操作系统实验四——文件系统的简单命令的设计与实现
要求:
实现文件系统的简单命令,此篇文件实现命令:cp。cp 是copy的缩写,使用格式为cp srcname dstname;
说明:此文件系统使用c++实现,我们要实现cp命令,大概分这几步:
1、打开源文件
2、读取源文件内容到缓冲区
3、创建目标文件
4、打开目标文件
5、将缓冲区内容写入目标文件
6、关闭目标文件
因为,cp命令的代码为:
int FILESYS::cp(char *src, char *dst)
{
bool open_flag = false;
int i;
//确保没有打开过该文件 = 相同名字 + 相同目录
for(i=0; if[i].type ==1 && strcmp(openedFiles->f [i].fname,src)==0
&&openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum == current)
{
open_flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(!open_flag) open(src);
char buf[BUFSIZ] = {'#'};
size_t size = read(src,buf);
create(dst);
open(dst);
write(dst,buf,size);
close(dst);
if(!open_flag) close(src);
printf("---------------------------------------------------copy done!\n\n");
return 1;
} 在此处,我们重载了 write 和 read函数
read函数:
/*---------选择一个打开的文件读取信息到缓冲区----------*/
int FILESYS::read(char *file, char *buf, size_t size)
{
int i,fileStartNum;
char *startPoint,*endPoint;
//在打开文件列表中查找 file(还需要考虑同名不同目录文件的情况!!!)
for(i=0; if [i].fname,file)==0 )
{
if(openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum ==current)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("该文件处于打开列表中,本系统只能阅读当前目录下文件!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
if(i==OPEN_MAX)
{
printf("该文件尚未打开,请先打开后读取信息!\n");
return 0;
}
int active=i;
//计算文件物理地址
fileStartNum = openedFiles->f[active].currentBlockNum - 3 ;
startPoint = data[fileStartNum];
endPoint = data[fileStartNum + 1];
//end_dir=(struct dirFile *)[BlockSize-1];
//q=(char *)end_dir;
//printf("该文件的内容为: ");
i = 0;
if(size<=0)
{
while((*startPoint)!='#'&& (startPoint < endPoint))
{
buf[i] = *startPoint++;
i++;
}
}
else
{
while((*startPoint)!='#'&& (startPoint < endPoint) && (i < size))
{
buf[i] = *startPoint++;
i++;
}
}
buf[i] = '#';
return i;
} write函数:
int FILESYS::write(char *name, char *buf, size_t size)
{
int i;
char *startPoint,*endPoint;
//在打开文件列表中查找 file(还需要考虑同名不同目录文件的情况!!!)
for(i=0; if [i].fname,name)==0 )
{
if(openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum ==current)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("该文件处于打开列表中,本系统只能改写当前目录下文件!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
if(i==OPEN_MAX)
{
printf("该文件尚未打开,请先打开后写入信息!!\n");
return 0;
}
int active=i;
int fileStartNum = openedFiles->f[active].currentBlockNum - 3 ;
startPoint = data[fileStartNum];
endPoint = data[fileStartNum + 1];
//printf("请输入文本以#号结束:\t");
char input;
i = 0;
do
{
if(startPoint < endPoint-1)
{
*startPoint++ = buf[i];
}
else
{
printf("达到单体文件最大容量!");
*startPoint++ = '#';
break;
}
}
while(++i < size);
*startPoint = '#';
return i;
} 最后,我们要处理键盘输入的命令,需要增加以下几行代码:
else if(cmd=="cp")
{
char src[BUFSIZ];
char dst[BUFSIZ];
cin>>src;
cin>>dst;
fileSystem.cp(src,dst);
}好了,上全部代码
// filesystem.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
//#include "stdafx.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
typedef struct
{
char fname[16]; //file name
int type; //1 for usual file, 2 for dir file, 0 for null
int size; //file size
