目录
- 学习《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)》第12、13、14、15章——
- 教材学习中的问题和解决过程
- 代码调试中的问题和解决过程
- [代码托管]
- statistics.sh脚本运行结果的截图
- 上周考试错题总结
- 学习进度条
- 参考资料
学习《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)》第12、13、14、15章——
第12章枚举
12.1概览
1.在保证变量只能被赋给一个有效值这方面,enum比静态final更好。枚举值是一个对象,它会编译为一个.class文件,并且其行为就像对象一样,例如,可以将其用作一个Map键。
12.6枚举成员
1.enum是一个类,它的构造方法必须是私有的或者默认的。如果一个enum定义包含常量以外的其他内容,常量必须在其他内容之前定义,并且最后的常量用一个分号结束。
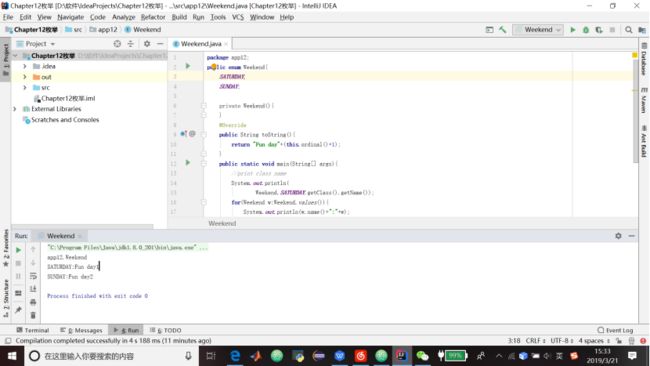
代码清单12.5 Weekend enum
package app12;
public enum Weekend{
SATURDAY;
SUNDAY;
private Weekend(){
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Fun day"+(this.ordinal()+1);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
//print class name
System.out.println(
Weekend.SATURDAY.getClass().getName());
for(Weekend w:Weekend.values()){
System.out.println(w.name()+":"+w);
}
}
}2.可以给构造方法传递值,在这种情况下,常量必须带着构造方法的参数。
代码清单12.6 FuelEfficiency enum
package com.example;
public enum FuelEfficiency{
EFFICIENT(33,55),
ACCEPTABLE(20,32),
GAS_GUZZLER(1,19);
private int min;
private int max;
FuelEfficiency(int min,int max){
this.min=min;
this.max=max;
}
public int getMin(){
return this.min;
}
public int getMax(){
return this.max;
}
}第13章 操作日期和时间
13.2 Instant类
1.Instant对象表示时间线上的一个时间点。引用的时间点是一个标准的Java新纪元时间,也就是1970-01-01 T00:00:00Z(GMT1970年1月1日00:00)。Instant类的EPOCH字段,返回了表示Java新纪元时间的一个Instant。新纪元时间之后的Instant为正值,而新纪元之前的Instant为负值。
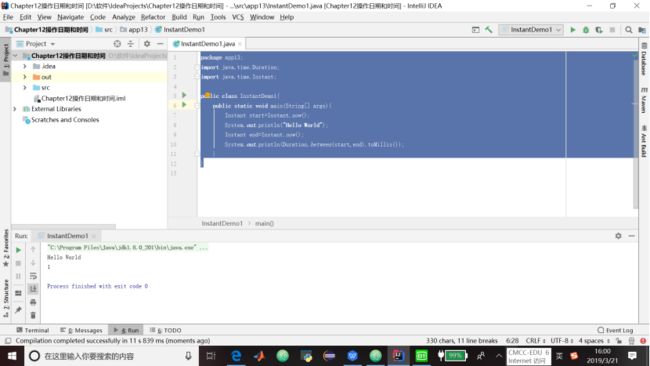
代码清单13.1 使用Instant来计时一项操作
package app13;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.Instant;
public class InstantDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
Instant start=Instant.now();
System.out.println("Hello World");
Instant end=Instant.now();
System.out.println(Duration.between(start,end).toMillis());
}
}13.3 LocalDate
1.LocalDate类建模了没有时间部分的日期。
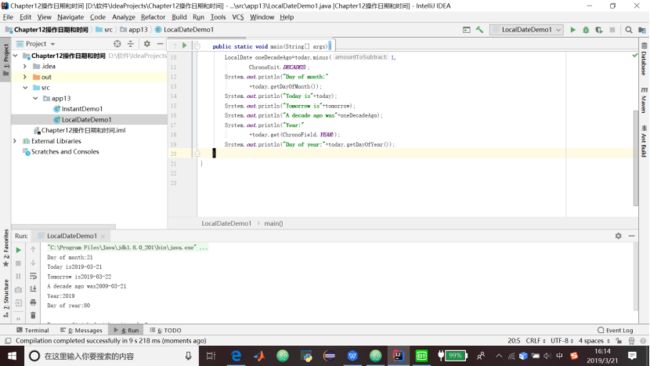
代码清单13.2 LocalDate示例
package app13;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoField;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
public class LocalDateDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
LocalDate today=LocalDate.now();
LocalDate tomorrow=today.plusDays(1);
LocalDate oneDecadeAgo=today.minus(1,
ChronoUnit.DECADES);
System.out.println("Day of month:"
+today.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println("Today is"+today);
System.out.println("Tomorrow is"+tomorrow);
System.out.println("A decade ago was"+oneDecadeAgo);
System.out.println("Year:"
+today.get(ChronoField.YEAR));
