Canny边缘检测及自适应门限
【概述】
Canny算子格式如下:
Canny
采用 Canny 算法做边缘检测
void cvCanny( const CvArr* image, CvArr* edges, double threshold1, double threshold2, int aperture_size=3 );
- image
- 单通道输入图像.
- edges
- 单通道存储边缘的输出图像
- threshold1
- 第一个阈值
- threshold2
- 第二个阈值
- aperture_size
Sobel 算子内核大小
【实现代码】
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
IplImage* pImg = NULL;
IplImage* pCannyImg = NULL;
double low_thresh = 50.0;
double high_thresh = 200.0;
if( argc == 2 && (pImg = cvLoadImage( argv[1], 0)) != 0 )
{
pCannyImg = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(pImg), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 1);
cvCanny(pImg, pCannyImg, low_thresh, high_thresh, 3);
cvNamedWindow("src", 1);
cvNamedWindow("canny",1);
cvShowImage( "src", pImg );
cvShowImage( "canny", pCannyImg );
cvWaitKey(0);
cvDestroyWindow( "src" );
cvDestroyWindow( "canny" );
cvReleaseImage( &pImg );
cvReleaseImage( &pCannyImg );
}
return 0;
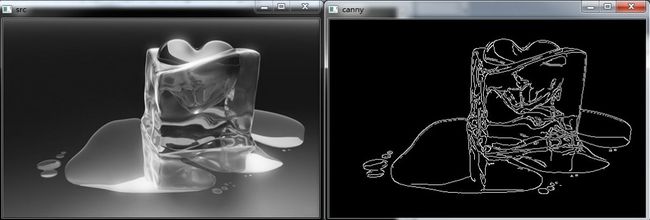
} 【运行截图】
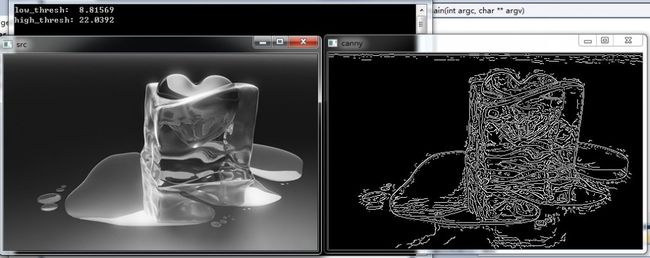
在OpenCV中用canny算子进行边缘检测速度很快,不过有点不爽的就是高低阈值需要输入。根据博文http://blog.csdn.net/sunlylorn/article/details/8015825实现了当用户没有指定高低阈值时,由函数自适应确定阈值。
【实现代码】
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void AdaptiveFindThreshold(const CvArr* image, double *low, double *high, int aperture_size=3);
void _AdaptiveFindThreshold(CvMat *dx, CvMat *dy, double *low, double *high);
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
IplImage* pImg = NULL;
IplImage* pCannyImg = NULL;
double low_thresh = 0.0;
double high_thresh = 0.0;
if( argc == 2 && (pImg = cvLoadImage( argv[1], 0)) != 0 )
{
pCannyImg = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(pImg), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 1);
CvMat *dx = (CvMat*)pImg;
CvMat *dy = (CvMat*)pCannyImg;
if(low_thresh == 0.0 && high_thresh == 0.0)
{
AdaptiveFindThreshold(pImg, &low_thresh, &high_thresh);
cout << "low_thresh: " << low_thresh << endl;
cout << "high_thresh: " << high_thresh << endl;
}
cvCanny(pImg, pCannyImg, low_thresh, high_thresh, 3);
cvNamedWindow("src", 1);
cvNamedWindow("canny",1);
cvShowImage( "src", pImg );
cvShowImage( "canny", pCannyImg );
cvWaitKey(0);
cvDestroyWindow( "src" );
cvDestroyWindow( "canny" );
cvReleaseImage( &pImg );
cvReleaseImage( &pCannyImg );
}
return 0;
}
void AdaptiveFindThreshold(const CvArr* image, double *low, double *high, int aperture_size)
{
cv::Mat src = cv::cvarrToMat(image);
const int cn = src.channels();
cv::Mat dx(src.rows, src.cols, CV_16SC(cn));
cv::Mat dy(src.rows, src.cols, CV_16SC(cn));
cv::Sobel(src, dx, CV_16S, 1, 0, aperture_size, 1, 0, cv::BORDER_REPLICATE);
cv::Sobel(src, dy, CV_16S, 0, 1, aperture_size, 1, 0, cv::BORDER_REPLICATE);
CvMat _dx = dx, _dy = dy;
_AdaptiveFindThreshold(&_dx, &_dy, low, high);
}
// 仿照matlab,自适应求高低两个门限
void _AdaptiveFindThreshold(CvMat *dx, CvMat *dy, double *low, double *high)
{
CvSize size;
IplImage *imge=0;
int i,j;
CvHistogram *hist;
int hist_size = 255;
float range_0[]={0,256};
float* ranges[] = { range_0 };
double PercentOfPixelsNotEdges = 0.7;
size = cvGetSize(dx);
imge = cvCreateImage(size, IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1);
// 计算边缘的强度, 并存于图像中
float maxv = 0;
for(i = 0; i < size.height; i++ )
{
const short* _dx = (short*)(dx->data.ptr + dx->step*i);
const short* _dy = (short*)(dy->data.ptr + dy->step*i);
float* _image = (float *)(imge->imageData + imge->widthStep*i);
for(j = 0; j < size.width; j++)
{
_image[j] = (float)(abs(_dx[j]) + abs(_dy[j]));
maxv = maxv < _image[j] ? _image[j]: maxv;
}
}
if(maxv == 0){
*high = 0;
*low = 0;
cvReleaseImage( &imge );
return;
}
// 计算直方图
range_0[1] = maxv;
hist_size = (int)(hist_size > maxv ? maxv:hist_size);
hist = cvCreateHist(1, &hist_size, CV_HIST_ARRAY, ranges, 1);
cvCalcHist( &imge, hist, 0, NULL );
int total = (int)(size.height * size.width * PercentOfPixelsNotEdges);
float sum=0;
int icount = hist->mat.dim[0].size;
float *h = (float*)cvPtr1D( hist->bins, 0 );
for(i = 0; i < icount; i++)
{
sum += h[i];
if( sum > total )
break;
}
// 计算高低门限
*high = (i+1) * maxv / hist_size ;
*low = *high * 0.4;
cvReleaseImage( &imge );
cvReleaseHist(&hist);
}
【运行截图】