两个输入:32 位的数据和 48 位的子密钥。然后:
-
通过表 E 进行扩展置换 (表),将输入的 32 位数据扩展为 48 位;
-
将扩展后的 48 位数据与 48 位的子密钥进行异或运算;
-
将异或得到的 48 位数据分成 8 个 6 位的块,每一个块通过对应的一个 S 表产生一个 4 位的输出。其中,每个 S 表都是 4 行 16 列。**具体的置换过程如下:**把 6 位输入中的第 1 位和第 6 位取出来行成一个两位的二进制数 x ,作为 Si 表中的行数(0~3);把 6 位输入的中间 4 位构成另外一个二进制数 y,作为 Si 表的列数(0~15);查出 Si 盒表(8 * 4 * 16 的矩阵)中 x 行 y 列所对应的整数,将该整数转换为一个 4 位的二进制数。
-
把通过 S 表置换得到的 8 个 4 位连在一起,形成一个 32 位的数据。然后将该 32 位数据通过表 P 进行置换(称为P-置换),置换后得到一个仍然是 32 位的结果数据,这就是
f(R, K)函数的输出。
三个表:E扩展置换表(8 * 6),S盒置换表(4 * 16),P-置换表(8 * 4)
子密钥生成
-
对密钥K中的56个非校验位实现PC-1置换,得到 C 0 D 0 C_0D_0 C0D0,即置换后的前28位和后28位。
-
对 C i − 1 D i − 1 C_{i-1} D_{i-1} Ci−1Di−1 分别进行循环左移操作,得到 C i D i C_{i}D_{i} CiDi,当 i = 1 , 2 , 9 , 16 i = 1,2,9,16 i=1,2,9,16时二进制串左移一个位置,否则左移两个位置。
-
对56位的 C i D i C_iD_i CiDi 实行PC-2压缩置换,得到48位的 K i K_i Ki 。 然后 i + + i++ i++。
-
如果已经得到 K 16 K_{16} K16,密码调度结束,否则转步骤2.
两个表:压缩置换表PC-1 PC-2
二、 代码模块
核心函数展示和描述
由于解密函数需要的模块基本与加密一致,所以不做呈现。
#####加密总函数############################################################################
# 1. 初始置换 2. 交叉迭代 3. 逆置换
def Encryption(plainText, secretKey):
if PRINT_FLAG == True:
print("> 开始加密64位明文")
M = list(plainText)
L0, R0 = InitialPermutation(M)
RL = CrossIterationInEncryption(L0, R0, secretKey)
cipherText = "".join(InversePermutation(RL))
return cipherText
##############################################################################################
######表格置换函数###########################################################################
"""
function: transfrom the binaryStr with the giver permutation table
condition: len(binaryStr) == len(PermutationTable)
return: the permutated binary List.
"""
# 传入01字符串列表和置换表,返回置换结果
def Permutation(binaryStr, PermutationTable):
length = len(PermutationTable)
PermutatedList = []
for i in range(0, length):
PermutatedList.extend(binaryStr[PermutationTable[i] - 1])
return PermutatedList
############################################################################################
#########加密过程的的交叉迭代####################################################################
"""
function: make cross iteration on L0, R0 for 16 times
input: L0--the front 32 bits of 64-bits plain text , R0--the back 32 bits of plain text
return: R16--the back iterated 32-bits result, L16--the front iterated 32-bits result
"""
# 16次交叉迭代,返回RL列表用于逆置换。
def CrossIterationInEncryption(L_0, R_0, SecretKey):
if PRINT_FLAG == True:
print("> 正在进行加密过程的交叉迭代")
R = ""
L = ""
tmp_R = R_0
tmp_L = L_0
sonKeyList = createSonKey(SecretKey)
for i in range(1,17):
L = tmp_R
R = XOROperation(tmp_L,Feistel(tmp_R,sonKeyList[i - 1]))
tmp_R = R
tmp_L = L
RL = R + L
return RL
##############################################################################################
####创建子密钥##################################################################################
"""
function: create the 16 son keys with the given key
return: sonKeysList: 16 son keys list
"""
def createSonKey(SecretKey):
# 提取密钥中的非校验位
if PRINT_FLAG == True:
print("> 正在生成16个子密钥")
str_56_bits_List = list(SecretKey)
sonKeyList = []
# 进行PC-1置换
Temp_PC_1_PermutationResult_C_i_1, Temp_PC_1_PermutationResult_D_i_1 = PC_1_Permutation(str_56_bits_List)
C_i = []
D_i = []
for i in range(1, 17):
# C_i-1 D_i-1
# 计算C_i D_i
# 循环左移
if i == 1 or i == 2 or i == 9 or i == 16:
C_i = shiftLeft(Temp_PC_1_PermutationResult_C_i_1, 1)
D_i = shiftLeft(Temp_PC_1_PermutationResult_D_i_1, 1)
else:
C_i = shiftLeft(Temp_PC_1_PermutationResult_C_i_1, 2)
D_i = shiftLeft(Temp_PC_1_PermutationResult_D_i_1, 2)
CD = C_i + D_i
# PC2压缩置换
sonKey_i = PC_2_Permutation(CD)
sonKeyList.append(sonKey_i)
Temp_PC_1_PermutationResult_C_i_1 = C_i
Temp_PC_1_PermutationResult_D_i_1 = D_i
if i == 16:
break
return sonKeyList
##############################################################################################
#####Feistel 函数#############################################################################
"""
function: Feistel function to create bit-stR_ing to permute with R_i -- a 32-bit stR_ing
input: R_i_1--the (i-1)th back 32 bits string, K_i--the son secret key