System.out.println("Day of year:"+today.getDayOfYear());
}
}13.4 Period
1.Period类表示基于日期的一个时间量。
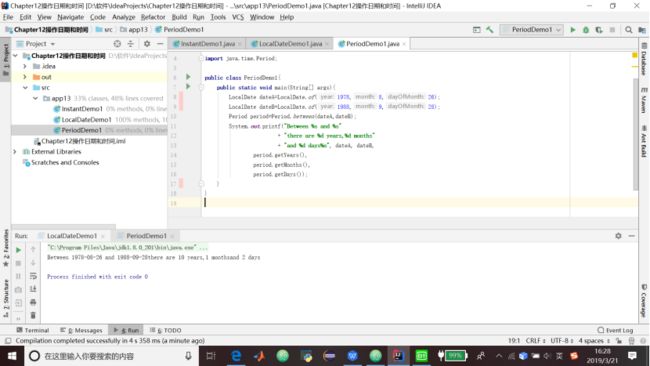
代码清单13.3 使用Period
import java.time.Period;
public class PeriodDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
LocalDate dateA=LocalDate.of(1978,8,26);
LocalDate dateB=LocalDate.of(1988,9,28);
Period period=Period.between(dateA,dateB);
System.out.printf("Between %s and %s"
+ "there are %d years,%d months"
+ "and %d days%n", dateA, dateB,
period.getYears(),
period.getMonths(),
period.getDays());
}
}13.5 LocalDateTime
1.LocalDateTime类表示一个没有时区的日期时间。
13.6 时区
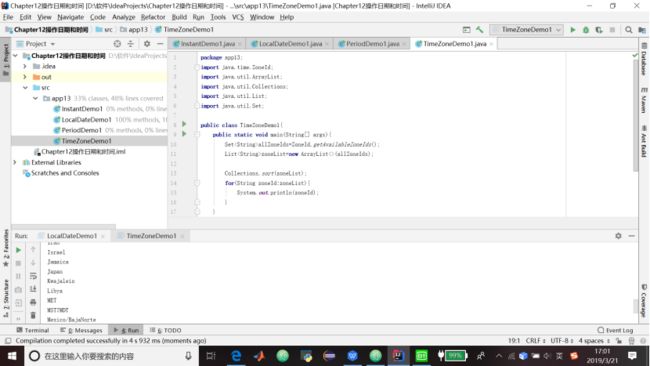
1.代码清单13.4 列出所有的时区标识符
package app13;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
public class TimeZoneDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
SetallZoneIds=ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();
ListzoneList=new ArrayList<>(allZoneIds);
Collections.sort(zoneList);
for(String zoneId:zoneList){
System.out.println(zoneId);
}
}
} 13.7 ZonedDateTime
1.ZonedDateTime类表示带有时区的日期时间。
13.8 Duration
1.Duration类表示基于时间的时间段。它类似于Period,只不过Duration的时间部分精确到纳秒,并且考虑到了ZonedDateTimes之间的时区。
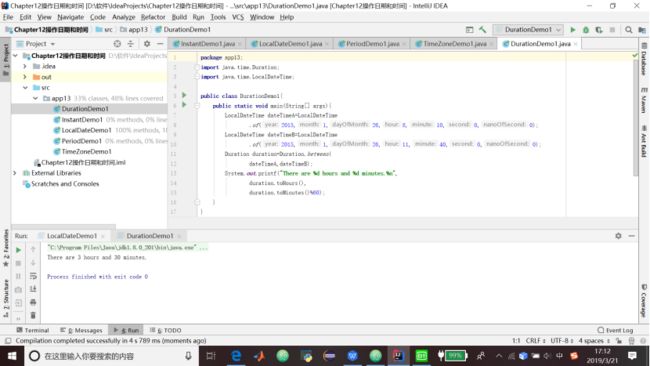
2.代码清单13.5 创建两个LocalDateTime之间的一个Duration
package app13;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class DurationDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
LocalDateTime dateTimeA=LocalDateTime
.of(2015,1,26,8,10,0,0);
LocalDateTime dateTimeB=LocalDateTime
.of(2015,1,26,11,40,0,0);
Duration duration=Duration.between(
dateTimeA,dateTimeB);
System.out.printf("There are %d hours and %d minutes.%n",
duration.toHours(),
duration.toMinutes()%60);
}
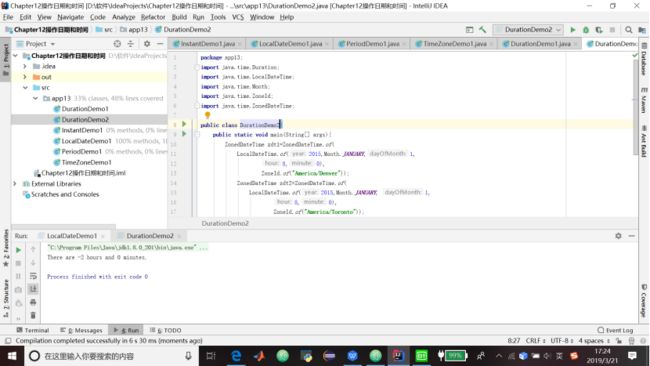
}3.代码清单13.6 创建两个ZoneDateTime之间的一个Duration
package app13;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.Month;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class DurationDemo2{
public static void main(String[] args){
ZonedDateTime zdt1=ZonedDateTime.of(
LocalDateTime.of(2015,Month.JANUARY,1,
8,0),
ZoneId.of("America/Denver"));
ZonedDateTime zdt2=ZonedDateTime.of(
LocalDateTime.of(2015,Month.JANUARY, 1,
8,0),
ZoneId.of("America/Toronto"));
Duration duration=Duration.between(zdt1,zdt2);
System.out.printf("There are %d hours and %d minutes.%n",
duration.toHours(),
duration.toMinutes()%60);
}
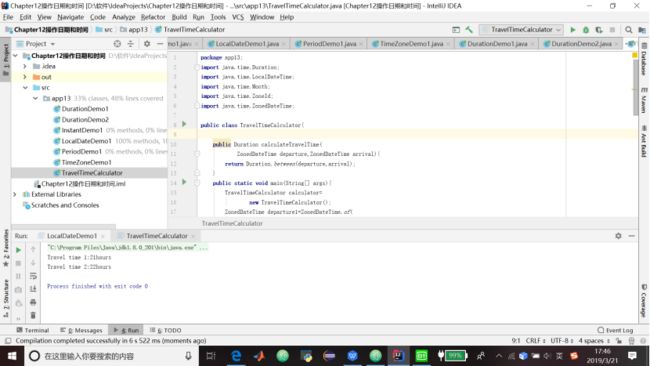
}4.代码清单13.7 旅行时间计算器
package app13;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.Month;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class TravelTimeCalculator{
