类命名空间
在一个类中它的函数(方法)属于动态属性,直接定义的变量属于静态属性
首先先定义一个类,并在这个类里面加入静态变量、属性等然后将一个对象实例化
class Fighter: #定义一个战机的类 price = 5000 #静态变量 def __init__(self,name,speed,atk,hp): self.name = name self.speed = speed self.atk = atk self.hp = hp def Attack(self): print('本次攻击造成了%s的伤害'%(self.atk)) f1 = Fighter('J-20',1000,400,5000) print(f1.__dict__) #{'name': 'J-20', 'speed': 1000, 'atk': 400, 'hp': 5000}
那如何修改一个静态属性,我们可以用类名.静态变量名等于我们想要赋值的内容就可以修改
Fighter.price = 4500 print(Fighter.__dict__) #{'__module__': '__main__', 'price': 4500,
'__init__':,
'Attack':,
'__dict__':,
'__weakref__':, '__doc__': None}
如果我们用__dict__方法去修改结果是不行的
Fighter.__dict__['price'] = 2500 print(Fighter.__dict__) #TypeError: 'mappingproxy' object does not support item assignment
关系图:
当我们使用f1.price的时候,f1会先在自己的命名空间去找,它会发现自己的内存空间里没有这个price,然后在通过类对象指针找到Fighter的命名空间,取得price这个变量
而Fighter.price是直接从自己的命名空间中取得,找到就返回
注意:只有实例化出来的对象才能找到类,而类并不能找到每一个对象
如果我们想用实例化出来的一个对象去修改类里面的静态变量,该怎么做?
可以看出在这里直接修改这个静态变量我们并没有修改成功,而是在我们的这个self;'字典'里新增了一个price属性
f1.price = 4500 print(f1.__dict__) #{'name': 'J-20', 'speed': 1000, 'atk': 400, 'hp': 5000, 'price': 4500} print(Fighter.__dict__) #{'__module__': '__main__', 'price': 5000,
'__init__':, 'Attack':, '__dict__': '__dict__' of 'Fighter' objects>, '__weakref__': '__weakref__' of 'Fighter' objects>, '__doc__': None}
那么再想用回类里面的静态变量的话只能删除price
del f1.price print(f1.price) #5000 print(f1.__dict__) #{'name': 'J-20', 'speed': 1000, 'atk': 400, 'hp': 5000}
对于像上面这种不可变数据类型而言,类变量最好用类操作
现在我们把这个静态变量改成列表的类型,可以看到我们运用修改索引值的方式成功修改了原来的列表的元素
class Fighter: #定义一个战机的类 price = [5000] #静态变量 def __init__(self,name,speed,atk,hp): self.name = name self.speed = speed self.atk = atk self.hp = hp def Attack(self): print('本次攻击造成了%s的伤害'%(self.atk)) f1 = Fighter('J-20',1000,400,5000) f1.price[0] = 6000 print(f1.__dict__) #{'name': 'J-20', 'speed': 1000, 'atk': 400, 'hp': 5000} print(Fighter.__dict__) #{'__module__': '__main__', 'price': [6000], '__init__':, 'Attack':, '__dict__': '__dict__' of 'Fighter' objects>, '__weakref__': '__weakref__' of 'Fighter' objects>, '__doc__': None}
这是因为像这种可变数据类型(列表),它所改变的值不影响它本身的内存地址,像price它所指向的还是列表这个内存地址,所以改变了它的内部的值不会有太大的影响
但是如果我们这样写的话就相当于开辟了一个新的内存空间存放新的列表了
f1.price = [6000] print(f1.__dict__) #{'name': 'J-20', 'speed': 1000, 'atk': 400, 'hp': 5000, 'price': [6000]} print(Fighter.__dict__) #{'__module__': '__main__', 'price': [5000], '__init__':,
'Attack':,
'__dict__':,
'__weakref__':, '__doc__': None}
最后静态变量和函数名不要相同
一个例子:创建一个类,每实例化一个对象就计数,最终所有的对象都共享这个数据
class Counter(): count = 0 def __init__(self): Counter.count += 1 print(Counter.count) #0 c1 = Counter() print(Counter.count) #1 c2 = Counter() print(Counter.count) #2
绑定方法:
一个类没有__init__也可以实例化,self仍能把自己传给f1
class Person: def fuc(self): print('Walking...') f1 = Person() print(f1.__dict__) #{} f1.fuc() #Walking...
