tf-faster-rcnn源码解读
目录
- _build_network
- _anchor_component
- _region_proposal
- _crop_pool_layer
- _region_classification
- loss
- 训练
- 训练自己的数据
參考自:
详细的Faster R-CNN源码解析之proposal_layer和proposal_target_layer源码解析
详细的Faster R-CNN源码解析之RPN源码解析
Tensorflow 版本 Faster RCNN 代码解读
Faster R-CNN 源码解析(Tensorflow版)
_build_network
里面包含了_region_proposal,_crop_pool_layer,_reigon_classification三个主要的方法,分别表示了方法最主要的流程走向,生成推荐区域,crop,再判定
先上源码及注释:
def _build_network(self, is_training=True):
# select initializers
# 里面包含了_region_proposal,_crop_pool_layer,_reigon_classification
# 三个主要的方法,分别表示了方法最主要的流程走向,生成推荐区域,crop,再判定
if cfg.TRAIN.TRUNCATED:
# 从截断的正态分布中获取随机值
# 从具有指定平均值和标准偏差的正态分布,如果生成的值大于平均值2个标准偏差的值则丢弃重新选择。
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.01)
initializer_bbox = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.001)
else:
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.01)
initializer_bbox = tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.001)
net_conv = self._image_to_head(is_training)
with tf.variable_scope(self._scope, self._scope):
# variable_scope建立一个变量的作用域
# build the anchors for the image
self._anchor_component()
# 建立anchor
# region proposal network
rois = self._region_proposal(net_conv, is_training, initializer)
# region of interest pooling
if cfg.POOLING_MODE == 'crop':
pool5 = self._crop_pool_layer(net_conv, rois, "pool5")
# 对生成的rois进行roi池化
else:
raise NotImplementedError
fc7 = self._head_to_tail(pool5, is_training)
with tf.variable_scope(self._scope, self._scope):
# region classification
cls_prob, bbox_pred = self._region_classification(fc7, is_training,
initializer, initializer_bbox)
self._score_summaries.update(self._predictions)
