Saiku调用WS接口
关于saiku集成系统单点登录告一段落,始终没想好怎么去做,主要是因为saiku有自己的权限定义,一直没想好关于saiku本身的权限信息以及用户信息怎么处理(在这里笔者希望已实现saiku单点登录的大佬不吝赐教,感激~)
这里实现了在saiku源码里面调用公司内部的WS接口来验证登录时的密码信息(因为saiku本身未使用dubbo,所以无法直接通过maven引入dubbo包去调用接口)
如果已查看了saiku登录源码追踪(十三)我们就已经大概知道saiku登录时代码执行过程啦,接下来我们就来更改这里的密码校验,调用其他组件的WS接口验证登录
>>调用WS接口
1.在saiku-webapp项目下 找到 WEB-INF/applicationContext-spring-security-jdbc.xml 文件
作出以下更改,替换原来的bean信息,将原来的 org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider 类 替换为自己定义的 org.saiku.service.util.security.authentication.UmServiceProvider 类
2.org.saiku.service.util.security.authentication.UmServiceProvider 类定义在saiku-service项目下的 对应包(org.saiku.service.util.security.authentication.)路径下
内容如下:(内容上基本语原来的DaoAuthenticationProvider 保持一致,更改密码校验方法:additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication))
思路: 注释掉源代码中的密码校验方法passwordEncoder.isPasswordValid,
新增自己的密码校验方法: validatePassword(UserDetails userDetails,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication,Object salt)
/*密码校验思路:
1.先判断密码是不是固定密码值,从properties文件中获取的自定义密码信息(我这里是因为嵌入系统时有用到固定密码对应用户以及角色信息气分享saiku数据信息所以才有,如果不需要可以去掉第一个if中的判断 fixedPassword)
2.再判断密码是否满足 WS接口(WS是公司自定义的相关接口信息,通过jar包引入saiku去调用的,下面会做出相应解析)
3.以上两种都不符合时,调用saiku自己的密码校验,如果失败就校验失败了。(以上任意一种校验方式成功都会成功登录哦)
*/
UmServiceProvider.java
package org.saiku.service.util.security.authentication;
import org.saiku.service.util.GetFixedPasswordUtil;
import org.saiku.service.util.UMLoginWSUtil;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.InternalAuthenticationServiceException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.SaltSource;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.encoding.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.encoding.PlaintextPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import com.imodule.ws.soa.um.result.xsd.UmLoginResult;
import clover.org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
public class UmServiceProvider extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider {
// ~ Static fields/initializers
// =====================================================================================
/**
* The plaintext password used to perform
* {@link PasswordEncoder#isPasswordValid(String, String, Object)} on when the user is
* not found to avoid SEC-2056.
*/
private static final String USER_NOT_FOUND_PASSWORD = "userNotFoundPassword";
// ~ Instance fields
// ================================================================================================
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
/**
* The password used to perform
* {@link PasswordEncoder#isPasswordValid(String, String, Object)} on when the user is
* not found to avoid SEC-2056. This is necessary, because some
* {@link PasswordEncoder} implementations will short circuit if the password is not
* in a valid format.
