Spring+Quartz框架实现定时任务(集群,分布式)
Spring+Quartz框架实现定时任务(集群,分布式)
1、定时任务的必要性:
定时任务在应用中的重要性不言而喻,大多是应用,特别是金融应用更是离不开定时任务,能用定时任务来处理异常订单,完成跑批,定时活动(双11)等。
在初期应用的访问量并不是那么大,一台服务器完全满足使用,但是随着用户量、业务量的逐日增加,应用中会有很多定时任务需要执行,一台服务器已经不能满足使用,
因此需要把应用给部署到集群中,前端通过nginx代理实现访问。
2、集群使用定时任务的问题:
目前大部分在集群中处理定时任务的方式不是正真的分布式处理方式,而是一种伪分布式,这种方式存在一个明显的缺陷就是当集群中机器宕机,
那么整个定时任务就会挂掉或者不能一次性跑完,会对业务产生严重的影响。
而且在集群环境中,同样的定时任务,在集群中的每台服务器都会执行,这样定时任务就会重复执行,不但会增加服务器的负担,还会因为定时任务重复执行造成额外的不可预期的错误。
解决方案是:
根据集群的数量,把定时任务中的任务平均分到集群中的每台机器上(这里的平均分是指以前多个定时任务本来是在一台机器上运行,先在人为的把这些任务分成几部分,让所有的机器分别去执行这些任务)
这就是采用了分布式定时任务来进行处理。
另外一种解决方式:
使用Quartz框架,在集群环境下,通过数据库锁机制来实现定时任务的执行,下面会介绍。
3、Quartz介绍:
Quartz是一个开放源码项目,专注于任务调度器,提供了极为广泛的特性如持久化任务,集群和分布式任务等。
Quartz核心是调度器,还采用多线程管理。quartz框架是原生就支持分布式定时任务的。
1.持久化任务(把调度信息存储到数据):当应用程序停止运行时,所有调度信息不被丢失,当你重新启动时,调度信息还存在,这就是持久化任务。
2.集群和分布式处理:当在集群环境下,当有配置Quartz的多个客户端时(节点),
采用Quartz的集群和分布式处理时,我们要了解几点好处
1) 一个节点无法完成的任务,会被集群中拥有相同的任务的节点取代执行。
2) Quartz调度是通过触发器的类别来识别不同的任务,在不同的节点定义相同的触发器的类别,这样在集群下能稳定的运行,一个节点无法完成的任务,会被集群中拥有相同的任务的节点取代执行。
3)分布式 体现在 当相同的任务定时在一个时间点,在那个时间点,不会被两个节点同时执行。
4、Quartz 在集群如何工作:
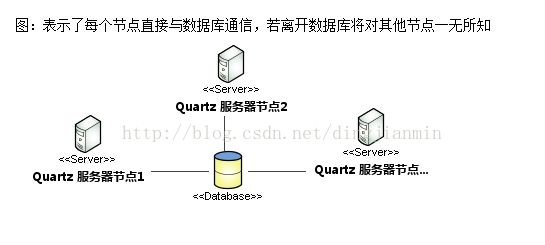
一个 Quartz 集群中的每个节点是一个独立的 Quartz 应用,你必须对每个节点分别启动或停止。
大多数应用服务器的集群,独立的 Quartz 节点并不与另一其的节点或是管理节点通信,彼此相互独立。
Quartz 应用是通过数据库表来感知到另一应用的,调度信息存储在数据库中,当集群定时任务操作数据库(读取任务信息,更新任务信息)
数据库就会被加锁,防止其他相同的任务也读取到该任务,避免任务的重复执行。
因为Quartz 集群依赖于数据库,所以必须首先创建Quartz数据库表。
Quartz 包括了所有被支持的数据库平台的 SQL 脚本。在
Quartz 2.2.3版本,总共11张表,不同版本,表个数可能不同。数据库为mysql,用tables_mysql_innodb.sql创建数据库表,数据库不同选择的建表sql也不同,根据自己选择。
6、环境搭建-配置 Quartz 使用集群
1.配置节点的 quartz.properties 文件
# Configure Main Scheduler Properties
# Needed to manage cluster instances
org.quartz.scheduler.instanceName = TestScheduler1
org.quartz.scheduler.instanceId = AUTO