return rois, cls_prob, bbox_pred
_anchor_component
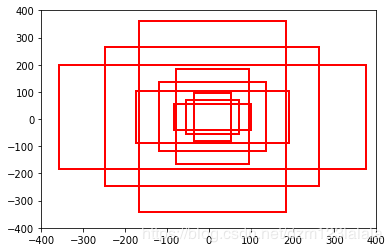
_anchor_component====>generate_anchors_pre_tf=====>generate_anchors
最终的目的是先根据(0,0,15,15)生成一组anchor,然后进行平移得到最后的anchor
# array([[ -83., -39., 100., 56.],
# [-175., -87., 192., 104.],
# [-359., -183., 376., 200.],
# [ -55., -55., 72., 72.],
# [-119., -119., 136., 136.],
# [-247., -247., 264., 264.],
# [ -35., -79., 52., 96.],
# [ -79., -167., 96., 184.],
# [-167., -343., 184., 360.]])
画出来:
_region_proposal
def _region_proposal(self, net_conv, is_training, initializer):
'''
:param net_conv:
:param is_training:
:param initializer:
:return:
'''
rpn = slim.conv2d(net_conv, cfg.RPN_CHANNELS, [3, 3], trainable=is_training, weights_initializer=initializer,
scope="rpn_conv/3x3")
# 第一层:3*3的卷积层,shape=(1,?,?,512)
self._act_summaries.append(rpn)
rpn_cls_score = slim.conv2d(rpn, self._num_anchors * 2, [1, 1], trainable=is_training,
weights_initializer=initializer,
padding='VALID', activation_fn=None, scope='rpn_cls_score')
# shape=(1,?,?,18),9个anchor,一个anchor两个分数
# change it so that the score has 2 as its channel size
rpn_cls_score_reshape = self._reshape_layer(rpn_cls_score, 2, 'rpn_cls_score_reshape')
# shape=(1,?,?,2)
rpn_cls_prob_reshape = self._softmax_layer(rpn_cls_score_reshape, "rpn_cls_prob_reshape")
# shape=(1,?,?,2)softmax,用于判断bbox中是否含有物体
rpn_cls_pred = tf.argmax(tf.reshape(rpn_cls_score_reshape, [-1, 2]), axis=1, name="rpn_cls_pred")
# 返回最大的值所在的下标,是/否含有物体
rpn_cls_prob = self._reshape_layer(rpn_cls_prob_reshape, self._num_anchors * 2, "rpn_cls_prob")
# shape=(1,?,?,36)
#####################################################################################
# 预测bbox的坐标,(height,width,9*4)
rpn_bbox_pred = slim.conv2d(rpn, self._num_anchors * 4, [1, 1], trainable=is_training,
weights_initializer=initializer,
padding='VALID', activation_fn=None, scope='rpn_bbox_pred')
上面这一部分搭建了rpn的结构:
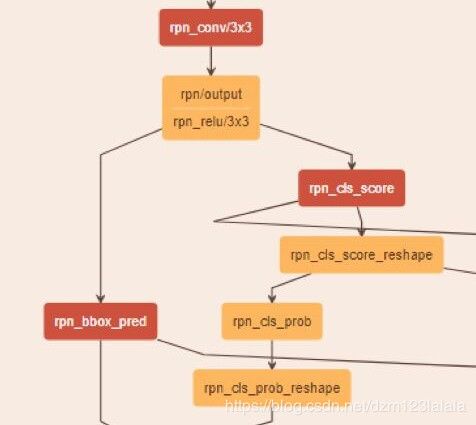
下面的部分主要是根据RPN输出的前景分数选择出roi和为选择出的roi置ground truth类别和坐标变换的代码
首先是如何选择出合适的rois,对应的函数是_proposal_layer;
其次是如何为选择出的rois找到训练所需的ground truth类别和坐标变换信息,该代码文件是proposal_target_layer.py
先放出_region_proposal中剩余部分的代码,然后再对这两部分进行讲解。
if is_training:
rois, roi_scores = self._proposal_layer(rpn_cls_prob, rpn_bbox_pred, "rois")
# rois是bbox的角点坐标,size=(?,5),roi_scores是bbox对应的分数
# 处理anchor,裁剪,nms,筛选
rpn_labels = self._anchor_target_layer(rpn_cls_score, "anchor")
# # rpn_labels是标签值,1,0,-1
# Try to have a deterministic order for the computing graph, for reproducibility
with tf.control_dependencies([rpn_labels]):
rois, _ = self._proposal_target_layer(rois, roi_scores, "rpn_rois")
else:
if cfg.TEST.MODE == 'nms':
rois, _ = self._proposal_layer(rpn_cls_prob, rpn_bbox_pred, "rois")
elif cfg.TEST.MODE == 'top':
rois, _ = self._proposal_top_layer(rpn_cls_prob, rpn_bbox_pred, "rois")
else:
raise NotImplementedError
self._predictions["rpn_cls_score"] = rpn_cls_score
self._predictions["rpn_cls_score_reshape"] = rpn_cls_score_reshape
self._predictions["rpn_cls_prob"] = rpn_cls_prob
self._predictions["rpn_cls_pred"] = rpn_cls_pred
self._predictions["rpn_bbox_pred"] = rpn_bbox_pred
self._predictions["rois"] = rois
return rois
proposal_layer的代码如下