*/
private String userNotFoundEncodedPassword;
private SaltSource saltSource;
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
private GetFixedPasswordUtil getFixedPasswordUtil;
public UmServiceProvider() {
setPasswordEncoder(new PlaintextPasswordEncoder());
}
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
/*密码校验思路: 1.先判断密码是不是固定密码值,从properties文件中获取的自定义密码信息(我这里是因为嵌入系统时有用到固定密码对应用户以及角色信息气分享saiku数据信息所以才有,如果不需要可以去掉第一个if中的判断 fixedPassword)
2.再判断密码是否满足 WS接口(WS是公司自定义的相关接口信息,通过jar包引入saiku去调用的,下面会做出相应解析)
3.以上两种都不符合时,调用saiku自己的密码校验,如果失败就校验失败了。(以上任意一种校验方式成功都会成功登录哦)
*/
private void validatePassword(UserDetails userDetails,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication,Object salt){
getFixedPasswordUtil = new GetFixedPasswordUtil();
UMLoginWSUtil umloginWS = new UMLoginWSUtil();
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString(); // get user input password
String fixedPassword = getFixedPasswordUtil.getSaikuUserPassword();
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(fixedPassword) && fixedPassword.equals(presentedPassword)){
logger.debug("Authentication successs: password match fixed value which store in properties file.");
}else {
//authentication.getName(): user input userid
UmLoginResult umloginResult = umloginWS.getUmLoginWS(authentication.getName(), presentedPassword);
//successs: umloginResult.getResultStatus()=0, fail:umloginResult.getResultStatus()=2
if(umloginResult.getResultStatus().equals("0")){// successs
logger.debug("Authentication success: password match stored value in um Database");
}else{
// if not match properties and um system,use saiku self validator to validate password.
if (!passwordEncoder.isPasswordValid(userDetails.getPassword(),
presentedPassword, salt)) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value(neither in properteis nor um system or saiku db.)");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Object salt = null;
if (this.saltSource != null) {
salt = this.saltSource.getSalt(userDetails);
}
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
validatePassword(userDetails,authentication,salt);
/*if (!passwordEncoder.isPasswordValid(userDetails.getPassword(),
presentedPassword, salt)) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}*/
}
protected void doAfterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(this.userDetailsService, "A UserDetailsService must be set");
}
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
UserDetails loadedUser;
try {
loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
if (authentication.getCredentials() != null) {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
passwordEncoder.isPasswordValid(userNotFoundEncodedPassword,
presentedPassword, null);
}
throw notFound;
}
catch (Exception repositoryProblem) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
repositoryProblem.getMessage(), repositoryProblem);
}
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
/**
* Sets the PasswordEncoder instance to be used to encode and validate passwords. If
* not set, the password will be compared as plain text.
*
* For systems which are already using salted password which are encoded with a
* previous release, the encoder should be of type
* {@code org.springframework.security.authentication.encoding.PasswordEncoder}.
* Otherwise, the recommended approach is to use
* {@code org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder}.
*
* @param passwordEncoder must be an instance of one of the {@code PasswordEncoder}
* types.
*/
public void setPasswordEncoder(Object passwordEncoder) {
Assert.notNull(passwordEncoder, "passwordEncoder cannot be null");
if (passwordEncoder instanceof PasswordEncoder) {
setPasswordEncoder((PasswordEncoder) passwordEncoder);
return;
}
if (passwordEncoder instanceof org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder) {
final org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder delegate = (org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder) passwordEncoder;
setPasswordEncoder(new PasswordEncoder() {
public String encodePassword(String rawPass, Object salt) {
checkSalt(salt);
return delegate.encode(rawPass);
}
public boolean isPasswordValid(String encPass, String rawPass, Object salt) {
checkSalt(salt);
return delegate.matches(rawPass, encPass);
}
private void checkSalt(Object salt) {
Assert.isNull(salt,
"Salt value must be null when used with crypto module PasswordEncoder");
}
});
return;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"passwordEncoder must be a PasswordEncoder instance");
}
private void setPasswordEncoder(PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) {
Assert.notNull(passwordEncoder, "passwordEncoder cannot be null");
this.userNotFoundEncodedPassword = passwordEncoder.encodePassword(
USER_NOT_FOUND_PASSWORD, null);
this.passwordEncoder = passwordEncoder;
}
protected PasswordEncoder getPasswordEncoder() {
return passwordEncoder;
}
/**
* The source of salts to use when decoding passwords. null is a valid
* value, meaning the DaoAuthenticationProvider will present
* null to the relevant PasswordEncoder.
*
* Instead, it is recommended that you use an encoder which uses a random salt and
* combines it with the password field. This is the default approach taken in the
* {@code org.springframework.security.crypto.password} package.