# Configure ThreadPool
org.quartz.threadPool.class = org.quartz.simpl.SimpleThreadPool
org.quartz.threadPool.threadCount = 10
org.quartz.threadPool.threadPriority = 5
org.quartz.threadPool.threadsInheritContextClassLoaderOfInitializingThread = true
# Configure JobStore
# Using Spring datasource in quartzJobsConfig.xml
# Spring uses LocalDataSourceJobStore extension of JobStoreCMT
org.quartz.jobStore.misfireThreshold = 60000
org.quartz.jobStore.class = org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.JobStoreTX
org.quartz.jobStore.driverDelegateClass=org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.StdJDBCDelegate
org.quartz.jobStore.tablePrefix = QRTZ_
org.quartz.jobStore.maxMisfiresToHandleAtATime=10
org.quartz.jobStore.isClustered = true
org.quartz.jobStore.clusterCheckinInterval = 20000
org.quartz.scheduler.instanceName:
属性可为任何值,用在 JDBC JobStore 中来唯一标识实例,但是所有集群节点中必须相同。
org.quartz.scheduler.instanceId:
属性为 AUTO即可,基于主机名和时间戳来产生实例 ID。
org.quartz.jobStore.class:
属性为 JobStoreTX,将任务持久化到数据中。因为集群中节点依赖于数据库来传播 Scheduler 实例的状态,你只能在使用 JDBC JobStore 时应用 Quartz 集群。
这意味着你必须使用 JobStoreTX 或是 JobStoreCMT 作为 Job 存储;你不能在集群中使用 RAMJobStore。
org.quartz.jobStore.isClustered:
属性为 true,你就告诉了 Scheduler 实例要它参与到一个集群当中。
这一属性会贯穿于调度框架的始终,用于修改集群环境中操作的默认行为。
org.quartz.jobStore.clusterCheckinInterval:
属性定义了Scheduler 实例检入到数据库中的频率(单位:毫秒)。
Scheduler 检查是否其他的实例到了它们应当检入的时候未检入;这能指出一个失败的 Scheduler 实例,且当前 Scheduler 会以此来接管任何执行失败并可恢复的 Job。
通过检入操作,Scheduler 也会更新自身的状态记录。clusterChedkinInterval 越小,Scheduler 节点检查失败的 Scheduler 实例就越频繁。默认值是 15000 (即15 秒)。
7、配置applicationContext-quartz.xml文件,在这里配置任务,数据库连接等
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
0/2 * * * * ?
execute
0/10 * * * * ?