public Duration calculateTravelTime(
ZonedDateTime departure,ZonedDateTime arrival){
return Duration.between(departure,arrival);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
TravelTimeCalculator calculator=
new TravelTimeCalculator();
ZonedDateTime departure1=ZonedDateTime.of(
LocalDateTime.of(2014,Month.MARCH,8,
8,0),
ZoneId.of("America/Denver"));
ZonedDateTime arrival1=ZonedDateTime.of(
LocalDateTime.of(2014,Month.MARCH,9,
8,0),
ZoneId.of("America/Toronto"));
Duration travelTime1=calculator
.calculateTravelTime(departure1,arrival1);
System.out.println("Travel time 1:"
+travelTime1.toHours()+"hours");
ZonedDateTime departure2=ZonedDateTime.of(
LocalDateTime.of(2014,Month.MARCH,18,
8,0),
ZoneId.of("America/Denver"));
ZonedDateTime arrival2=ZonedDateTime.of(
LocalDateTime.of(2014,Month.MARCH,19,
8,0),
ZoneId.of("America/Toronto"));
Duration travelTime2=calculator
.calculateTravelTime(departure2,arrival2);
System.out.println("Travel time 2:"
+travelTime2.toHours()+"hours");
}
}13.9 格式化日期时间
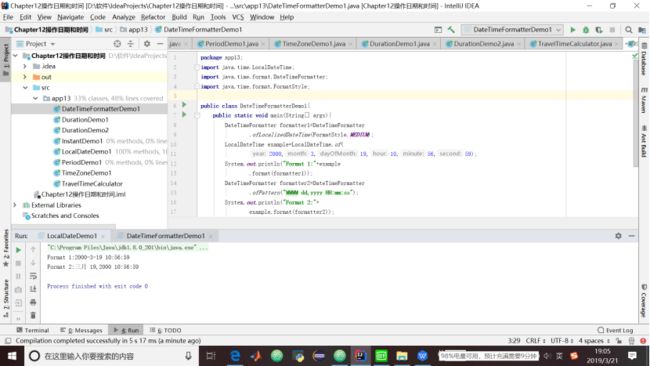
1.代码清单13.8 格式化日期
package app13;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.format.FormatStyle;
public class DateTimeFormatterDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
DateTimeFormatter formatter1=DateTimeFormatter
.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.MEDIUM);
LocalDateTime example=LocalDateTime.of(
2000,3,19,10,56,59);
System.out.println("Format 1:"+example
.format(formatter1));
DateTimeFormatter formatter2=DateTimeFormatter
.ofPattern("MMMM dd,yyyy HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("Format 2:"+
example.format(formatter2));
}
}13.10 解析一个日期时间
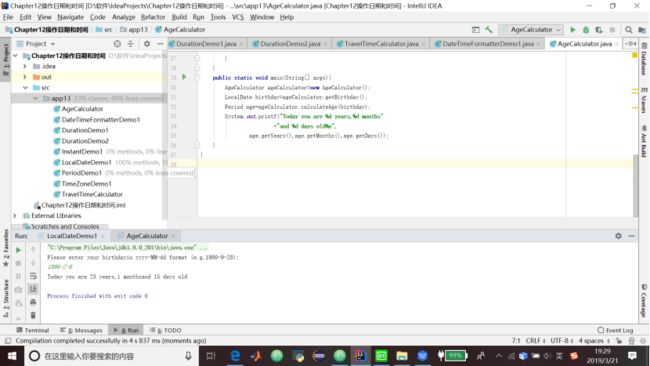
1.代码清单13.9 一个年龄计算器
package app13;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.format.DateTimeParseException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AgeCalculator {
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-M-d");
public Period calculateAge(LocalDate birthday){
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
return Period.between(birthday,today);}
public LocalDate getBirthday(){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
LocalDate birthday;
while(true){
System.out.println("Please enter your birthday"
+"in yyyy-MM-dd format (e.g.1980-9-28):");
String input=scanner.nextLine();
try{
birthday=LocalDate.parse(input,formatter);
return birthday;
}catch(DateTimeParseException e){
System.out.println("Error!Please try again");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AgeCalculator ageCalculator=new AgeCalculator();