*
* @param saltSource to use when attempting to decode passwords via the
* PasswordEncoder
*/
public void setSaltSource(SaltSource saltSource) {
this.saltSource = saltSource;
}
protected SaltSource getSaltSource() {
return saltSource;
}
public void setUserDetailsService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService) {
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
}
protected UserDetailsService getUserDetailsService() {
return userDetailsService;
}
}
3.关于从配置文件中读取固定密码信息。 saikuUser.properties中读取 fixedPassword
在saiku-service中新建Util类: /saiku-service/src/main/java/org/saiku/service/util/GetFixedPasswordUtil.java
package org.saiku.service.util;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import com.imodule.ws.soa.um.UmSoaPortTypeProxy;
import com.imodule.ws.soa.um.result.xsd.UmLoginResult;
/**
* Get password from properties file,for validate password.
* ps: properties file path keep on with this Class path .
* @author S0111
*
*/
public class GetFixedPasswordUtil {
private String SAIKU_USER_PASSWORD = "saikuUserPassword";
private String FILE_NAME = "saikuUser.properties";
// FileInputStream in = null;
InputStream ins = null;
String saikuUserPassword = null;
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
/**
* Get local password from properties file.
* @return
*/
public String getSaikuUserPassword(){
try{
Properties properties = new Properties();
// ins = new FileInputStream(this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath()+FILE_NAME);
// ins = getClass().getResourceAsStream(FILE_NAME);
ins = GetFixedPasswordUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(FILE_NAME);
properties.load(ins);
saikuUserPassword = properties.getProperty(SAIKU_USER_PASSWORD);
logger.debug("GetFixedPasswordUtil - getSaikuUserPassword ,read the properties file,password value is:"+saikuUserPassword);
}catch(Exception e){
logger.debug("GetFixedPasswordUtil - getSaikuUserPassword failed, Caused by:"+e);
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(ins != null){
try{
ins.close();
}catch(Exception e){
logger.debug("GetFixedPasswordUtil - getSaikuUserPassword failed, Caused by:"+e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return saikuUserPassword;
}
}
相应的在 saiku-service项目中的 src/main/resources目录下新建properties文件: /saiku-service/src/main/resources/saikuUser.properties (这里表示不管啥用户只有是saiku有的用户,使用密码saiku123都能登录saiku)
saikuUserPassword=saiku123
4.关于saiku源码中调用其他WS接口的Util类:/saiku-service/src/main/java/org/saiku/service/util/UMLoginWSUtil.java
package org.saiku.service.util;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import com.imodule.ws.soa.um.UmSoaPortTypeProxy;
import com.imodule.ws.soa.um.result.xsd.UmLoginResult;
/**