applicationContextSchedulerContextKey:
是org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.SchedulerFactoryBean这个类中把spring上下文以key/value的方式存放在了SchedulerContext中了,
可以用applicationContextSchedulerContextKey所定义的key得到对应spring 的ApplicationContext;
会在后面的类里用到
configLocation:用于指明quartz的配置文件的位置
requestsRecovery:
属性必须设置为 true,当Quartz服务被中止后,再次启动或集群中其他机器接手任务时会尝试恢复执行之前未完成的所有任务。
8、介绍相关的类:
1、
这个类的作用:
/**
* @author
* @description 使我们的任务类支持Spring的自动注入
*/
public class AutowiringSpringBeanJobFactory extends SpringBeanJobFactory
implements ApplicationContextAware {
private transient AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory;
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext)
throws BeansException {
beanFactory = applicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory();
}
@Override
protected Object createJobInstance(TriggerFiredBundle bundle)
throws Exception {
Object job = super.createJobInstance(bundle);
beanFactory.autowireBean(job);
return job;
}
}调用我们任务类的实现:
/**
* @author
* @description 当前任务是每隔一定时间打印当前的时间
*/
public class PrintCurrentTimeJobs extends QuartzJobBean {
private static final Log LOG_RECORD = LogFactory
.getLog(PrintCurrentTimeJobs.class);
/*
* 这里就是因为有上文中的AutowiringSpringBeanJobFactory才可以使用像@Autowired的注解,当然还可以使用Spring的其他注解
* 否则只能在配置文件中设置这属性的值,另一种方式下面说到
*/
@Autowired
private ClusterQuartz clusterQuartz;
protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext jobExecutionContext)
throws JobExecutionException {
LOG_RECORD.info("begin to execute task,"
+ DateUtil.dateFmtToString(new Date()));
//我们真正要执行的任务
clusterQuartz.printUserInfo();
LOG_RECORD.info("end to execute task,"
+ DateUtil.dateFmtToString(new Date()));
}
}
我们定时任务的具体逻辑实现:(我们很熟悉的Spring,注解开发)
@Service("ClusterQuartz")
public class ClusterQuartz {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(ClusterQuartz.class);
/*在这里可以使用spring的注解,引入各种服务之类的*/
/*@Resource(name = "miService")
private MiService miService;
@Autowired
private PushServiceI pushRecordService;*/
public void printUserInfo() {
System.out.println("定时任务的实现逻辑代码");
}
}
2、如果不配置上面1的那个property,我们的定时任务这样实现:
//执行定时任务的类
@PersistJobDataAfterExecution
@DisallowConcurrentExecution
// 不允许并发执行
public class MyQuartzJobBean1 extends QuartzJobBean {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(MyQuartzJobBean1.class);
@Override
protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext jobexecutioncontext)
throws JobExecutionException {
SimpleService simpleService = getApplicationContext(jobexecutioncontext)
.getBean("simpleService", SimpleService.class);
//我们定时任务的方法
simpleService.testMethod1();
}
private ApplicationContext getApplicationContext(
final JobExecutionContext jobexecutioncontext) {
try {
//在这里用applicationContextSchedulerContextKey所定义的key得到对应spring 的ApplicationContext;
return (ApplicationContext) jobexecutioncontext.getScheduler()
.getContext().get("applicationContextKey");
} catch (SchedulerException e) {
logger.error(
"jobexecutioncontext.getScheduler().getContext() error!", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
而定时任务的具体逻辑业务,还是和上面的一样。
@Service("simpleService")
public class SimpleService {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SimpleService.class);
public void testMethod1(){
//这里执行定时调度业务
logger.info("testMethod1.......1");
System.out.println("2--testMethod1......."+System.currentTimeMillis()/1000);
}
public void testMethod2(){
logger.info("testMethod2.......2");
}
}9、运行测试Quartz集群定时任务:
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext springContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
new String[] { "classpath:applicationContext.xml",
