一、boston房价预测
1. 读取数据集
2. 训练集与测试集划分
3. 线性回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。
4. 多项式回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。
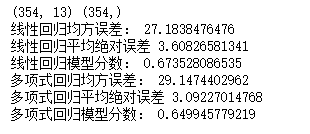
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston #导入Boston房价数据集 boston = load_boston() #读取数据集 # boston.keys() #查看key值 x = boston.data y = boston.target #训练集与测试集划分 from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=0) #其中 test_size是样本占比,如果是整数的话就是样本的数量; #random_state是随机数的种子,不同的种子会造成不同的随机采样结果,相同的种子采样结果相同。 print(x_train.shape,y_train.shape) #建立一元线性回归模型 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression lr = LinearRegression() lr.fit(x_train,y_train) lr.coef_ #系数 lr.intercept_ #截距 #检测模型好坏 from sklearn.metrics import regression y_pred = lr.predict(x_test) #预测 n = regression.mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred) #预测模型均方误差 print("线性回归均方误差:",n) a = regression.mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_pred) print("线性回归平均绝对误差",a) s = lr.score(x_test,y_test) #模型分数 print("线性回归模型分数:",s) #多元多项式回归模型 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures poly= PolynomialFeatures(degree=2) x_poly_train= poly.fit_transform(x_train) #多项式化 x_poly_test = poly.transform(x_test) #建立模型 lr2 = LinearRegression() lr2.fit(x_poly_train,y_train) #预测 y_pred2 = lr2.predict(x_poly_test) #检测模型好坏,计算模型的预测指标 n2 = regression.mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred2) print("多项式回归均方误差:",n2) a2 = regression.mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_pred2) print("多项式回归平均绝对误差",a2) s2 = lr2.score(x_poly_test,y_test) print("多项式回归模型分数:",s2)
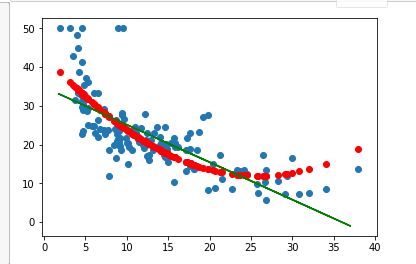
# 用一元线性回归拟合观察效果 lr2 = LinearRegression() lr2.fit(x,y_train) # 建立多项式模型 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures # 多项式化x x = x_train[:,12].reshape(-1,1) poly= PolynomialFeatures(degree=2) x_poly = poly.fit_transform(x) # 用多项式后的x建立多项式回归模型 lrp = LinearRegression() lrp.fit(x_poly,y_train) # 预测 x_poly2 = poly.transform(x_test[:, 12].reshape(-1,1)) y_ploy_predict = lrp.predict(x_poly2) # 图形化,将元数据,一元拟合,多元拟合进行绘图观察 plt.scatter(x_test[:,12], y_test) plt.plot(x, lr2.coef_* x + lr2.intercept_, 'g') plt.scatter(x_test[:,12], y_ploy_predict, c='r') plt.show()
5、比较线性模型与非线性模型的性能,并说明原因。
如上图可知,非线性模型的性能比较好,因为非线性模型(即多项式回归模型)的曲线比线性模型直线更能契合人口密度与房屋样本的分布状况,而且从上述分析可知多项式回归的误差跟线性回归误差相比较小。
二、中文文本分类
import os import numpy as np import sys from datetime import datetime import gc path = 'E:\\大三\\数据挖掘\\qimo\\0369' # 导入结巴库,并将需要用到的词库加进字典 import jieba # 导入停用词: with open(r'E:\大三\数据挖掘\qimo\stopsCN.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f: stopwords = f.read().split('\n') #预处理数据,先定义一个函数,然后封装 def processing(tokens): # 去掉非字母汉字的字符,isalpha判断字符ch是否为英文字母,若为英文字母,返回非0(小写字母为2,大写字母为1)。若不是字母,返回0。 tokens = "".join([char for char in tokens if char.isalpha()]) # 结巴分词,砍掉大于等于2个以上的词,(即将一句话拆分为各个词语) tokens = [token for token in jieba.cut(tokens,cut_all=True) if len(token) >=2] # 去掉停用词 tokens = " ".join([token for token in tokens if token not in stopwords]) return tokens tokenList = [] targetList = [] # 用os.walk获取需要的变量,并拼接文件路径再打开每一个文件 for root,dirs,files in os.walk(path): for f in files: # print(root) #当前目录路径 # print(dirs) #当前路径下所有子目录 # print(files) #当前路径下所有非目录子文件 filePath = os.path.join(root,f) with open(filePath, encoding='utf-8') as f: content = f.read() #存放读取的数据 # 获取新闻类别标签,并处理该新闻 target = filePath.split('\\')[-2] targetList.append(target) #获取的新闻文本的类别,追加到targetList里 tokenList.append(processing(content)) #获取的各新闻文本里的详细内容,预处理后追加到tokenList import pandas datas = pandas.DataFrame({ 'targetList': targetList, 'tokenList': tokenList }) print(datas)
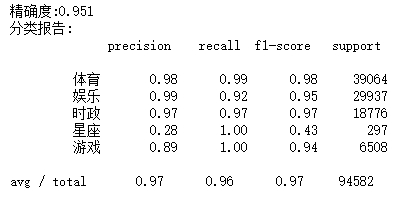
#划分训练集测试集并建立特征向量,为建立模型做准备 #划分训练集、测试集 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test= train_test_split(tokenList,targetList,test_size=0.3,stratify=targetList) #转化为特征向量。 from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer vec = TfidfVectorizer() x_train = vec.fit_transform(x_train) x_test = vec.transform(x_test) #建立模型,因为样本特征的a分布大部分是多元离散值,所以用多项式朴素贝叶斯 from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB,MultinomialNB mnb = MultinomialNB() module = mnb.fit(x_train,y_train) #进行预测 y_pred = module.predict(x_test) #输出模型精确度 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score scores = cross_val_score(mnb,x_test,y_test,cv=5) print("精确度:%.3f"%scores.mean()) #输出模型评估报告, from sklearn.metrics import classification_report print("分类报告:\n",classification_report(y_pred,y_test))
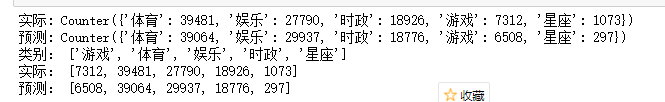
#将预测结果和实际结果进行对比 import collections import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from pylab import mpl # mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FangSong'] #指定默认仿宋字体 # mpl.reParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False #解决保存图像是负号‘-’显示为方块的问题、 mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FangSong'] # 指定默认字体 mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题 #统计测试集和预测集的各类新闻文本个数 testCount = collections.Counter(y_test) predCount = collections.Counter(y_pred) print('实际:',testCount) print('预测:',predCount) #建立标签列表,实际结果列表和预测结果列表 nameList = list(testCount.keys()) testList = list(testCount.values()) predList = list(predCount.values()) x = list(range(len(nameList))) print("类别:",nameList) print("实际:",testList) print("预测:",predList)