使用bbox_transform_inv函数对anchor进行坐标变换,从ctr_x,ctr_y,w,h变换成anchor的左下角和右上角;
使用clip_boxes将改变坐标信息后超过图像边界的框的边框裁剪一下,使之在图像边界之内
pre_nms_topN ,post_nms_topN ,nms_thresh 是用来筛选anchors的三个指标:
pre_nms_topN取的6000,将scores降序排序,取前pre_nms_topN;- 用
nms函数进行非极大值抑制,把ioU大于nms_thresh的删掉。 - 再次按照nms后的foreground softmax由大到小排列,提取前
post_nms_topN(300)结果作为proposals的输出
proposal_layer
def proposal_layer(rpn_cls_prob, rpn_bbox_pred, im_info, cfg_key, _feat_stride, anchors, num_anchors):
'''
A simplified version compared to fast/er RCNN
For details please see the technical report
:param rpn_cls_prob:
:param rpn_bbox_pred:
:param im_info: [M,N,scale_factor]保存了将任意图像缩放到M×N的所有信息
:param cfg_key:
:param _feat_stride:feat_stride=16用于计算anchor的偏移量
:param anchors:
:param num_anchors:
:return:
'''
if type(cfg_key) == bytes:
cfg_key = cfg_key.decode('utf-8')
pre_nms_topN = cfg[cfg_key].RPN_PRE_NMS_TOP_N
post_nms_topN = cfg[cfg_key].RPN_POST_NMS_TOP_N
nms_thresh = cfg[cfg_key].RPN_NMS_THRESH
# Get the scores and bounding boxes
scores = rpn_cls_prob[:, :, :, num_anchors:]
rpn_bbox_pred = rpn_bbox_pred.reshape((-1, 4))
scores = scores.reshape((-1, 1))
proposals = bbox_transform_inv(anchors, rpn_bbox_pred)
# 计算得到bbox四个顶点坐标
proposals = clip_boxes(proposals, im_info[:2])
# Pick the top region proposals
'''
按照输入的foreground softmax降序排列,提取前pre_nms_topN(6000)的结果
提取修正后的foreground anchor
'''
order = scores.ravel().argsort()[::-1]
# ravel数组扁平化,降序排列
if pre_nms_topN > 0:
order = order[:pre_nms_topN]
proposals = proposals[order, :]
# anchor坐标
scores = scores[order]
# anchor分数
# Non-maximal suppression
keep = nms(np.hstack((proposals, scores)), nms_thresh)
# Pick th top region proposals after NMS
'''
再次按照nms后的foreground softmax由大到小排列,提取前post_nms_topN(300)结果作为proposals的输出
'''
if post_nms_topN > 0:
keep = keep[:post_nms_topN]
proposals = proposals[keep, :]
scores = scores[keep]
# Only support single image as input
batch_inds = np.zeros((proposals.shape[0], 1), dtype=np.float32)
# 因为要进行roi_pooling,在保留框的坐标信息前面插入batch中图片的编号信息。此时,由于batch_size为1,因此都插入0
blob = np.hstack((batch_inds, proposals.astype(np.float32, copy=False)))
return blob, scores
proposal_target_layer
proposal_target_layer的作用是再训练时为选出的框(roi)置ground truth类别和坐标变换信息。
- 在
proposal_target_layer函数中,首先将ground truth框加入了根据RPN输出选择出的框,相当于增加前景的数量,此时,roi的数量变成了N(根据RPN的输出选出的)+M(ground truth框)。 - 进入
_sample_rois函数,首先计算所有的roi和ground truth框的重合度(IoU),然后对于每个roi,找到对应的ground truth框和正确的类别标签。
overlaps = bbox_overlaps(
np.ascontiguousarray(all_rois[:, 1:5], dtype=np.float),
np.ascontiguousarray(gt_boxes[:, :4], dtype=np.float))
# bbox_overlaps计算重合度
gt_assignment = overlaps.argmax(axis=1)
# 返回每个anchor对应的最匹配的gt_box的编号
# axis=1:找每一行的最大值,拿出第1+1维度进行比较
max_overlaps = overlaps.max(axis=1)
# 返回每个anchor对应的最匹配的gt_box的overlap值
labels = gt_boxes[gt_assignment, 4]
# 对每个rois,找到归属的类别(-1,0,1)
- 为一个训练batch,在全部roi中选择前景框(前景框不能太多,最多只能占训练batch的1/4)和背景框。
- 为进行该batch训练的框置分类标签,并通过
_compute_targets函数计算坐标回归标签。 - 通过
_get_bbox_regression_labels函数将坐标回归标签扩充,变成训练所需的格式。
def proposal_target_layer(rpn_rois, rpn_scores, gt_boxes, _num_classes):
"""
Assign object detection proposals to ground-truth targets. Produces proposal
classification labels and bounding-box regression targets.