int fatherBlockNum; //father dir block num
int currentBlockNum; //current block num
} FCB;
/*const setting*/
const char* FilePath = "C:\\myfiles";
const int BlockSize = 512; //block size
const int OPEN_MAX = 5; //MAX FILE OPENED
const int BlockCount = BlockSize/sizeof(int); //BLOCK ITEMS IN A BLOCK
const int DiskSize = BlockSize*BlockCount; //DISK CONTENT
const int BlockFcbCount = BlockSize/sizeof(FCB);//FILE ITEMS IN A DIR
const int PATHLEN=256;
int OpenFileCount = 0;
class OPENLIST
{
public:
int files;
FCB *f;
public:
OPENLIST();
~OPENLIST();
};
OPENLIST::OPENLIST()
{
f=new FCB[OPEN_MAX];
}
OPENLIST::~OPENLIST()
{
//delete [OPEN_MAX]f;
delete f;
}
class dirFile
{
public:
FCB fcb[BlockFcbCount];
dirFile();
void initDir(int _FatherBlockNum,int _CurrentBlockNum,const char *name);//父块号,当前块号,目录名
void initFile(FCB &filefcb);
};
dirFile::dirFile()
{
//printf("");
return;
}
void dirFile::initDir(int _FatherBlockNum,int _CurrentBlockNum,const char *name)//父块号,当前块号,目录名
{
strcpy(fcb[0].fname,name); //本身的FCB
fcb[0].fatherBlockNum=_FatherBlockNum;
fcb[0].currentBlockNum=_CurrentBlockNum;
fcb[0].type=2; //标记目录文件
for(int i=1; iinitDir(2,2,"G:\\");
}
DISK::~DISK()
{
free(BaseAddr);
free(data);
}
FILE *fp; //磁盘文件地址
int current=2; //当前目录的盘块号
char command[32];
class CfileSysStringOp
{
char str[PATHLEN];
public:
CfileSysStringOp();
CfileSysStringOp(char *initstr);
~CfileSysStringOp();
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &stream, CfileSysStringOp &string);
friend istream &operator>>(istream &stream, CfileSysStringOp &string);
bool operator==(char *input);
CfileSysStringOp &operator=(CfileSysStringOp &stringOp);
CfileSysStringOp &operator-(char *string);
CfileSysStringOp &operator+(char *string);
void initialize(char *init);
void parseCmd();
};
CfileSysStringOp::CfileSysStringOp()
{
printf("address of op in construction=%0x\n", this);
return;
}
CfileSysStringOp::CfileSysStringOp(char *initstr)
{
strcpy(str, initstr);
}
CfileSysStringOp::~CfileSysStringOp()
{
printf("address of op in deconstruction=%0x\n", this);
return;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &stream, CfileSysStringOp &string)
{
stream<>(istream &stream, CfileSysStringOp &string)
{
stream>>string.str;
return stream;
}
bool CfileSysStringOp::operator ==(char *input)
{
return (strcmp(str, input)==0);
}
CfileSysStringOp &CfileSysStringOp::operator=(CfileSysStringOp &stringOp)
{
strcpy(str, stringOp.str);
return *this;
}
CfileSysStringOp &CfileSysStringOp::operator-(char *string)
{
int i=0;
int pos=0;
int strlen=sizeof(string);
char *sstr=NULL;
sstr=(char *)malloc(strlen);
for(i=PATHLEN-strlen-2; i>=0; i--)
{
strcpy(sstr, str+i);
if(strcmp(sstr, string)==0)
break;
}
if(i!=(PATHLEN-strlen))
str[i]='\0';
free(sstr);
return *this;
}
CfileSysStringOp &CfileSysStringOp::operator+(char *string)
{
strcat(str, string);
return *this;
}
void CfileSysStringOp::initialize(char *init)
{
strcpy(str, init);
}
void CfileSysStringOp::parseCmd()
{