LocalDate birthday=ageCalculator.getBirthday();
Period age=ageCalculator.calculateAge(birthday);
System.out.printf("Today you are %d years,%d months"
+"and %d days old%n",
age.getYears(),age.getMonths(),age.getDays());
}
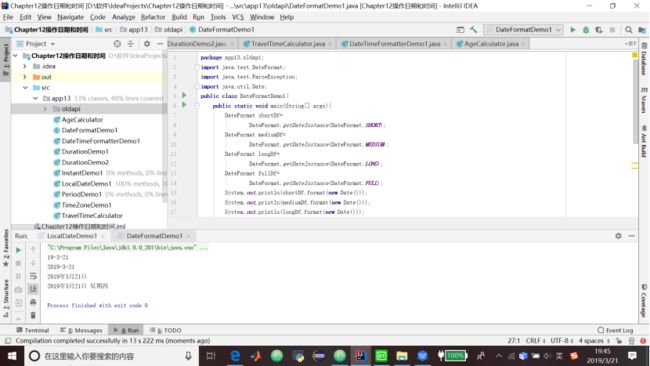
}13.11.3 使用DateFormat解析和格式化
1.DateFormat是一个抽象类,带有静态的getInstance方法,它允许获取子类的一个实例。
代码清单13.10 DateFormatDemo1类
package app13.oldapi;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateFormatDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
DateFormat shortDf=
DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.SHORT);
DateFormat mediumDf=
DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM);
DateFormat longDf=
DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.LONG);
DateFormat fullDf=
DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.FULL);
System.out.println(shortDf.format(new Date()));
System.out.println(mediumDf.format(new Date()));
System.out.println(longDf.format(new Date()));
System.out.println(fullDf.format(new Date()));
//parsing
try{
Date date=shortDf.parse("12/12/2016");
}catch(ParseException e){
}
}
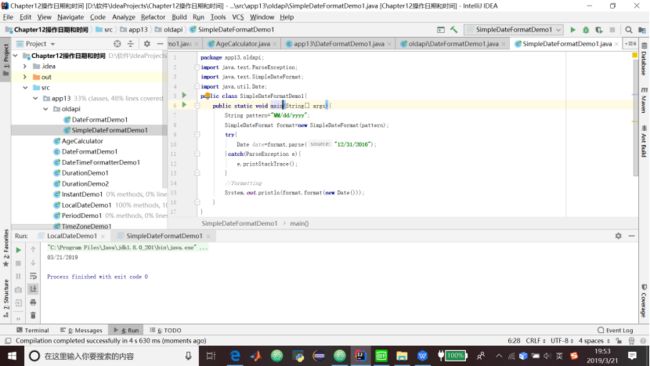
}3.可以使用SimpleDateFormat来解析和格式化日期。较为常用的模式是:使用y(表示一个年份数字)、M(表示一个月份数字)和d(表示一个日期数字)的一种组合。
代码清单13.11 SimpleDateFormatDemo1类
package app13.oldapi;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class SimpleDateFormatDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
String pattern="MM/dd/yyyy";
SimpleDateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);
try{
Date date=format.parse("12/31/2016");
}catch(ParseException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//formatting
System.out.println(format.format(new Date()));
}
}第14章集合框架
14.1 集合框架概览
1.由于数组缺乏快速开发应用程序所需要的灵活性,例如,数组不能修改其大小。所以要使用接口和类,使得操作成组的对象更为容易。
2.集合框架的核心类型是java.util.Collection接口,它有三个直接的子接口:List、Set和Queue。每种子类型都带有几个实现。有同步的实现和非同步的实现两种。通常更倾向于使用非同步的实现,因为它们更快;还有一个Map接口,用于存储键/值对。Map的两个主要实现是HashMap和Hashtable。HashMap比Hashtable更快,因为HashMap是非同步的,而Hashtable是同步的;java.lang.Comparable和java.util.Comparator接口使得对象可以比较且可以排序。
14.3 List和ArrayList
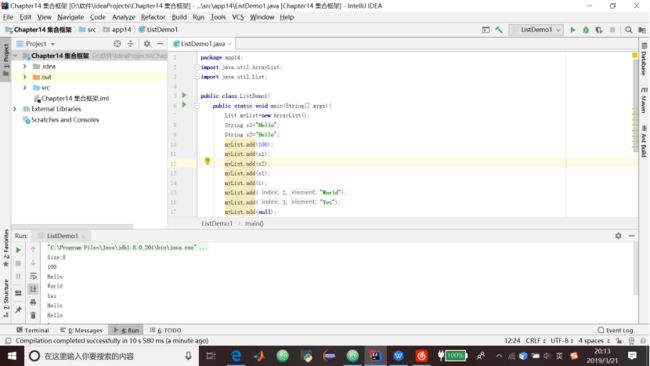
1.List是Collection最为常用的接口,而ArrayList是最为常用的List的实现。List又叫作序列,它是一个有序的集合。List使用add方法在任何位置插入一个元素,使用set和remove来替换和删除一个角色。
2.代码清单14.1 使用List
package app14;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ListDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
List myList=new ArrayList();
String s1="Hello";
String s2="Hello";
myList.add(100);
