用线性回归模型预测房价
本文使用sklearn 中自带的波士顿房价数据集来训练模型,然后利用模型来预测房价。这份收据中共收集了13个特征。
1.输入特征
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
boston = load_boston()
X = boston.data
y = boston.target
X.shape
输出为:“(506,13)”共有506个样本 13个特征。
print(X[0])
输出结果为:
array([ 6.32000000e-03, 1.80000000e+01, 2.31000000e+00,
0.00000000e+00, 5.38000000e-01, 6.57500000e+00,
6.52000000e+01, 4.09000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00,
2.96000000e+02, 1.53000000e+01, 3.96900000e+02,
4.98000000e+00])
可以通过boston.feature_names 来查看这些特征的标签
array(['CRIM', 'ZN', 'INDUS', 'CHAS', 'NOX', 'RM', 'AGE', 'DIS', 'RAD',
'TAX', 'PTRATIO', 'B', 'LSTAT'],
dtype='|S7')
2.模型训练
LinearRegression 类实现了线性回归算法。在训练之前先把数据集分为两份。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=3)
训练模型并测试模型准确性
import time
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression()
start = time.clock()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_score = model.score(X_train, y_train)
cv_score = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print('elaspe: {0:.6f}; train_score: {1:0.6f}; cv_score: {2:.6f}'.format(time.clock()-start, train_score, cv_score))
统计了模型的训练时间,统计模型对训练样本的准确性得分(即对训练样本的拟合好坏程度)train_score,还统计了模型对测试样本的得分 cv_score
运行结果如下:
elaspe: 0.002447; train_score: 0.723941; cv_score: 0.794958
从结果可以看出模型拟合效果一般。
3.模型优化
模型优化的方式
1.观察特征的变化范围从 1 0 − 3 10^{-3} 10−3级别到 1 0 2 10^2 102,先将数据进行归一化的处理,可以加快算法的收敛速度。
2.增加多项式特征
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
def polynomial_model(degree=1):
polynomial_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree,
include_bias=False)
linear_regression = LinearRegression(normalize=True)
pipeline = Pipeline([("polynomial_features", polynomial_features),
("linear_regression", linear_regression)])
return pipeline
接着我们使用二阶多项式来你和数据:
model = polynomial_model(degree=2)
start = time.clock()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_score = model.score(X_train, y_train)
cv_score = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print('elaspe: {0:.6f}; train_score: {1:0.6f}; cv_score: {2:.6f}'.format(time.clock()-start, train_score, cv_score))
输出结果是:
elaspe: 0.016412; train_score: 0.930547; cv_score: 0.860465
训练样本分数和测试样本分数都提高了,模型得到了优化。
把多项式特征改为三阶查看效果。
运行结果为 :
elaspe: 0.133220; train_score: 1.000000; cv_score: -105.517016
针对训练样本的分数达到了1 ,而对测试样本的分数却是负数,产生了过拟合。
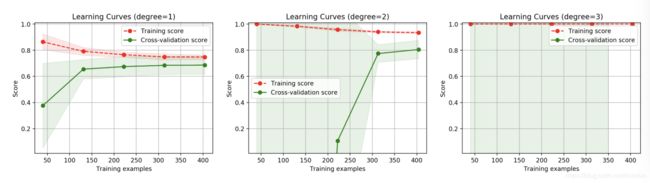
4.学习曲线
通过画出学习曲线,来对模型的状态及优化的方向直观的观察。
from common.utils import plot_learning_curve
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit
cv = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=10, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 4), dpi=200)
title = 'Learning Curves (degree={0})'
degrees = [1, 2, 3]
start = time.clock()
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 4), dpi=200)
for i in range(len(degrees)):
plt.subplot(1, 3, i + 1)
plot_learning_curve(plt, polynomial_model(degrees[i]), title.format(degrees[i]), X, y, ylim=(0.01, 1.01), cv=cv)
print('elaspe: {0:.6f}'.format(time.clock()-start))