图像拼接 随机抽样一致算法(Random sample consensus,RANSAC)【转】
作者:桂。
时间:2017-04-25 21:05:07
链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xingshansi/p/6763668.html
前言
仍然是昨天的问题,别人问到最小二乘、霍夫变换、RANSAC在直线拟合上的区别。昨天梳理了霍夫变换,今天打算抽空梳理一下RANSAC算法,主要包括:
1)RANSAC理论介绍
2)RANSAC应用简介;
内容为自己的学习记录,其中很多地方借鉴了别人,最后一起给出链接。
一、RANSAC理论介绍
普通最小二乘是保守派:在现有数据下,如何实现最优。是从一个整体误差最小的角度去考虑,尽量谁也不得罪。
RANSAC是改革派:首先假设数据具有某种特性(目的),为了达到目的,适当割舍一些现有的数据。
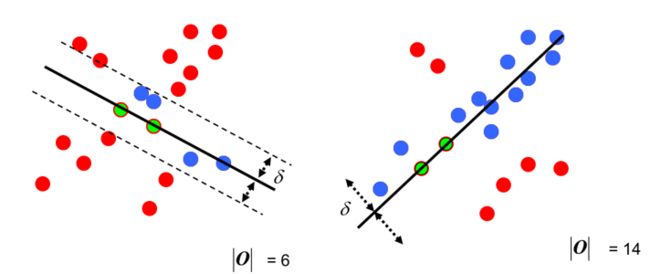
给出最小二乘拟合(红线)、RANSAC(绿线)对于一阶直线、二阶曲线的拟合对比:
可以看到RANSAC可以很好的拟合。RANSAC可以理解为一种采样的方式,所以对于多项式拟合、混合高斯模型(GMM)等理论上都是适用的。
RANSAC的算法大致可以表述为(来自wikipedia):
Given:
data – a set of observed data points
model – a model that can be fitted to data points
n – the minimum number of data values required to fit the model
k – the maximum number of iterations allowed in the algorithm
t – a threshold value for determining when a data point fits a model
d – the number of close data values required to assert that a model fits well to data
Return:
bestfit – model parameters which best fit the data (or nul if no good model is found)
iterations = 0
bestfit = nul
besterr = something really large
while iterations < k {
maybeinliers = n randomly selected values from data
maybemodel = model parameters fitted to maybeinliers
alsoinliers = empty set
for every point in data not in maybeinliers {
if point fits maybemodel with an error smaller than t
add point to alsoinliers
}
if the number of elements in alsoinliers is > d {
% this implies that we may have found a good model
% now test how good it is
bettermodel = model parameters fitted to all points in maybeinliers and alsoinliers
thiserr = a measure of how well model fits these points
if thiserr < besterr {
bestfit = bettermodel
besterr = thiserr
}
}
increment iterations
}
return bestfit
RANSAC简化版的思路就是:
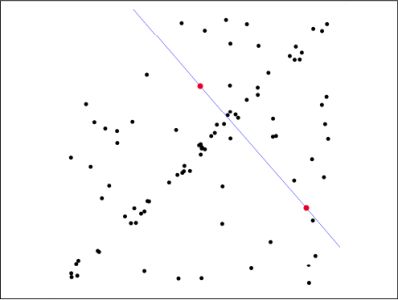
第一步:假定模型(如直线方程),并随机抽取Nums个(以2个为例)样本点,对模型进行拟合:
第二步:由于不是严格线性,数据点都有一定波动,假设容差范围为:sigma,找出距离拟合曲线容差范围内的点,并统计点的个数:
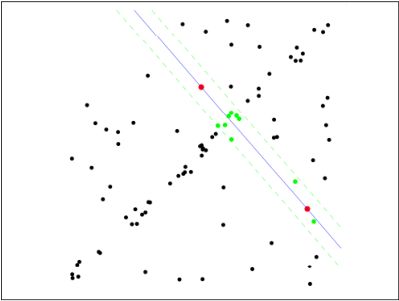
第三步:重新随机选取Nums个点,重复第一步~第二步的操作,直到结束迭代:
第四步:每一次拟合后,容差范围内都有对应的数据点数,找出数据点个数最多的情况,就是最终的拟合结果:
至此:完成了RANSAC的简化版求解。
这个RANSAC的简化版,只是给定迭代次数,迭代结束找出最优。如果样本个数非常多的情况下,难不成一直迭代下去?其实RANSAC忽略了几个问题:
- 每一次随机样本数Nums的选取:如二次曲线最少需要3个点确定,一般来说,Nums少一些易得出较优结果;
- 抽样迭代次数Iter的选取:即重复多少次抽取,就认为是符合要求从而停止运算?太多计算量大,太少性能可能不够理想;
- 容差Sigma的选取:sigma取大取小,对最终结果影响较大;
这些参数细节信息参考:维基百科。
RANSAC的作用有点类似:将数据一切两段,一部分是自己人,一部分是敌人,自己人留下商量事,敌人赶出去。RANSAC开的是家庭会议,不像最小二乘总是开全体会议。
附上最开始一阶直线、二阶曲线拟合的code(只是为了说明最基本的思路,用的是RANSAC的简化版):
一阶直线拟合:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
|
二阶曲线拟合:
+ View Code
二、RANSAC应用简介
RANSAC其实就是一种采样方式,例如在图像拼接(Image stitching)技术中:
第一步:预处理后(据说桶形变换,没有去了解过)提取图像特征(如SIFT)
第二步:特征点进行匹配,可利用归一化互相关(Normalized Cross Correlation method, NCC)等方法。
但这个时候会有很多匹配错误的点:
这就好比拟合曲线,有很多的误差点,这个时候就想到了RANSAC算法:我不要再兼顾所有了,每次选取Nums个点匹配 → 计算匹配后容差范围内的点数 → 重复实验,迭代结束后,找出点数最多的情况,就是最优的匹配。
利用RANSAC匹配:
第三步:图像拼接,这个就涉及拼接技术了,直接给出结果:
参考:
- RANSAC:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_sample_consensus
- 图像拼接:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaoch1222/article/details/53510895