myList.add(s1);
myList.add(s2);
myList.add(s1);
myList.add(1);
myList.add(2,"World");
myList.add(3,"Yes");
myList.add(null);
System.out.println("Size:"+myList.size());
for(Object object:myList){
System.out.println(object);
}
}
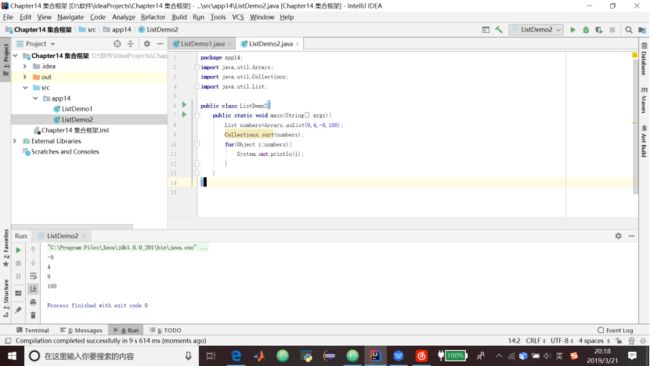
}4.代码清单14.2 排序一个List
package app14;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class ListDemo2{
public static void main(String[] args){
List numbers=Arrays.asList(9,4,-9,100);
Collections.sort(numbers);
for(Object i:numbers){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}14.6 Queue和LinkedList
1.Queue通过添加支持按照先进先出(FIFO)的方式排序元素的方法,扩展了Collection。
14.9 使得对象可比较和可排序
14.9.1 使用java.lang.Comparable
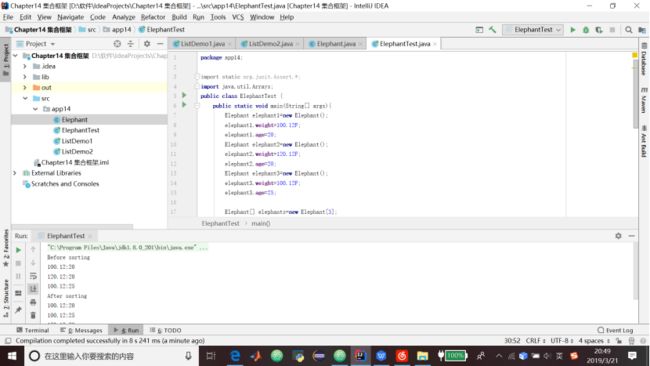
1.代码清单14.5 实现了Comparable的Elephant类及其测试类
package app14;
public class Elephant implements Comparable{
public float weight;
public int age;
public float tuskLength;
public int compareTo(Object obj){
Elephant anotherElephant=(Elephant)obj;
if(this.weight>anotherElephant.weight){
return 1;
}else if (this.weightpublic static void main(String[] args){
Elephant elephant1=new Elephant();
elephant1.weight=100.12F;
elephant1.age=20;
Elephant elephant2=new Elephant();
elephant2.weight=120.12F;
elephant2.age=20;
Elephant elephant3=new Elephant();
elephant3.weight=100.12F;
elephant3.age=25;
Elephant[] elephants=new Elephant[3];
elephants[0]=elephant1;
elephants[1]=elephant2;
elephants[2]=elephant3;
System.out.println("Before sorting");
for(Elephant elephant:elephants){
System.out.println(elephant.weight+":"+
elephant.age);
}
Arrays.sort(elephants);
System.out.println("After sorting");
for(Elephant elephant:elephants){
System.out.println(elephant.weight+":"+
elephant.age);
}
}
}14.9.2 使用Comparator
1.代码清单14.7 实现了Comparable的Person类
package app14;
public class Person implements Comparable{
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private int age;
public String getFirstName(){
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName(){
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName){
this.lastName=lastName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName){
this.firstName=firstName;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age=age;
}
public int compareTo(Object anotherPerson)
throws ClassCastException{
if(!(anotherPerson instanceof Person)){
throw new ClassCastException(
"A Person Object expected.");
}
int anotherPersonAge=((Person)anotherPerson).getAge();
return this.age - anotherPersonAge;
}
}2.代码清单14.8 LastNameComparator类
