Kaldi 学习总结
0. 看语音识别相关英文著作时, word 的理解
1. 声学训练时,HMM,GMM 都用在什么地方
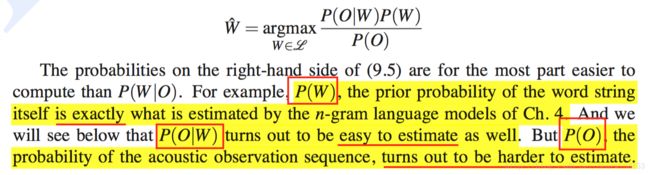
2. P(W|O) 的深入理解
likelihood 的简单理解:
P(O|W): 给定 O, 调整 W,使得 P(O|W) 最大
3. 语音识别过程理解
参看这个链接就可以了! 点击打开链接
3.1 解码阶段的总结
解码阶段可总结为:
教材上的总结
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
只看标出色彩后的部分
In the decoding phase, we take the acoustic model (AM), which consists of this sequence of acoustic likelihoods, plus an HMM dictionary of word pronunciations, combined with the language model (LM) (generally an N-gram grammar), and output the most likely sequence of words.
acoustic model (AM): consists of this sequence of acoustic likelihoods
HMM dictionary of word pronunciations: is lexicon
An HMM dictionary -> is a list of word pronunciations
Each pronunciation represented by a string of phones.
Each word can then be thought of as an HMM, where the phones (or sometimes subphones) are states in the HMM, and the Gaussian likelihood estimators supply the HMM output likelihood function for each state.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4. HMM 在语音识别中 Self-loop state 有什么意义 ?
因为被识别的语音需要分帧(大约20ms/帧),帧与帧之间还需要有(10ms)重叠,这样同样的 phone 可能出现在连续的多帧中,而 phone / subphone 就是 HMM 的对应State,这时Self-loops 就 派上用场了,这段语音中部分语音片段对应的 HMM 的状态就是 Self-loops 。
5. 为什么简单的语言识别可以 “build an HMM whose states correspond to entire words”?
上面截图 提到了,但为什么呢?
下面的截图中也找到了答案 [在 LVCSR 中,因为一个 phone 可能需要 1s 的持续时间,处理的语音需要按 10ms 一帧切分,大约就是 100 帧,这 100 帧不是声学相同的,因此,phone 需要更细拆分。]
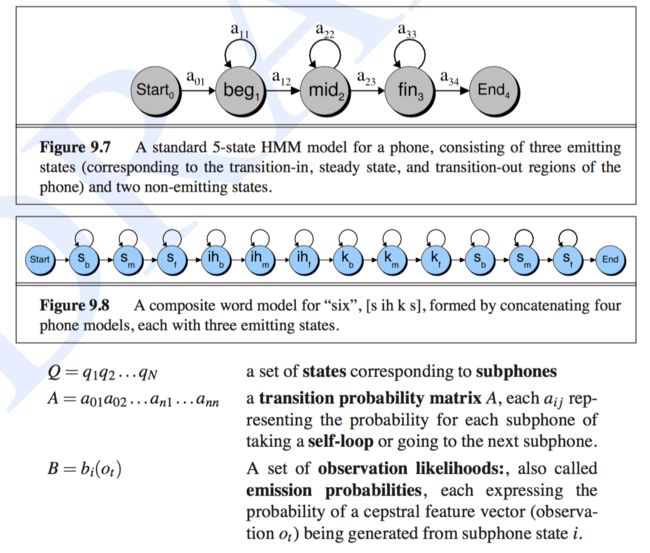
6. LVCSR 使用 phone HMM 或者 subphone HMM 都是什么原理?
上面截图是提到 LVCSR 使用以 word_model / phone_model 的 HMM 建模的两种方式
1. 其中 word model 最小建模单位是 word (英语单词) ,一个 word unit 对应 一个 5-state phone HMM
2. 而 phone model 则是 word 分解为 phone, 每个 phone 对应 3-state 的 HMM,再将 每个 state 称作 subphone。
7. MFCC 特征提取
MFCC 的提取过程参考这个链接:点击打开链接
MFCC 梅尔频率倒谱系数 有什么特点,为什么要用它?
如上所述:原来,cepstral系数非常有用的属性,不同的方差系数往往是不相关的,不需要表示所有MFCC特征方差之间的关系,极大的节省参数个数。但是,对于频谱系数,不同频带是相关的
7. Computing Acoustic Likelihoods
一些参数的说明
Q [ = q1 q2 ...qN ]: 状态集合,对应 subphones
A [ = a01a02 ...an1 ...ann ]: 转移概率矩阵
B [ = bi(Ot) ]: 观察似然的集合
bi(Ot): observation likelihood function