char tempStr[PATHLEN];
int i=0;
memset(tempStr, 0, PATHLEN);
while(str[i]==' ')
i++;
strcpy(tempStr, str+i);
strcpy(str, tempStr);
i=0;
while(str[i]!=' ')
i++;
memset(tempStr, 0, PATHLEN);
if(if[i].type ==1 && strcmp(openedFiles->f [i].fname,src)==0
&&openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum == current)
{
open_flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(!open_flag) open(src);
char buf[BUFSIZ] = {'#'};
size_t size = read(src,buf);
create(dst);
open(dst);
write(dst,buf,size);
close(dst);
printf("---------------------------------------------------copy done!\n\n");
return 1;
}
int FILESYS::format()
{
fp = fopen(FilePath,"w+");
fwrite(BaseAddr,sizeof(char),DiskSize,fp);
fclose(fp);
printf("----------------------------------------------------------done\n\n");
return 1;
}
/*-----------------------创建子目录-------------------*/
int FILESYS::mkdir(char *sonfname)
{
//判断是否有重名
//寻找空白子目录项
//寻找空白盘块号
//当前目录下增加该子目录项
//分配子目录盘块,并且初始化
//修改fat表
int i,temp,iFAT;
if(current==2)
dir=root;
else
dir=(dirFile *)(data[current-3]);
/*--------为了避免该目录下同名文件夹--------*/
for(i = 1; ifcb[i].type==2 && strcmp(dir->fcb[i].fname,sonfname)==0 )
{
printf("该文件夹下已经有同名的文件夹存在了!\n");
return 0;
}
}
//查找空白fcb序号
for(i=1; ifcb[i].type==0)
break;
}
if(i==BlockFcbCount)
{
printf("该目录已满!请选择新的目录下创建!\n");
return 0;
}
temp=i;
for(i = 3; i < BlockCount; i++)
{
if(FAT1[i] == 0)
break;
}
if(i == BlockCount)
{
printf("磁盘已满!\n");
return 0;
}
iFAT=i;
/*-------------接下来进行分配----------*/
FAT1[iFAT]=FAT2[iFAT] = 2; //2表示分配给下级目录文件
//填写该分派新的盘块的参数
strcpy(dir->fcb[temp].fname,sonfname);
dir->fcb[temp].type=2;
dir->fcb[temp].fatherBlockNum=current;
dir->fcb[temp].currentBlockNum=iFAT;
//初始化子目录文件盘块
dir=(dirFile*)(data[iFAT-3]); //定位到子目录盘块号
dir->initDir(current,iFAT,sonfname);//iFAT是要分配的块号,这里的current用来指要分配的块的父块号
printf("---------------------------------------------------------------done\n\n");
return 1;
}
/*-------删除当前目录下的文件夹--------*/
int FILESYS::rmdir(char *sonfname)
{
//if(子目录不存在) return error
//if(子目录不是空文件夹) return error
//回收子目录磁盘块号b(修改fat)
//回收子目录占据目录项
int i,temp,j;//确保当前目录下有该文件,并记录下该FCB下标
if(current==2)
dir=root;
else
dir=(dirFile *)(data[current-3]);
for(i=1; ifcb[i].type==2 && strcmp(dir->fcb[i].fname,sonfname)==0)
{
break;
}
}
temp=i;
if(i==BlockFcbCount)
{
printf("当前目录下不存在该子目录!\n");
return 0;
}
j = dir->fcb[temp].currentBlockNum;
dirFile *sonDir; //当前子目录的指针
sonDir=(dirFile *)(data[ j - 3]);
for(i=1; ifcb[i].type!=0)
{
printf("该文件夹为非空文件夹,为确保安全,请清空后再删除!\n");
return 0;
}
}
/*开始删除子目录操作*/
FAT1[j] = FAT2[j]=0; //fat清空
char *p=data[j-3]; //格式化子目录
memset(p,0,BlockSize);
dir->initFile(dir->fcb[temp]); //回收子目录占据目录项
printf("---------------------------------------------------------------done\n\n");
return 1;
}
/*-------查询子目录------------*/
int FILESYS::listshow()
{
int i,DirCount=0,FileCount=0;
int fileList[BlockFcbCount];
int dirList[BlockFcbCount];
int j, k;
memset(fileList, 0, BlockFcbCount);
memset(dirList, 0, BlockFcbCount);
j=k=0;
//搜索当前目录
if(current==2)