package app14;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class LastNameComparator implements Comparator{
public int compare(Object person,Object anotherPerson){
String lastName1=((Person)
person).getLastName().toUpperCase();
String firstName1=((Person)
person).getFirstName().toUpperCase();
String lastName2=((Person)
person).getLastName().toUpperCase();
String firstName2=((Person)
person).getFirstName().toUpperCase();
if(lastName1.equals(lastName2)){
return firstName1.compareTo(firstName2);
}else{
return firstName1.compareTo(lastName2);
}
}
}3.代码清单14.9 FirstNameComparator类
package app14;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class FirstNameComparator implements Comparator{
public int compare(Object person,Object anotherPerson){
String lastName1=((Person)person).getLastName().toUpperCase();
String firstName1=((Person)person).getFirstName().toUpperCase();
String lastName2=((Person)person).getLastName().toUpperCase();
String firstName2=((Person)person).getFirstName().toUpperCase();
if(firstName1.equals(firstName2)){
return lastName1.compareTo(lastName2);
}else{
return firstName1.compareTo(firstName2);
}
}
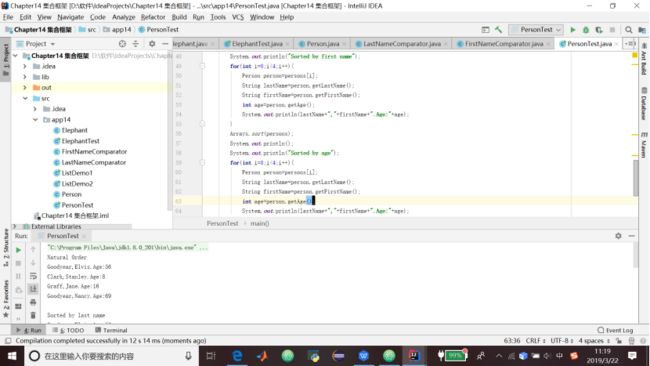
}4.代码清单14.10 PersonTest类
package app14;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
Person[] persons=new Person[4];
persons[0]=new Person();
persons[0].setFirstName("Elvis");
persons[0].setLastName("Goodyear");
persons[0].setAge(56);
persons[1]=new Person();
persons[1].setFirstName("Stanley");
persons[1].setLastName("Clark");
persons[1].setAge(8);
persons[2]=new Person();
persons[2].setFirstName("Jane");
persons[2].setLastName("Graff");
persons[2].setAge(16);
persons[3]=new Person();
persons[3].setFirstName("Nancy");
persons[3].setLastName("Goodyear");
persons[3].setAge(69);
System.out.println("Natural Order");
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
Person person=persons[i];
String lastName=person.getLastName();
String firstName=person.getFirstName();
int age=person.getAge();
System.out.println(lastName+","+firstName+".Age:"+age);
}
Arrays.sort(persons,new LastNameComparator());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Sorted by last name");
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
Person person=persons[i];
String lastName=person.getLastName();
String firstName=person.getFirstName();
int age=person.getAge();
System.out.println(lastName+","+firstName+".Age:"+age);
}
Arrays.sort(persons,new FirstNameComparator());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Sorted by first name");