将目标检测方案分配给ground truth目标。生成建议分类标签和边界框回归目标。
"""
# Proposal ROIs (0, x1, y1, x2, y2) coming from RPN
# (i.e., rpn.proposal_layer.ProposalLayer), or any other source
all_rois = rpn_rois
# 边框角点坐标
all_scores = rpn_scores
# 边框得分
# Include ground-truth boxes in the set of candidate rois
# 将ground-truth boxes包括进候选框集
if cfg.TRAIN.USE_GT:
zeros = np.zeros((gt_boxes.shape[0], 1), dtype=gt_boxes.dtype)
all_rois = np.vstack(
(all_rois, np.hstack((zeros, gt_boxes[:, :-1])))
)
# vstack竖直方向堆叠,hstack水平堆叠
# 将gt_boxes加入到all_rois,hstack是为了整格式
# gt_boxes[:,:-1]取每行除了最后一个之外的其他元素
# not sure if it a wise appending, but anyway i am not using it
# 不确定它是否是一个明智的附加物,但无论如何,我没有使用它
all_scores = np.vstack((all_scores, zeros))
# 将gt_boxes的scores也加上,但为啥是0?
"""
在一个batch中,确定每张图片roi的数量:rois_per_image是总的,fg_rois_per_image是前景,相减是背景
为一个训练batch,在全部roi中选择前景框(前景框不能太多,最多只能占训练batch的1/4)和背景框。
"""
num_images = 1
rois_per_image = cfg.TRAIN.BATCH_SIZE / num_images
fg_rois_per_image = np.round(cfg.TRAIN.FG_FRACTION * rois_per_image)
# Sample rois with classification labels and bounding box regression
# 采样roi带有分类标签和边界框
# targets
labels, rois, roi_scores, bbox_targets, bbox_inside_weights = _sample_rois(
all_rois, all_scores, gt_boxes, fg_rois_per_image,
rois_per_image, _num_classes)
# 调用sample_rois函数对roi做抽样,目的是让roi总数保持为rois_per_image(默认是128),
# _sample_rois选择进行分类训练的框,并求取他们类别和坐标的ground truth和
# 计算边框损失loss时需要的bbox_inside_weights
rois = rois.reshape(-1, 5)
roi_scores = roi_scores.reshape(-1)
labels = labels.reshape(-1, 1)
bbox_targets = bbox_targets.reshape(-1, _num_classes * 4)
bbox_inside_weights = bbox_inside_weights.reshape(-1, _num_classes * 4)
bbox_outside_weights = np.array(bbox_inside_weights > 0).astype(np.float32)
return rois, roi_scores, labels, bbox_targets, bbox_inside_weights, bbox_outside_weights
_crop_pool_layer
这个函数在做的工作是ROI Pooling。
FC layer需要固定尺寸的输入。在最早的R-CNN算法中,将输入的图像直接resize成相同的尺寸。而Faster R-CNN对输入图像的尺寸没有要求,经过Proposal layer和 Proposal target layer之后,会得到许多不同尺寸的RoI。Faster R-CNN采用RoI Pooling层(原理参考SPPNet 论文),将不同尺寸ROI对应的特征图采样为相同尺寸,然后输入后续的FC层。这版代码中没有实现RoI pooling layer, 而是把RoI对应的特征图resize成相同尺寸后,再进行max pooling。巧妙的利用了TensorFlow中tf.image.crop_and_resize函数:从输入图片张量中抽取相应的截断部分并且调整它们的大小完成roi池化。
def _crop_pool_layer(self, bottom, rois, name):
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
batch_ids = tf.squeeze(tf.slice(rois, [0, 0], [-1, 1], name="batch_id"), [1])
# tf.squeeze从tensor中删除所有大小是1的维度
# tf.slice从由begin指定位置开始的张量input中提取一个尺寸size的切片
# Get the normalized coordinates of bboxes
bottom_shape = tf.shape(bottom)
height = (tf.to_float(bottom_shape[1]) - 1.) * np.float32(self._feat_stride[0])
width = (tf.to_float(bottom_shape[2]) - 1.) * np.float32(self._feat_stride[0])