dir=root;
else
dir=(dirFile *)(data[current-3]);
for(i=1; ifcb[i].type==1)
{
//查找普通文件
FileCount++;
fileList[j]=i;
j++;
printf("%s 文本文件.\n",dir->fcb[i].fname);
}
if(dir->fcb[i].type==2)
{
//查找目录文件
DirCount++;
dirList[k]=i;
k++;
printf("%s 文件夹.\n",dir->fcb[i].fname);
}
}
printf("\n该目录下共有 %d 个文本文件\n\n",FileCount);
j=k=0;
while(fileList[j]!=0)
{
printf("%s\n", dir->fcb[fileList[j]].fname);
j++;
}
printf("\n该目录下共有 %d 个文件夹\n\n",DirCount);
while(dirList[k]!=0)
{
printf("%s\n", dir->fcb[dirList[k]].fname);
k++;
}
printf("--------------------------------------------------------done\n\n");
return 1;
}
/*--------------进入当前目录下的子目录--------------*/
int FILESYS::changePath(char *sonfname)
{
if(current==2)
dir=root;
else
dir=(dirFile *)(data[current-3]);
/*回到父目录*/
if(strcmp(sonfname,"..")==0)
{
if(current==2)
{
printf("already in root dir!\n");
return 0;
}
current = dir->fcb[0].fatherBlockNum ;
currentPath = currentPath-"\\";
currentPath = currentPath-dir->fcb[0].fname;
return 1;
}
/*进入子目录*/
int i,temp;
//确保当前目录下有该目录,并且记录下它的FCB下标
for(i = 1; i < BlockFcbCount; i++)
{
//查找该文件
if(dir->fcb[i].type==2 && strcmp(dir->fcb[i].fname,sonfname)==0 )
{
temp=i;
break;
}
}
if(i==BlockFcbCount)
{
printf("不存在该目录!\n");
return 0;
}
//修改当前文件信息
current=dir->fcb [temp].currentBlockNum ;
currentPath = currentPath+dir->fcb [temp].fname;
currentPath=currentPath+"\\";
printf("-------------------------------------------------------------done\n\n");
return 1;
}
/*-----------在当前目录下创建文本文件---------------*/
int FILESYS::create(char *name)
{
int i,iFAT;//temp,
int emptyNum = 0,isFound = 0; //空闲目录项个数
if(current==2)
dir=root;
else
dir=(dirFile *)(data[current-3]);
//查看目录是否已满
//为了避免同名的文本文件
for(i=1; ifcb[i].type == 0 && isFound == 0)
{
emptyNum = i;
isFound = 1;
}
else if(dir->fcb[i].type==1 && strcmp(dir->fcb[i].fname,name)==0 )
{
printf("无法在同一目录下创建同名文件!\n");
return 0;
}
}
if(emptyNum == 0)
{
printf("已经达到目录项容纳上限,无法创建新目录!\n");
return 0;
}
//查找FAT表寻找空白区,用来分配磁盘块号j
for(i = 3; ifcb[emptyNum].fname,name);
dir->fcb[emptyNum].type=1;
dir->fcb[emptyNum].fatherBlockNum=current;
dir->fcb[emptyNum].currentBlockNum=iFAT;
dir->fcb[emptyNum].size =0;
char* p = data[iFAT -3];
memset(p,'#',BlockSize);
printf("----------------------------------------------------------------done\n\n");
return 1;
}
/*当前目录下添加一个打开文件*/
int FILESYS::open(char *file)//打开文件
{
int i,FcbIndex;
//确保没有打开过该文件 = 相同名字 + 相同目录
for(i=0; if[i].type ==1 && strcmp(openedFiles->f [i].fname,file)==0
&&openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum == current)
{
printf("该文件已经被打开!\n");
return 0;
}
}
//确保有空的打开文件项
if(openedFiles->files == OPEN_MAX)
{
printf("打开文件数目达到上限!无法再打开新文件.\n");
return 0;
}
//确保当前目录下有该文件,并且记录下它的FCB下标
if(current==2)
dir=root;
else
dir=(dirFile *)(data[current-3]);
for(i = 1; i< BlockFcbCount; i++)
{
//查找该文件
if(dir->fcb[i].type==1 && strcmp(dir->fcb[i].fname,file)==0 )
{
FcbIndex=i;
break;
}
}
if(i==BlockFcbCount)
{
printf("当前目录下不存在该文件!\n");
return 0;
}
//装载新文件进入打开文件列表,(FCB信息,文件数++) ??难道名字过不来?