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
Person person=persons[i];
String lastName=person.getLastName();
String firstName=person.getFirstName();
int age=person.getAge();
System.out.println(lastName+","+firstName+".Age:"+age);
}
Arrays.sort(persons);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Sorted by age");
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
Person person=persons[i];
String lastName=person.getLastName();
String firstName=person.getFirstName();
int age=person.getAge();
System.out.println(lastName+","+firstName+".Age:"+age);
}
}
}第15章泛型
通过泛型,我们可以编写一个参数化的类型,并且通过传递一种或多种引用类型来创建该类型的实例。对象会将其限定为该类型。泛型的第一个好处是在编译时进行较为严格的类型检查。此外,泛型避免了在使用集合框架的时候必须执行的大多数类型强制装换。
15.2 泛型类型
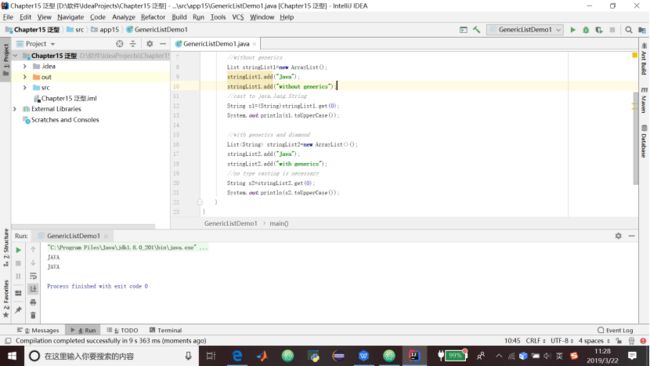
1.代码清单15.1 使用泛型List
package app15;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GenericListDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
//without generics
List stringList1=new ArrayList();
stringList1.add("Java");
stringList1.add("without generics");
//cast to java.lang.String
String s1=(String)stringList1.get(0);
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());
//with generics and diamond
List stringList2=new ArrayList<>();
stringList2.add("Java");
stringList2.add("with generics");
//no type casting is necessary
String s2=stringList2.get(0);
System.out.println(s2.toUpperCase());
}
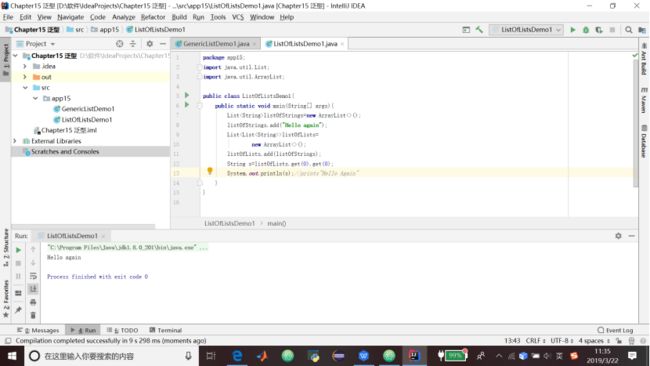
} 15.2 操作List的List
package app15;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ListOfListsDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
ListlistOfStrings=new ArrayList<>();
listOfStrings.add("Hello again");
List>listOfLists=
new ArrayList<>();
listOfLists.add(listOfStrings);
String s=listOfLists.get(0).get(0);
System.out.println(s);//prints"Hello Again"
}
} 3.使用泛型Map
package app15;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapDemo1{
public static void main(String[] args){
Mapmap=new HashMap<>();
map.put("key1","value1");
map.put("key2","value2");
String value1=map.get("key1");
}
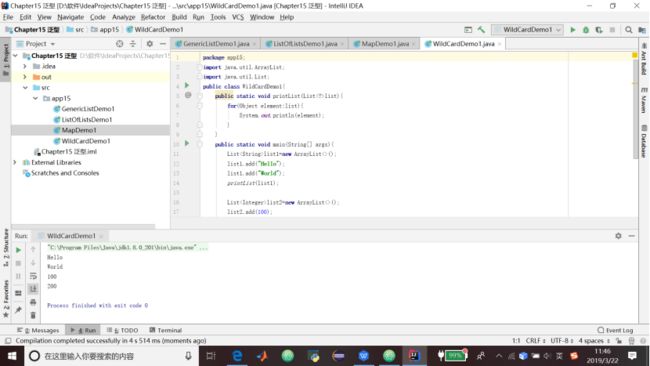
} 15.4 使用?通配符
1.代码清单15.5 使用?通配符
package app15;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class WildCardDemo1{
public static void printList(Listlist){
for(Object element:list){
System.out.println(element);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Listlist1=new ArrayList<>();
list1.add("Hello");
list1.add("World");
printList(list1);
Listlist2=new ArrayList<>();
list2.add(100);
list2.add(200);
printList(list2);
}
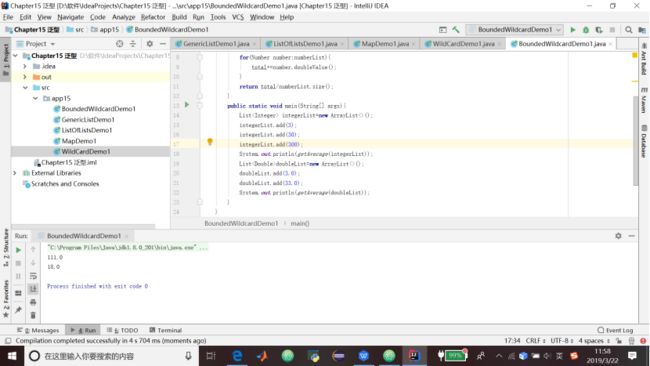