x1 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 1], [-1, 1], name="x1") / width
# 取每行的第2个元素shape=(rois.shape[0],1)
y1 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 2], [-1, 1], name="y1") / height
x2 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 3], [-1, 1], name="x2") / width
y2 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 4], [-1, 1], name="y2") / height
# Won't be back-propagated to rois anyway, but to save time
bboxes = tf.stop_gradient(tf.concat([y1, x1, y2, x2], 1))
if cfg.RESNET.MAX_POOL:
pre_pool_size = cfg.POOLING_SIZE * 2
crops = tf.image.crop_and_resize(bottom, bboxes, tf.to_int32(batch_ids), [pre_pool_size, pre_pool_size],
name="crops")
# 从输入图片张量中抽取相应的截断部分并且调整它们的大小。
crops = slim.max_pool2d(crops, [2, 2], padding='SAME')
else:
crops = tf.image.crop_and_resize(bottom, bboxes, tf.to_int32(batch_ids), [cfg.POOLING_SIZE, cfg.POOLING_SIZE],
name="crops")
return crops
_region_classification
def _region_classification(self, fc7, is_training, initializer, initializer_bbox):
cls_score = slim.fully_connected(fc7, self._num_classes,
weights_initializer=initializer,
trainable=is_training,
activation_fn=None, scope='cls_score')
cls_prob = self._softmax_layer(cls_score, "cls_prob")
cls_pred = tf.argmax(cls_score, axis=1, name="cls_pred")
bbox_pred = slim.fully_connected(fc7, self._num_classes * 4,
weights_initializer=initializer_bbox,
trainable=is_training,
activation_fn=None, scope='bbox_pred')
self._predictions["cls_score"] = cls_score
self._predictions["cls_pred"] = cls_pred
self._predictions["cls_prob"] = cls_prob
self._predictions["bbox_pred"] = bbox_pred
return cls_prob, bbox_pred
至此,数据准备和整个Faster R-CNN的网络已经搭建完成。为了训练网络,需要构建损失函数。
loss
rpn的多任务损失函数:
L ( { p i } , { t i } ) = 1 N c l s ∑ i L c l s ( p i , p i ∗ ) + λ N r e g ∑ i p i ∗ L r e g ( t i , t i ∗ ) L(\{p_i\},\{t_i\})=\frac{1}{N_{cls}}\sum_{i}L_{cls}(p_i,p_i^*)+\frac{\lambda}{N_{reg}}\sum_{i}p_i^*L_{reg}(t_i,t_i^*) L({pi},{ti})=Ncls1i∑Lcls(pi,pi∗)+Nregλi∑pi∗Lreg(ti,ti∗)
式中, i i i是anchor在mini-batch中的索引
p i p_i pi是把 a n c h o r i anchor_i anchori预测为一个目标的概率;
p i ∗ p_i^* pi∗是ground-truth标签, p i ∗ p_i^* pi∗ is 1 if the anchor is positive, and is 0 if the anchor is negative
t i t_i ti是预测出的bounding box的位置坐标
t i ∗ t_i^* ti∗是positive anchor的ground-truth框
L c l s L_{cls} Lcls是分类损失,交叉熵损失
L r e g L_{reg} Lreg是回归损失, L r e g ( t i , t i ∗ ) = R ( t i − t i ∗ ) L_{reg}(t_i,t_i^*)=R(t_i-t_i^*) Lreg(ti,ti∗)=R(ti−ti∗), R R R是 s m o o t h L 1 smooth \ L_1 smooth L1损失,公式为:
s m o o t h L 1 = { 0.5 x 2 x=0 ∣ x ∣ − 0.5 o t h e r w i z e smooth \ L_1=\left\{ \begin{aligned} 0.5x^2 &&\text{x=0}\\ |x|-0.5&&otherwize\\ \end{aligned} \right. smooth L1={0.5x2∣x∣−0.5x=0otherwize

