LeetCode 刷题记录 39. Combination Sum
题目:
Given a set of candidate numbers (candidates) (without duplicates) and a target number (target), find all unique combinations in candidates where the candidate numbers sums to target.
The same repeated number may be chosen from candidates unlimited number of times.
Note:
All numbers (including target) will be positive integers.
The solution set must not contain duplicate combinations.
Example 1:
Input: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
A solution set is:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
Example 2:
Input: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
A solution set is:
[
[2,2,2,2],
[2,3,3],
[3,5]
]
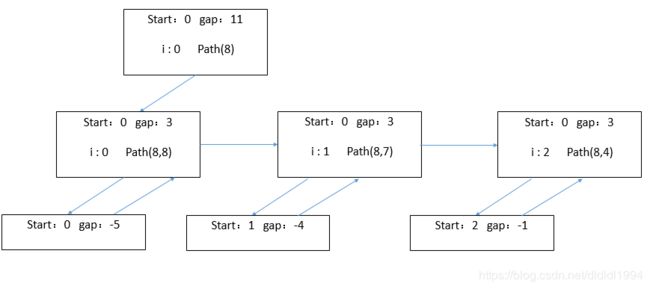
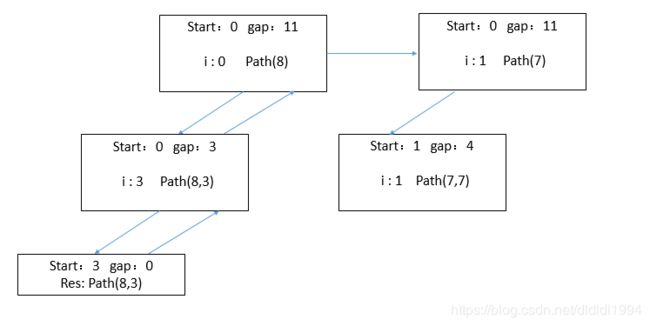
解法1:
递归法 用dfs
dfs函数有5个参数,candidates,其中一个解 vector& path,最终结果vector
递归采用的起点是target,终点是 gap <=0,采用减法操作,这里不采用加法操作的原因是如果用加法递归采用的起点是0,终点是 gap>= target,在递归函数中我们还要多传一个参数target,start当前递归的坐标,参数最好加入引用
递归基:如果gap<0,直接返回
gap=0,我们找到一个解,将解path加入到 res并返回
i 从start到candidates.size() - 1,依次尝试candidates中的数,首先path先加入这个数,继续递归,gap变为 gap - candidates[i],start还是i,因为本题中的数可以重复,递归成功后我们需要弹出我们之前加的数
c++:
class Solution {
public:
vector> combinationSum(vector& candidates, int target) {
vector> res;
vector path;
DFS(candidates, path, res, target, 0);
return res;
}
void DFS(vector& candidates, vector& path,vector>& res,int gap,int start){
if(gap < 0) return;
if(gap == 0){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.size(); ++i){
path.push_back(candidates[i]);
DFS(candidates, path, res, gap - candidates[i], i);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};
java:
- java中函数参数要写List path,List
- res,并且在添加结果时res.add(new ArrayList<>(path))而不是res.add(path)
因为new ArrayList<>(path)是一个对象,是对path的拷贝,而path是List,只是这个对象的引用,这个对象的内容每次都会改变 - remove操作我们要取出末尾元素
class Solution {
public List> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
List path = new ArrayList<>();
//sort(candidates.begin(),candidates.end());
//DFS(candidates, new ArrayList<>(), res, target, 0);
DFS(candidates, path, res, target, 0);
return res;
}
private void DFS(int[] candidates,List path,List> res,int gap,int start){
if(gap < 0) return;
if(gap == 0){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; ++i){
// cout << candidates[i] << endl;
// if(gap < candidates[i]) return;
path.add(candidates[i]);
DFS(candidates, path, res, gap - candidates[i], i);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
python:
- python 不能用append和pop,因为python是引用传递,所以最后会得到空, 而path + [candidates[i]] 会形成一个新的列表
- path + [candidates[i]] 相当于append操作,当函数返回,函数参数仍为path,即完成pop操作
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum(self, candidates, target):
"""
:type candidates: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
self.DFS(candidates, [], res, target, 0)
return res
def DFS(self, candidates, path, res,gap,start):
if gap < 0: return
if gap == 0:
res.append(path)
return
for i in xrange(start, len(candidates)):
#path.append(candidates[i])
self.DFS(candidates, path + [candidates[i]], res, gap - candidates[i], i)
#path.pop()
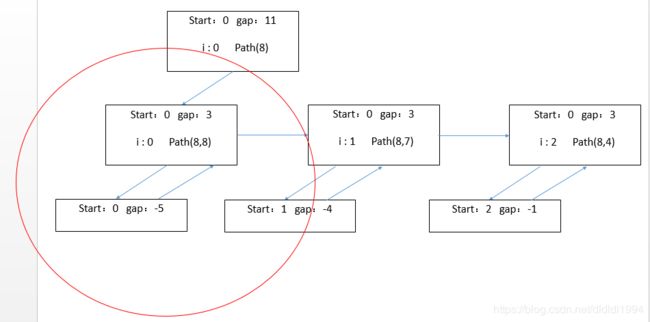
解法2:
递归法:剪枝
画圈的部分的递归是完全不需要的,如path(8) gap 3,我们在加入8时,只需做一个判断,gap < 8,说明这是我们不需要的,立即返回就可以了,但是我们要保证我们剪枝是正确的,即加入8不行,后面的就更加不行,这就要求我们先对数组进行排序
c++:
class Solution {
public:
vector> combinationSum(vector& candidates, int target) {
vector> res;
vector path;
sort(candidates.begin(),candidates.end());
DFS(candidates, path, res, target, 0);
return res;
}
void DFS(vector& candidates, vector& path,vector>& res,int gap,int start){
//if(gap < 0) return;
if(gap == 0){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.size(); ++i){
// cout << candidates[i] << endl;
if(gap < candidates[i]) return;
path.push_back(candidates[i]);
DFS(candidates, path, res, gap - candidates[i], i);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};
java:
class Solution {
public List> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
//List path = new ArrayList<>();
//sort(candidates.begin(),candidates.end());
Arrays.sort(candidates);
DFS(candidates, new ArrayList<>(), res, target, 0);
return res;
}
private void DFS(int[] candidates,List path,List> res,int gap,int start){
//if(gap < 0) return;
if(gap == 0){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; ++i){
// cout << candidates[i] << endl;
if(gap < candidates[i]) return;
path.add(candidates[i]);
DFS(candidates, path, res, gap - candidates[i], i);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
python:
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum(self, candidates, target):
"""
:type candidates: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
candidates.sort()
self.DFS(candidates, [], res, target, 0)
return res
def DFS(self, candidates, path, res,gap,start):
#if gap < 0: return
if gap == 0:
res.append(path)
return
for i in xrange(start, len(candidates)):
#path.append(candidates[i])
if gap < candidates[i]: return
self.DFS(candidates, path + [candidates[i]], res, gap - candidates[i], i)
#path.pop()