现在再定义一个函数
def func(): print('Testing...') class Person: def fuc(self): print('Walking...') f1 = Person() print(func) #print(Person.fuc) # print(f1.fuc) # > print(f1) #<__main__.Person object at 0x0000000002737A58>
当对象去调用方法的时候就是把里面的值传给这个方法那么他们之间就发生了一种绑定关系
import
当我们引入一个包的时候就相当于实例化了一个对象
组合
表示在一个类中以另外一个类的对象作为数据属性,称为类的组合
我们先声明三个类玩家的战机类、敌机的类和武器的类:
class Fighter: #定义一个玩家战机的类 def __init__(self,name,atk,hp,speed,money): self.name = name self.atk = atk self.hp = hp self.speed = speed self.money = 0 def playerAttack(self,enemyfighter): enemyfighter.hp -= self.atk class EnemyFighter: #定义个敌机的类 def __init__(self,name,atk,hp,speed,kind): self.name = name self.atk = atk self.hp = hp self.speed = speed self.kind = kind def enemyFighterAttack(self,fighter): fighter.hp -= self.atk class Weapon: #定义一个武器的类 def __init__(self,name,atk,durability,price): self.name = name self.atk = atk self.durability = durability self.price = price playerFighter1 = Fighter('Player1',200,1500,300,0) Boss1 = EnemyFighter('lazerBoss',1000,7000,50,'Boss') w1 = Weapon('AMR-123',1000,10,300) print(w1.__dict__) #{'name': 'AMR-123', 'atk': 1000, 'durability': 10, 'price': 300} print(Boss1.__dict__) #{'name': 'lazerBoss', 'atk': 1000, 'hp': 7000, 'speed': 50, 'kind': 'Boss'} print(playerFighter1.__dict__) #{'name': 'Player1', 'atk': 200, 'hp': 1500, 'speed': 300, 'money': 0}
如何将我们的装备装备到我们玩家的战机上?在玩家的身上写一个get_weapon函数让一个武器的对象作为参数传给这个函数,再让玩家或得到武器的这些属性
class Fighter: #定义一个玩家战机的类 def __init__(self,name,atk,hp,speed,money = 0): self.name = name self.atk = atk self.hp = hp self.speed = speed self.money = money def playerAttack(self,enemyfighter): enemyfighter.hp -= self.atk def get_weapon(self,weapon): #玩家获得武器属性的函数 if self.money >= weapon.price: #如果玩家的金钱大于武器的价格 self.money -= weapon.price self.weapon = weapon #给玩家添加武器的属性 self.hp += weapon.maxHp self.atk += weapon.atk else: print('余额不足请先充值!') class EnemyFighter: #定义个敌机的类 def __init__(self,name,atk,hp,speed,kind): self.name = name self.atk = atk self.hp = hp self.speed = speed self.kind = kind def enemyFighterAttack(self,fighter): fighter.hp -= self.atk class Weapon: #定义一个武器的类 def __init__(self,name,atk,maxHp,durability,price): self.name = name self.atk = atk self.maxHp = maxHp self.durability = durability self.price = price playerFighter1 = Fighter('Player1',200,1500,300,500) Boss1 = EnemyFighter('lazerBoss',1000,7000,50,'Boss') w1 = Weapon('AMR-123',1000,1000,10,300) print(playerFighter1.__dict__)#{'name': 'Player1', 'atk': 200, 'hp': 1500, 'speed': 300, 'money': 500} playerFighter1.get_weapon(w1) print(playerFighter1.__dict__)#{'name': 'Player1', 'atk': 1200, 'hp': 2500, 'speed': 300, 'money': 200,
'weapon':<__main__.Weapon object at 0x000000000280D518>}
现在我们给武器设计一个招数,给怪物一个致命一击
class Fighter: #定义一个玩家战机的类 def __init__(self,name,atk,hp,speed,money = 0): self.name = name self.atk = atk self.hp = hp self.speed = speed self.money = money def playerAttack(self,enemyfighter): enemyfighter.hp -= self.atk def get_weapon(self,weapon): #玩家获得武器属性的函数 if self.money >= weapon.price: #如果玩家的金钱大于武器的价格 self.money -= weapon.price self.weapon = weapon #给玩家添加武器的属性 self.hp += weapon.maxHp self.atk += weapon.atk else: print('余额不足请先充值!') class EnemyFighter: #定义个敌机的类 def __init__(self,name,atk,hp,speed,kind): self.name = name self.atk = atk self.hp = hp self.speed = speed self.kind = kind def enemyFighterAttack(self,fighter): fighter.hp -= self.atk class Weapon: #定义一个武器的类 def __init__(self,name,atk,maxHp,durability,price): self.name = name self.atk = atk self.maxHp = maxHp self.durability = durability self.price = price def lazerBullet(self,enemyFighter,fighter): if self.durability > 0: enemyFighter.hp -= self.atk*2 + fighter.atk self.durability -= 5 else: print('您的武器耐久度为0,不可再使用!请重新充值!') playerFighter1 = Fighter('Player1',200,1500,300,500) Boss1 = EnemyFighter('lazerBoss',1000,7000,50,'Boss') w1 = Weapon('AMR-123',1000,1000,10,300) #初始的怪物和玩家属性 print(Boss1.__dict__) #{'name': 'lazerBoss', 'atk': 1000, 'hp': 7000, 'speed': 50, 'kind': 'Boss'} print(playerFighter1.__dict__) #{'name': 'Player1', 'atk': 200, 'hp': 1500, 'speed': 300, 'money': 500} #玩家装备上武器后属性 playerFighter1.get_weapon(w1) print(playerFighter1.__dict__) #{'name': 'Player1', 'atk': 1200, 'hp': 2500, 'speed': 300, 'money': 200,
'weapon': <__main__.Weapon object at 0x000000000280D518>} #第一回合玩家用武器大招攻击 playerFighter1.weapon.lazerBullet(Boss1,playerFighter1) print(Boss1.__dict__) #{'name': 'lazerBoss', 'atk': 1000, 'hp': 3800, 'speed': 50, 'kind': 'Boss'} #第二回合Boss攻击玩家 Boss1.enemyFighterAttack(playerFighter1) print(playerFighter1.__dict__) #{'name': 'Player1', 'atk': 1200, 'hp': 1500, 'speed': 300, 'money': 200,
'weapon': <__main__.Weapon object at 0x000000000279D4A8>} #第三回合玩家用武器大招攻击 playerFighter1.weapon.lazerBullet(Boss1,playerFighter1) print(Boss1.__dict__) #{'name': 'lazerBoss', 'atk': 1000, 'hp': 600, 'speed': 50, 'kind': 'Boss'} playerFighter1.weapon.lazerBullet(Boss1,playerFighter1) #您的武器耐久度为0,不可再使用!请重新充值! print(Boss1.__dict__) #{'name': 'lazerBoss', 'atk': 1000, 'hp': 600, 'speed': 50, 'kind': 'Boss'}
组合练习
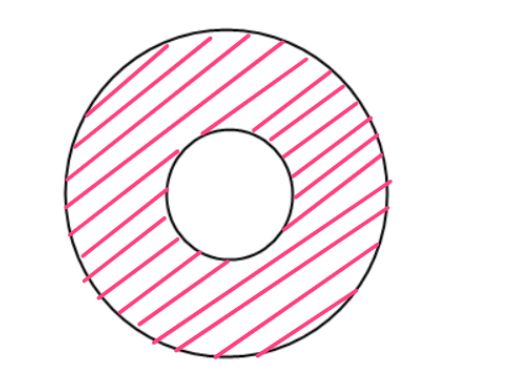
1.用组合的方法求这个图形的面积,假设这里大圆半径为10,小圆半径为
from math import pi as P class Cicle: def __init__(self,r): self.r = r def S(self): return P*self.r**2 def L(self): return 2*P*self.r class Ring: def __init__(self,outside_r,inside_r): self.outside_c = Cicle(outside_r) self.inside_c = Cicle(inside_r) def ret_S(self): return self.outside_c.S() - self.inside_c.S() def ret_L(self): return self.outside_c.L() + self.inside_c.L() ring = Ring(10,5) print(ring.ret_S()) #235.61944901923448 print(ring.ret_L()) #94.24777960769379
2.创建一个老师类,老师有生日、课程,生日和课程可以是一个类,用组合的方式表示
class Teacher: def __init__(self,name,age,gender,course,birthday): self.name = name self.age = age self.gender = gender self.course = course self.birthday = birthday class Course: def __init__(self,name,price,period): self.name = name self.price = price self.period = period class Birthday: def __init__(self,year,month,day): self.year = year self.month = month self.day = day p1 = Teacher('Jackson',25,'male',Course('python',15000,'7 months'),Birthday(1994,6,12)) print(p1.__dict__) #{'name': 'Jackson', 'age': 25, 'gender': 'male',
'course': <__main__.Course object at 0x00000000024AD390>,
'birthday': <__main__.Birthday object at 0x00000000024AD400>} print(p1.course.name,p1.course.price,p1.course.period) #python 15000 7 months print(p1.birthday.year,p1.birthday.month,p1.birthday.day) #1994 6 12