} 15.5 在方法中使用界限通配符
1.代码清单15.6 使用一个界限通配符(一个方法接收不同类型的List)
package app15;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class BoundedWildcardDemo1{
public static double getAverage(
ListnumberList){
double total=0.0;
for(Number number:numberList){
total+=number.doubleValue();
}
return total/numberList.size();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
List integerList=new ArrayList<>();
integerList.add(3);
integerList.add(30);
integerList.add(300);
System.out.println(getAverage(integerList));
ListdoubleList=new ArrayList<>();
doubleList.add(3.0);
doubleList.add(33.0);
System.out.println(getAverage(doubleList));
}
} 15.7 编写泛型类型
1.代码清单15.7 generic Point类
package app15;
public class Point{
T x;
T y;
public Point(T x,T y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public T getx(){
return x;
}
public T gety(){
return y;
}
public void setX(T x){
this.x=x;
}
public void setY(T y){
this.y=y;
}
} 教材学习中的问题和解决过程
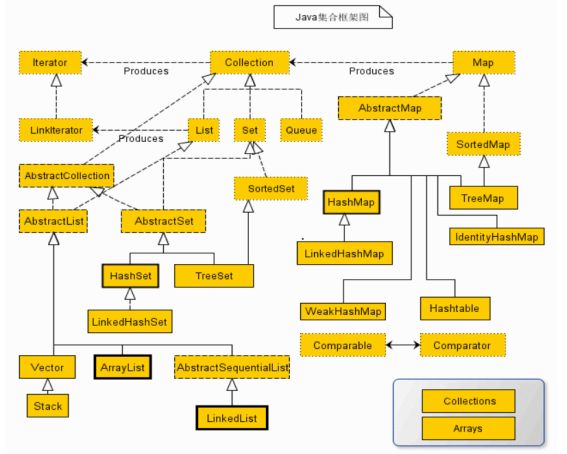
1.所有集合类都位于java.util包下。Java的集合类主要由两个接口派生而出:Collection和Map,Collection和Map是Java集合框架的根接口,这两个接口又包含了一些子接口或实现类。
- 集合接口:6个接口(短虚线表示),表示不同集合类型,是集合框架的基础。
- 抽象类:5个抽象类(长虚线表示),对集合接口的部分实现。可扩展为自定义集合类。
- 实现类:8个实现类(实线表示),对接口的具体实现。
- Collection 接口是一组允许重复的对象。
- Set 接口继承 Collection,集合元素不重复。
- List 接口继承 Collection,允许重复,维护元素插入顺序。
- Map接口是键-值对象,与Collection接口没有什么关系。
9.Set、List和Map可以看做集合的三大类:
List集合是有序集合,集合中的元素可以重复,访问集合中的元素可以根据元素的索引来访问。
Set集合是无序集合,集合中的元素不可以重复,访问集合中的元素只能根据元素本身来访问(也是集合里元素不允许重复的原因)。
Map集合中保存Key-value对形式的元素,访问时只能根据每项元素的key来访问其value。
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:对Android Studio不够了解
- 问题1解决方案:下载和安装Android Studio
[代码托管]
https://gitee.com/EvelynYang/9230/tree/master/src
statistics.sh脚本运行结果的截图
上周考试错题总结
14.p75 代码清单6.1中 Arrays.binarySearch(primes,19)的值是()
A .5
B .6
C .7
D .8
正确答案: C 我的答案: D
16.String [] name = new String[4];执行完创建()个String对象。
A .4
B .0
C .2
D .1
27.double d = 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1, System.out.println(i);的结果是0.3.
A .正确
B .错误
正确答案: B 我的答案: A
28.~0b1011的十进制值是( )
A .-12
B .-13
C .-10
D .-11
正确答案: A 我的答案: D
29.jdb命令中list找不到源代码,要用()命令设置环境变量。
A .use
B .sourcepath
C .trace
D .list
正确答案: A B 我的答案: B
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 200/200 | 2/2 | 20/20 | |
| 第二周 | 300/500 | 1/3 | 18/38 | |
| 第三周 | 500/1000 | 1/4 | 38/76 | |
| 第四周 | 1000/2000 | 1/5 | 20/96 |
参考资料
- 《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(Java for Android.2nd)》
-[Java集合框架综述](https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxi/p/6089984.html)