openedFiles->f[OpenFileCount] = dir->fcb[FcbIndex]; //FCB拷贝
openedFiles->files ++;
printf("文件打开成功!\n");
OpenFileCount++;
return 1;
}
/*-------------在指定的文件里记录信息---------------*/
int FILESYS::write(char *name)
{
int i;
char *startPoint,*endPoint;
//在打开文件列表中查找 file(还需要考虑同名不同目录文件的情况!!!)
for(i=0; if [i].fname,name)==0 )
{
if(openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum ==current)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("该文件处于打开列表中,本系统只能改写当前目录下文件!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
if(i==OPEN_MAX)
{
printf("该文件尚未打开,请先打开后写入信息!!\n");
return 0;
}
int active=i;
int fileStartNum = openedFiles->f[active].currentBlockNum - 3 ;
startPoint = data[fileStartNum];
endPoint = data[fileStartNum + 1];
printf("请输入文本以#号结束:\t");
char input;
while(((input=getchar())!='#'))
{
if(startPoint < endPoint-1)
{
*startPoint++ = input;
}
else
{
printf("达到单体文件最大容量!");
*startPoint++ = '#';
break;
}
}
return 1;
}
int FILESYS::write(char *name, char *buf, size_t size)
{
int i;
char *startPoint,*endPoint;
//在打开文件列表中查找 file(还需要考虑同名不同目录文件的情况!!!)
for(i=0; if [i].fname,name)==0 )
{
if(openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum ==current)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("该文件处于打开列表中,本系统只能改写当前目录下文件!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
if(i==OPEN_MAX)
{
printf("该文件尚未打开,请先打开后写入信息!!\n");
return 0;
}
int active=i;
int fileStartNum = openedFiles->f[active].currentBlockNum - 3 ;
startPoint = data[fileStartNum];
endPoint = data[fileStartNum + 1];
//printf("请输入文本以#号结束:\t");
char input;
i = 0;
do
{
if(startPoint < endPoint-1)
{
*startPoint++ = buf[i];
}
else
{
printf("达到单体文件最大容量!");
*startPoint++ = '#';
break;
}
}
while(++i < size);
*startPoint = '#';
return i;
}
/*---------选择一个打开的文件读取信息----------*/
int FILESYS::read(char *file)
{
int i,fileStartNum;
char *startPoint,*endPoint;
//在打开文件列表中查找 file(还需要考虑同名不同目录文件的情况!!!)
for(i=0; if [i].fname,file)==0 )
{
if(openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum ==current)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("该文件处于打开列表中,本系统只能阅读当前目录下文件!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
if(i==OPEN_MAX)
{
printf("该文件尚未打开,请先打开后读取信息!\n");
return 0;
}
int active=i;
//计算文件物理地址
fileStartNum = openedFiles->f[active].currentBlockNum - 3 ;
startPoint = data[fileStartNum];
endPoint = data[fileStartNum + 1];
//end_dir=(struct dirFile *)[BlockSize-1];
//q=(char *)end_dir;
printf("该文件的内容为: ");
while((*startPoint)!='#'&& (startPoint < endPoint))
{
putchar(*startPoint++);
}
printf("\n");
return 1;
}
/*---------选择一个打开的文件读取信息----------*/
int FILESYS::read(char *file, char *buf, size_t size)
{
int i,fileStartNum;
char *startPoint,*endPoint;
//在打开文件列表中查找 file(还需要考虑同名不同目录文件的情况!!!)
