Java多线程与并发 面试十大常考题目。
1 进程和线程的区别?
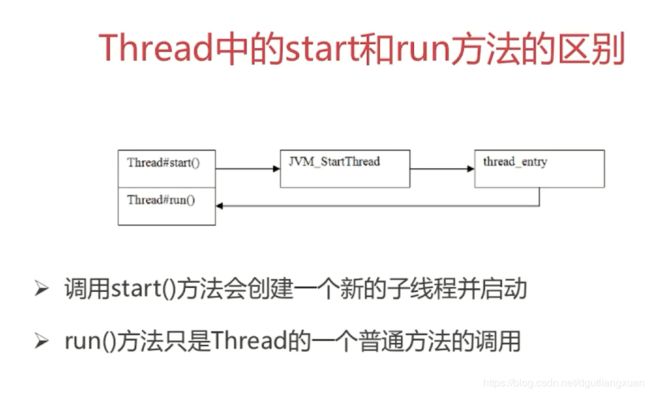
2 线程的start和run方法的区别.
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
public class ThreadStartOrRunMethodDiff {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
t.run();
}
}
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
public class ThreadStartOrRunMethodDiff {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
t.start();
}
}
3 Thread和Runnable的关系?
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private String name;
public MyRunnable(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run(){
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
System.out.println("Thread start : " + this.name + ",i= " + i);
}
}
}
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
public class RunnableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnable mr1 = new MyRunnable("Runnable1");
MyRunnable mr2 = new MyRunnable("Runnable2");
MyRunnable mr3 = new MyRunnable("Runnable3");
Thread t1 = new Thread(mr1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(mr2);
Thread t3 = new Thread(mr3);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
4 如何实现处理线程的返回值?
成员变量传参,可以看上面的代码 MyRunnable的实现。
4 如何实现处理线程的返回值?
1 主线程等待法
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
public class CycleWait implements Runnable{
private String value;
public void run() {
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
value = "we have data now";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CycleWait cw = new CycleWait();
Thread t = new Thread(cw);
t.start();
// while (cw.value == null){
// Thread.currentThread().sleep(100);
// }
// t.join();
System.out.println("value : " + cw.value);
}
}
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
public class CycleWait implements Runnable{
private String value;
public void run() {
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
value = "we have data now";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CycleWait cw = new CycleWait();
Thread t = new Thread(cw);
t.start();
while (cw.value == null){
Thread.currentThread().sleep(100);
}
System.out.println("value : " + cw.value);
}
}
主线程等待法 的缺点
1.无法做到精确的时间控制
2.成员变量多的话,一大堆if else
通过加入 join()方法
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
public class CycleWait implements Runnable{
private String value;
public void run() {
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
value = "we have data now";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CycleWait cw = new CycleWait();
Thread t = new Thread(cw);
t.start();
t.join();
System.out.println("value : " + cw.value);
}
}
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class MyCallable implements Callable {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception{
String value="test";
System.out.println("Ready to work");
Thread.currentThread().sleep(5000);
System.out.println("task done");
return value;
}
}
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class FutureTaskDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask task = new FutureTask(new MyCallable());
new Thread(task).start();
if(!task.isDone()){
System.out.println("task has not finished, please wait!");
}
System.out.println("task return: " + task.get());
}
}
线程池
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class ThreadPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future future = newCachedThreadPool.submit(new MyCallable());
if(!future.isDone()){
System.out.println("task has not finished, please wait!");
}
try {
System.out.println(future.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
newCachedThreadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
8-5 线程的状态?
package com.interview.javabasic.thread;
public class ThreadTest {
private static void attack() {
System.out.println("Fight");
System.out.println("Current Thread is : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(){
public void run(){
attack();
}
};
System.out.println("current main thread is : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
t.start();
t.join();
t.start();
}
}