* Use UM system login interface to validate userid and password
* @author S0111
*
*/
public class UMLoginWSUtil {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
public UmLoginResult getUmLoginWS(String username ,String password){
UmSoaPortTypeProxy um = new UmSoaPortTypeProxy();
UmLoginResult result = null;
try {
result = um.umLogin(username, password);
logger.debug("UMLoginWSUtil - getUmLoginWS,validate userid and password by UM interface success !!!");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
logger.debug("UMLoginWSUtil - getUmLoginWS,validate userid and password by UM interface failed !!!,Caused by:"+e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
5.关于调用其他WS接口验证
首先需要得到WS接口地址信息: http://11.22.33.44:8080/demo-ws/services/demo-soa?wsdl #这只是个示例地址,每个公司提供的接口地址都不同
验证地址: 在浏览器中输入 http://11.22.33.44:8080/demo-ws/services/demo-soa?wsdl 去访问,正确的WS接口信息会返回
使用Eclipse新建Maven项目 saiku-um-ws (项目命名随自己啦嘻嘻)
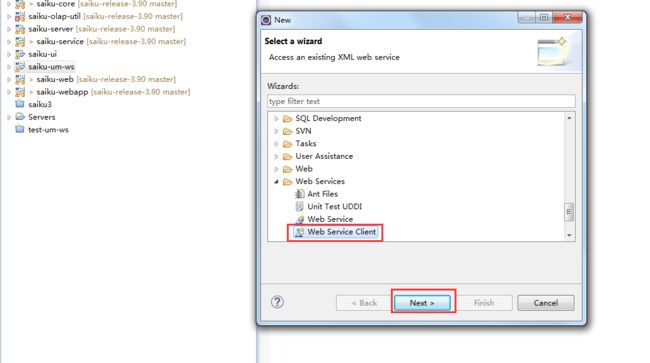
右击新建的羡慕 saiku-um-ws --> new --> others --> 选中下图中的 Web Service Client --> 点击 next
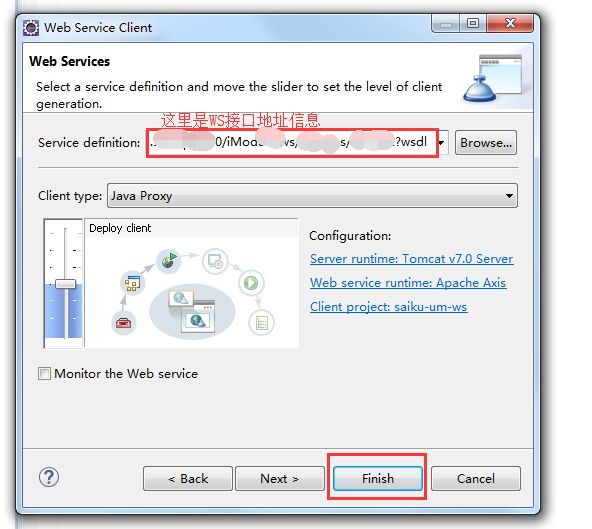
进入如下页面,在Service definition 处输入WS接口地址信息:http://11.22.33.44:8080/demo-ws/services/demo-soa?wsdl 然后点击finish 即可
再进去看就会看到新建的maven项目 saiku-um-ws已经被填充好了
pom.xml中内容如下:
4.0.0 com.saiku.ws saiku-um-ws 1.0 jar saiku-um-ws http://maven.apache.org UTF-8 junit junit 3.8.1 test org.apache.axis axis 1.4 javax.xml jaxrpc-api 1.1 commons-discovery commons-discovery 0.2 commons-logging commons-logging 1.1.1 xml-apis xml-apis 1.4.01 wsdl4j wsdl4j 1.5.1 soap soap 2.3
将saiku-um-ws项目打包: mvn clean install
再将saiku-um-ws相关的依赖引入 saiku-service项目中的 pom.xml即可
com.saiku.ws saiku-um-ws 0.0.1-SNA xml-apis xml-apis 1.4.01
最后,重新编译整个saiku项目, mvn clean install
获取saiku-server下的 target/dist/saiku-server 双击脚本saiku-start.bat 文件 启动saiku就可以啦~~~~~~~~~
======================二次更新 关于ws接口打包后的使用 start 20190627==============================
public class TestLogin {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UmSoaPortTypeProxy um = new UmSoaPortTypeProxy();
UmLoginResult result = null;
try {
result = um.umLogin("test", "111");
System.out.println(result.getResultStatus());
System.out.println(result.getResultStatus().equals("0"));
result = um.umLogin("test", "123");
System.out.println(result.getResultStatus());
System.out.println(result.getResultStatus()=="0");
// logger.debug("UMLoginWSUtil - getUmLoginWS,validate userid and password by UM interface success !!!");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// logger.debug("UMLoginWSUtil - getUmLoginWS,validate userid and password by UM interface failed !!!,Caused by:"+e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("result:"+result);
}
}
======================二次更新 关于ws接口打包后的使用 end 20190627==============================