"classpath:applicationContext-quartz.xml" });
}
}
10、在Spring中使用Quartz有两种方式实现:
第一种是任务类继承QuartzJobBean,第二种则是在配置文件里定义任务类和要执行的方法,类和方法仍然是普通类。
很显然,第二种方式远比第一种方式来的灵活。我们发现上面采用的就是第一种方法,下面说下第二种方法。
1、配置XML如下:
2、任务类:(普通的Java类)
public class SpringQtz {
private static int counter = 0;
protected void execute() {
long ms = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("\t\t" + new Date(ms));
System.out.println("(" + counter++ + ")");
}
}
11、Quartz版本问题:
spring3.1以下的版本必须使用quartz1.x系列,3.1以上的版本才支持quartz 2.x,不然会出错。
不匹配异常:
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.CannotLoadBeanClassException: Error loading class [org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.CronTriggerBean] for bean with name 'mytrigger' defined in class path resource [applicationContext.xml]: problem with class file or dependent class; nested exception is java.lang.IncompatibleClassChangeError: class org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.CronTriggerBean has interface org.quartz.CronTrigger as super class
异常原因:
spring3.0.5中org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.CronTriggerBean继承了org.quartz.CronTrigger(public class CronTriggerBeanextends CronTrigger),
而在quartz2.1.3中org.quartz.CronTrigger是个接口(publicabstract interface CronTrigger extends Trigger),
而在quartz1.8.5及1.8.4中org.quartz.CronTrigger是个类(publicclass CronTrigger extends Trigger),
从而造成无法在applicationContext中配置触发器。这是spring3.1以下版本和quartz2版本不兼容的一个bug。
12、关于cronExpression表达式,这里提一下:
字段 允许值 允许的特殊字符
秒 0-59 , - * /
分 0-59 , - * /
小时 0-23 , - * /
日期 1-31 , - * ? / L W C
月份 1-12 或者 JAN-DEC , - * /
星期 1-7 或者 SUN-SAT , - * ? / L C #
年(可选) 留空, 1970-2099 , - * /
表达式意义
"0 0 12 * * ?" 每天中午12点触发
"0 15 10 ? * *" 每天上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ?" 每天上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ? *" 每天上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ? 2005" 2005年的每天上午10:15触发
"0 * 14 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到下午2:59期间的每1分钟触发
"0 0/5 14 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到下午2:55期间的每5分钟触发
"0 0/5 14,18 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到2:55期间和下午6点到6:55期间的每5分钟触发
"0 0-5 14 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到下午2:05期间的每1分钟触发
"0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED" 每年三月的星期三的下午2:10和2:44触发
"0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI" 周一至周五的上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 15 * ?" 每月15日上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 L * ?" 每月最后一日的上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 ? * 6L" 每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 ? * 6L 2002-2005" 2002年至2005年的每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 ? * 6#3" 每月的第三个星期五上午10:15触发
每天早上6点
0 6 * * *
每两个小时
0 */2 * * *
晚上11点到早上8点之间每两个小时,早上八点
0 23-7/2,8 * * *
每个月的4号和每个礼拜的礼拜一到礼拜三的早上11点
0 11 4 * 1-3
1月1日早上4点
0 4 1 1 *
13、一般applicationContext-quartz.xml的框架配置:
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
14、Quartz运行解释:
Quartz 实际并不关心你是在相同的还是不同的机器上运行节点。
当集群是放置在不同的机器上时,通常称之为水平集群。节点是跑在同一台机器是,称之为垂直集群。
对于垂直集群,存在着单点故障的问题。这对高可用性的应用来说是个坏消息,因为一旦机器崩溃了,所有的节点也就被有效的终止了。
当你运行水平集群时,时钟应当要同步,以免出现离奇且不可预知的行为。
假如时钟没能够同步,Scheduler 实例将对其他节点的状态产生混乱。
有几种简单的方法来保证时钟何持同步,而且也没有理由不这么做。最简单的同步计算机时钟的方式是使用某一个 Internet 时间服务器(Internet Time Server ITS)。
没什么会阻止你在相同环境中使用集群的和非集群的 Quartz 应用。
唯一要注意的是这两个环境不要混用在相同的数据库表。
意思是非集群环境不要使用与集群应用相同的一套数据库表;否则将得到希奇古怪的结果,集群和非集群的 Job 都会遇到问题。
假如你让一个非集群的 Quartz 应用与集群节点并行着运行,设法使用 JobInitializationPlugin和 RAMJobStore。
15、配置数据库连接,
1、通用的
2、JNDI连接数据库
3、Druid连接池(公司用)
在我的资源里上传了上面实例的代码,有需要的支持下,有不当之处,望各位猿友之处,万分感谢。
相信您一定对定时任务又有了深刻的认识
每天努力一点,每天都在进步。