for(i=0; if [i].fname,file)==0 )
{
if(openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum ==current)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("该文件处于打开列表中,本系统只能阅读当前目录下文件!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
if(i==OPEN_MAX)
{
printf("该文件尚未打开,请先打开后读取信息!\n");
return 0;
}
int active=i;
//计算文件物理地址
fileStartNum = openedFiles->f[active].currentBlockNum - 3 ;
startPoint = data[fileStartNum];
endPoint = data[fileStartNum + 1];
//end_dir=(struct dirFile *)[BlockSize-1];
//q=(char *)end_dir;
//printf("该文件的内容为: ");
i = 0;
if(size<=0)
{
while((*startPoint)!='#'&& (startPoint < endPoint))
{
buf[i] = *startPoint++;
i++;
}
}
else
{
while((*startPoint)!='#'&& (startPoint < endPoint) && (i < size))
{
buf[i] = *startPoint++;
i++;
}
}
buf[i] = '#';
return i;
}
int FILESYS::close(char *file)
{
//释放该文件所占内存
//释放用户打开文件列表表项
int i;
//在打开文件列表中查找 file(还需要考虑同名不同目录文件的情况!!!)
for(i=0; if [i].type = 1)&&
(strcmp(openedFiles->f [i].fname,file)==0))
{
if(openedFiles->f[i].fatherBlockNum == current)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("该文件已打开,但未在当前目录下,无法关闭!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
if(i==OPEN_MAX)
{
printf("该文件未在打开列表中!\n");
return 0;
}
int active=i;
openedFiles->files --;
dir->initFile(openedFiles->f[active]);
OpenFileCount--;
printf("该文件已关闭!\n");
return 1;
}
/*---------在当前目录下删除文件-----------*/
int FILESYS::delfile(char *name)
{
int i,temp,j;
//确保当前目录下有该文件,并且记录下它的FCB下标
if(current==2)
dir=root;
else
dir=(dirFile *)(data[current-3]);
for(i=1; ifcb[i].type==1 && strcmp(dir->fcb[i].fname,name)==0)
{
break;
}
}
if(i==BlockFcbCount)
{
printf("当前目录下不存在该文件!\n");
return 0;
}
//从打开列表中删除
close(name);
temp=i;
/*开始删除文件操作*/
j = dir->fcb [temp].currentBlockNum ; //查找盘块号j
FAT1[j]=FAT2[j]=0; //fat1,fat2表标记为空白
char *p=data[j - 3];
memset(p,0,BlockSize); //清除原文本文件的内容
dir->initFile(dir->fcb[temp]); //type=0; //标记该目录项为空文件
printf("------------------------------------------------------------done\n\n");
return 1;
}
/*--------System exit---------------------*/
int FILESYS::exit()
{
//将所有文件都关闭
//保存到磁盘上C:\myfiles
fp=fopen(FilePath,"w+");
fwrite(BaseAddr,sizeof(char),DiskSize,fp);
fclose(fp);
printf("---------------------------------------------------------done\n\n");