N c l s = 256 a n d N c l s ≈ 2400 N_{cls}=256 \; and \; N_{cls} \approx 2400 Ncls=256andNcls≈2400
RCNN使用的loss和RPN类似。
def _add_losses(self, sigma_rpn=3.0):
with tf.variable_scope('LOSS_' + self._tag) as scope:
# RPN, class loss
rpn_cls_score = tf.reshape(self._predictions['rpn_cls_score_reshape'], [-1, 2])
rpn_label = tf.reshape(self._anchor_targets['rpn_labels'], [-1])
rpn_select = tf.where(tf.not_equal(rpn_label, -1))
rpn_cls_score = tf.reshape(tf.gather(rpn_cls_score, rpn_select), [-1, 2])
rpn_label = tf.reshape(tf.gather(rpn_label, rpn_select), [-1])
rpn_cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=rpn_cls_score, labels=rpn_label))
# RPN, bbox loss
rpn_bbox_pred = self._predictions['rpn_bbox_pred']
rpn_bbox_targets = self._anchor_targets['rpn_bbox_targets']
rpn_bbox_inside_weights = self._anchor_targets['rpn_bbox_inside_weights']
rpn_bbox_outside_weights = self._anchor_targets['rpn_bbox_outside_weights']
rpn_loss_box = self._smooth_l1_loss(rpn_bbox_pred, rpn_bbox_targets, rpn_bbox_inside_weights,
rpn_bbox_outside_weights, sigma=sigma_rpn, dim=[1, 2, 3])
# RCNN, class loss
cls_score = self._predictions["cls_score"]
label = tf.reshape(self._proposal_targets["labels"], [-1])
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=cls_score, labels=label))
# RCNN, bbox loss
bbox_pred = self._predictions['bbox_pred']
bbox_targets = self._proposal_targets['bbox_targets']
bbox_inside_weights = self._proposal_targets['bbox_inside_weights']
bbox_outside_weights = self._proposal_targets['bbox_outside_weights']
loss_box = self._smooth_l1_loss(bbox_pred, bbox_targets, bbox_inside_weights, bbox_outside_weights)
self._losses['cross_entropy'] = cross_entropy
self._losses['loss_box'] = loss_box
self._losses['rpn_cross_entropy'] = rpn_cross_entropy
self._losses['rpn_loss_box'] = rpn_loss_box
loss = cross_entropy + loss_box + rpn_cross_entropy + rpn_loss_box
regularization_loss = tf.add_n(tf.losses.get_regularization_losses(), 'regu')
self._losses['total_loss'] = loss + regularization_loss
self._event_summaries.update(self._losses)
return loss
训练
- 论文中采用4步交替训练策略。
- 先用预训练好的ImageNet来初始化RPN网络,然后微调(finetune)RPN网络;
- 根据第一步训练好的RPN来生成RoIs,然后单独训练 Fast R-CNN。在这一步训练过程中,Fast R-CNN的参数初始化也是采用ImageNet预训练的模型。两个网络完全分开训练,不存在共享网络层。
- 采用上一步Fast R-CNN训练好的网络参数,来重新初始化RPN的共享卷积层。(注意:这一步只对RPN的局部网络进行微调,前半部分和Fast R-CNN共享的卷积层训练好后就固定不变了)
- 继续固定共享网络层参数,用步骤3微调后的RPN网络生成的bbox对Fast R-CNN的非共享层进行参数微调。
- 本文所用的代码采用近似联合训练策略。
思路:把RPN的损失函数和Fast R-CNN的损失函数根据一定比例加在一起,然后进行整体的SGD训练
问题: RPN后续的网络层,无法对RPN的bbox坐标进行求导更新,即ROI的误差无法反向传播到RPN网络,因此只能称之为近似联合训练。没看懂。。。感觉他的意思是说RPN后面的回归和分类任务的损失包括了rpn的损失,但rpn的损失无法包括后面的,因为rpn的loss公式里考虑不到后面层的损失。
loss = cross_entropy + loss_box + rpn_cross_entropy + rpn_loss_box
训练自己的数据
参考Faster R-CNN(Tensorflow版) 训练自己的数据集