return: Feistel result (string type)
"""
# 轮函数:1. E扩展置换; 2. 扩展结果和子密钥进行异或运算 3. 进行S盒6-4转换
def Feistel(R_i_1, K_i):
if PRINT_FLAG == True:
print("> 正在执行feistel轮函数")
E_ExpandResult = E_Expand(R_i_1)
xorResult = XOROperation(E_ExpandResult, K_i)
str_32_bits = []
for i in range(8):
str_6_bits = xorResult[i * 6: i * 6 + 6]
str_32_bits += S_Box_Transformation(str_6_bits, i + 1)
return "".join(P_Permutation(str_32_bits))
##############################################################################################
####随机生成64位key,8个字符#####################################################################
"""
return: a 64-bits (8 bytes) string as a secret key
"""
def createSecrteKey():
seed = "1234567890abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ!@#$%^&*()_+=-"
key = []
for i in range(8):
key.append(random.choice(seed))
randomSecretKey = ''.join(key)
return randomSecretKey
################################################################################################
##########8个字符的字符串转为ascii,然后转 0 1串####################################
def ToBitString(string_8_char):
strList = []
for i in range(8):
strList.append(str(int2bin(ord(string_8_char[i]), 8)))
return "".join(strList)
##################################################################################
########64位bits转为8个ascci字符###################################################
def ToAsciiChar(string_64_bits):
strList = []
bitList = list(string_64_bits)
for i in range(8):
if int("".join(bitList[i * 8: i * 8 + 8]), 2) < 8:
continue
# 八个bit一个处理单元,先转为10进制,然后转ascii,存入列表
strList.append(chr(int("".join(bitList[i * 8: i * 8 + 8]), 2)))
return "".join(strList)
##################################################################################
############ 加密过程和解密过程
while True:
text_8_bytes = PlainTextFile.read(8) # 读取8个ascii字符
if not text_8_bytes:
print("读取明文文件到结尾啦")
break
if len(text_8_bytes) != 8:
full_flag = False
else:
bitString = ToBitString(text_8_bytes) # 8个ascii字符转十进制int,然后再转为64位01
# 加密
encryptStr = Encryption(bitString, secretKeyBitString)
# 加密结果写入文件
CipherTextFile.write(str(ToAsciiChar(encryptStr)))
# 解密
decryptStr = Decryption(encryptStr, secretKeyBitString)
# 解密结果写入文件
DecryptTextFile.write(str(ToAsciiChar(decryptStr)))
if full_flag == False: # 如果尾部字节不足8个,那么每个字节都填入缺失的字节数量
NumOfLostBytes = 8 - len(text_8_bytes)
bitStringList = []
for i in range(len(text_8_bytes)):
bitStringList.append(int2bin(ord(text_8_bytes[i]), 8))
full_8_bits = int2bin(NumOfLostBytes, 8) # 填充的比特串
# 填充的字节数 转为bitstring
for i in range(NumOfLostBytes):
bitStringList.append(full_8_bits)
bitString = "".join(bitStringList) #补全64位分组
# 加密
encryptStr = Encryption(bitString, secretKeyBitString)
# 加密结果写入文件
CipherTextFile.write(str(ToAsciiChar(encryptStr)))
# 解密
decryptStr = Decryption(encryptStr, secretKeyBitString)
# 解密结果写入文件
DecryptTextFile.write(str(ToAsciiChar(decryptStr)))
# 读取完整的8个字节分组字节,尾部填充8个字节,取值都为08
if full_flag == True:
zero_eight = "00001000"
tmpList = []
for i in range(8):
tmpList.append(zero_eight)
bitString = "".join(tmpList)
# 加密
encryptStr = Encryption(bitString, secretKeyBitString)
# 加密结果写入文件
CipherTextFile.write(str(ToAsciiChar(encryptStr)))
# 解密
decryptStr = Decryption(encryptStr, secretKeyBitString)
# 解密结果写入文件
DecryptTextFile.write(str(ToAsciiChar(decryptStr)))
数据结构说明
- 明文,密文,解密后的数据
从明文文件中读取8个ascii字符,存放在string结构中,然后再转换为64个ascii字符的0 1 字符串作为加密的明文。加密结果和解密结果也是转换为ascii字符串,存放在文件中。
- 加密解密过程的0 1 字符串数据
在实际操作中,由于python中的string不支持赋值以及增删操作,所以通过python里的list即列表来存放字符串,通过list 方便的操作接口来执行加密解密。而string和list之间的转换方式也很简单,如下。
List = list(str) # string 转 list
str = "".join(List) # list 转string
三、运行说明
在实际的运行过程中,本实验计划读取明文文件,随机生成密钥文件,然后将加密后的密文和解密后的结果保存文件中,可在代码文件中修改文件命名格式和路径.
#########文件变量
CIPHER_TEXT_FILE = "cipherText.txt" #密文文件
PLAIN_TEXT_FILE = "plainText.txt" #明文文件
SECRET_KEY_FILE = "secretKey.txt" #密钥文件
DECRYPT_TEXT_FILE = "decryptText.txt" #解密文
每次从明文中读取8个字节的内容就转换位64个01字符串,然后对字符串进行加密,同时输出加密结果到控制台和加密文件中,加密之后,对密文进行执行解密,将解密结果输出到控制台和解密文件中。
由于只对ascii字符进行转换,如果明文文件中出现中文或者其它非ascii字符那么解密结果仍会出现其他乱码文字。
如果明文中出现中文,那么解密后的结果的中文位置将会出现乱码。
四、完整源码
代码仅供参考,见 gihub。