Android 自定义View 带你飞(二)
在上一节我们简单的介绍了自定义View的相关知识,并写了一个简单的Demo,让我们回顾一下自定义View的几个步骤:
- 定义一个类继承View,实现几个构造方法(还记得不同参数的区别吧,不记得请看上一篇文章)
- res/values/ 下建立一个attrs.xml,定义view所需要的属性
- 在构造方法里获得我们定义的属性(TypedArray要记得释放哦!)
- 重写onDraw()方法
这样就实现了一个简单的自定义View,是不是很简单呢。
我们继续来看上一节写的view,不知道大家有没有发现一个问题,在布局文件中 修改layout_width、layout_height两个属性,不论是wrap_content还是match_parent最后的效果都是布满整个屏幕的,而这显然不是我们需要的效果,大家还记得上一节中我们提及的onMeasure()方法么,现在我们就需要重写这个方法来解决这个问题。
我们先看onMeasure()的默认实现:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
//再看它调用的父类的onMeasure()方法:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}这里的MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED、MeasureSpec.AT_MOST这些东西是什么呢,终于说到重点了,MeasureSpec这个类对于学习自定义view非常非常重要,MeasureSpc类封装了父View传递给子View的布局(layout)要求,MeasureSpec的值由specSize和specMode共同组成的,其中specSize记录的是大小,specMode记录的是规格。它有三种模式:
1. EXACTLY(一般对应布局的match_parent或者指定大小)
表示父视图希望子视图的大小应该是由specSize的值来决定的,系统默认会按照这个规则来设置子视图的大小,开发人员当然也可以按照自己的意愿设置成任意的大小。
2. AT_MOST(一般对应布局的wrap_content )
表示子视图最多只能是specSize中指定的大小,开发人员应该尽可能小得去设置这个视图,并且保证不会超过specSize。系统默认会按照这个规则来设置子视图的大小,开发人员当然也可以按照自己的意愿设置成任意的大小。
3. UNSPECIFIED
表示开发人员可以将视图按照自己的意愿设置成任意的大小,没有任何限制。这种情况比较少见,不太会用到。
常用的三个函数:
static int getMode(int measureSpec) : 根据提供的测量值(格式)提取模式(上述三个模式之一)
static int getSize(int measureSpec) : 根据提供的测量值(格式)提取大小值(这个大小也就是我们通常所说的大小)
static int makeMeasureSpec(int size,int mode) : 根据提供的大小值和模式创建一个测量值(格式)
这样我们再来看getDefaultSize方法就可以理解为什么总是布满屏幕了。
不知道大家有没有注意到我上面说了子view的大小是受父view控制的,一开始学习这个方法的时候我实在是不能理解,后来看了源码终于是能理解了。大家不要急,我们一起来看下:
子view的父布局那不就是viewGroup么,我们来看下ViewGroup这个类。viewGroup类是一个容器类,里面装载view,它规定了view如何布局,也会控制view的大小。我们在ViewGroup里发现一个方法measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,int parentHeightMeasureSpec),来看看他是如何实现的:
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
// 获取子元素的布局参数
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
//将父容器的测量规格以及上下和左右的边距还有子元素本身的布局参数传入getChildMeasureSpec方法计算最终测量要求
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
// 将计算好的宽高详细测量值传入measure方法,完成最后的测量
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
//在最后它调用了子view的measure()方法,接着看:
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
.....
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
....
}
终于发现了onMeasure方法里面的参数是如何来的,就是将viewGroup的measureChild方法里面得到的childWidthMeasureSpec 、childHeightMeasureSpec 传入了子view的onMeasure方法里面去。下面我们来看看这个getChildMeasureSpec里面到底是什么东东:
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec); //获得父View的mode
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec); //获得父View的实际值
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding); //父View为子View设定的大小,减去边距值,
int resultSize = 0; //子View对应地 size 实际值 ,由下面的逻辑条件赋值
int resultMode = 0; //子View对应地 mode 值 , 由下面的逻辑条件赋值
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
//1、父View是EXACTLY的 !
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
//1.1、子View的width或height是个精确值 (an exactly size)
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension; //size为精确值
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; //mode为 EXACTLY 。
}
//1.2、子View的width或height为 MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT
else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size; //size为父视图大小
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; //mode为 EXACTLY 。
}
//1.3、子View的width或height为 WRAP_CONTENT
else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size; //size为父视图大小
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST; //mode为AT_MOST 。
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
//2、父View是AT_MOST的 !
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
//2.1、子View的width或height是个精确值 (an exactly size)
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension; //size为精确值
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; //mode为 EXACTLY 。
}
//2.2、子View的width或height为 MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT
else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size; //size为父视图大小
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST; //mode为AT_MOST
}
//2.3、子View的width或height为 WRAP_CONTENT
else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size; //size为父视图大小
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST; //mode为AT_MOST
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
//3、父View是UNSPECIFIED的 !
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
//3.1、子View的width或height是个精确值 (an exactly size)
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension; //size为精确值
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; //mode为 EXACTLY
}
//3.2、子View的width或height为 MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT
else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = 0; //size为0! ,其值未定
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED; //mode为 UNSPECIFIED
}
//3.3、子View的width或height为 WRAP_CONTENT
else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = 0; //size为0! ,其值未定
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED; //mode为 UNSPECIFIED
}
break;
}
//根据上面逻辑条件获取的mode和size构建MeasureSpec对象。
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
这边我直接复制了网上一位大神的讲解,注释解释的很好,大家应该都能看懂。借鉴那位大神的图:
注释转化为图片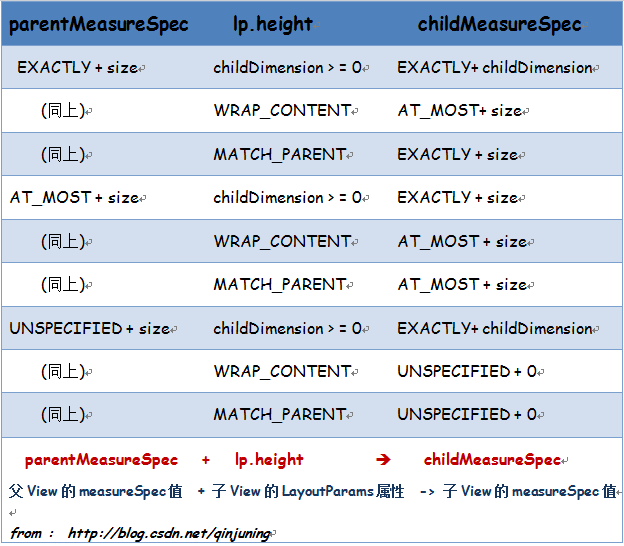
到此就可以证实我上面说的子view的大小是由父view以及他自身所控制的,然而最终view的测量大小还是由setMeasuredDimension()决定。
接下来我们重写onMeasure方法:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getMeasureW(widthMeasureSpec), getMeasureH(heightMeasureSpec));//注意最后要调用这个方法
}
private int getMeasureW(int measureSpec) {
int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int size = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
int result;
if (mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = size;
} else {
int textWidth = mBoundRect.width() + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
if (mode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
result = Math.min(size, textWidth);
} else {
result = size;
}
}
return result;
}
private int getMeasureH(int measureSpec) {
int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int size = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
int result;
if (mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = size;
} else if (mode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
int textHeight = getPaddingBottom() + getPaddingTop() + mBoundRect.height();
result = Math.min(size, textHeight);
} else
result = size;
return result;
}好啦,onMeasure()方法终于告一段落,因为太仓促如有讲错的地方,欢迎指正!
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/dreamfree3/article/details/52117654