return 1;
}
int main()
{
FILESYS fileSystem;
current = 2;
currentPath.initialize("G:\\"); //当前路径
/*********************************************************************/
printf("-----Welcome To My Operate System Of File(FAT)-----\n");
//使用说明书
printf("\n 以下是使用说明书:\n");
printf("--------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("|| format :对磁盘格式化. || \n");
printf("|| exit :安全退出该文件系统,保存信息. || \n");
printf("|| mkdir dirname :创建子目录. || \n");
printf("|| rmdir dirname :删除子目录. || \n");
printf("|| ls dirname :显示当前目录下信息. || \n");
printf("|| cd dirname :更改当前目录. || \n");
printf("|| create filename :创建一个新文件,并且打开. || \n");
printf("|| write filename :选择一个打开的文件写入信息 || \n");
printf("|| read filename :选择一个打开的文件读取信息. || \n");
printf("|| rm filename :删除文件. || \n");
printf("|| open filename :打开文件. || \n");
printf("|| close filename :关闭文件. || \n");
printf("-------------------------------------------------------------\n\n");
if((fp=fopen(FilePath,"r"))!=NULL)
{
fread(fileSystem.BaseAddr,sizeof(char),DiskSize,fp);
printf("加载磁盘文件( %s )成功,现在可以进行操作了!\n\n",FilePath);
fclose(fp);
}
else
{
printf("这是你第一次使用该文件管理系统!\t正在初始化...\n");
fileSystem.format();
printf("初始化已经完成,现在可以进行操作了!\n\n");
}
printf("--------------------------------------------------------------\n\n");
while(1)
{
cout<>cmd;
// cmd.parseCmd();
if(cmd=="format")
{
fileSystem.format();
}
else if(cmd=="mkdir")
{
cin>>command;
fileSystem.mkdir(command);
}
else if(cmd=="rmdir")
{
cin>>command;
fileSystem.rmdir(command);
}
else if(cmd=="ls")
{
fileSystem.listshow();
}
else if(cmd=="cd")
{
cin>>command;
fileSystem.changePath(command);
}
else if(cmd=="create")
{
cin>>command;
fileSystem.create(command);
}
else if(cmd=="open")
{
cin>>command;
fileSystem.open(command);
}
else if(cmd=="write")
{
cin>>command;
fileSystem.write(command);
}
else if(cmd=="read")
{
cin>>command;
fileSystem.read(command);
}
else if(cmd=="close")
{
cin>>command;
fileSystem.close(command);
}
else if(cmd=="rm")
{
cin>>command;
fileSystem.delfile(command);
}
else if(cmd=="exit")
{
fileSystem.exit();
break;
}
else if(cmd=="cp")
{
char src[BUFSIZ];
char dst[BUFSIZ];
cin>>src;
cin>>dst;
fileSystem.cp(src,dst);
}
else
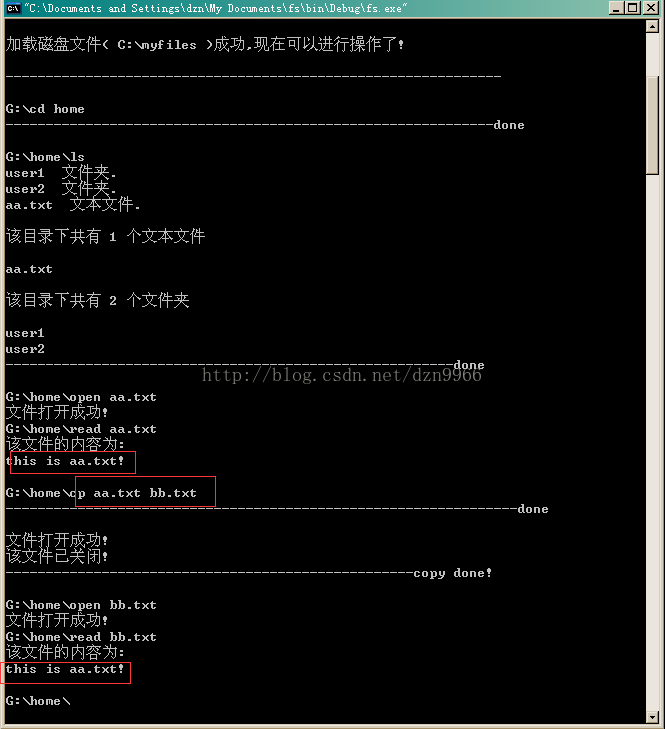
cout<<"无效指令,请重新输入:"< 运行截图:
over!