RPN 预备编程知识(二) : 函数篇章 bbox_transform.py
目录
1. bbox_transform 计算与anchor有最大IOU的GT的偏移量
2. bbox_transform_batch
3. bbox_transform_inv 根据anchor和偏移量计算proposals
4. clip_boxes 将proposals的边界限制在图片内
5. clip_boxes_batch
6. bbox_overlaps (附手绘理解IOU源码)
7. bbox_overlaps_batch
这个代码里面主要是一些在anchor_targte_layer.py和proposals_layers.py中使用到的一些函数,比较简单,主要是帮助以上两个代码理解。
(2) 为什么要做Bounding-box regression?

如上图所示,绿色的框为飞机的Ground Truth,红色的框是提取的Region Proposal.那么即便红色的框被分类器识别为飞机,但是由于红色的框定位不准(IoU<0.5),那么这张图相当于没有正确的检测出飞机.如果我们能对红色的框进行微调,使得经过微调后的窗口跟Ground Truth更接近,这样岂不是定位会更准确.确实,Bounding-box regression 就是用来微调这个窗口的.
(3) 回归/微调的对象是什么?
(4) Bounding-box regression(边框回归)
那么经过何种变换才能从图11中的窗口P变为窗口呢?比较简单的思路就是:
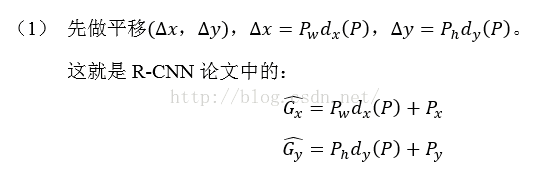

注意:只有当Proposal和Ground Truth比较接近时(线性问题),因为有e,我们才能将其作为训练样本训练我们的线性回归模型,否则会导致训练的回归模型不work(当Proposal跟GT离得较远,就是复杂的非线性问题了,此时用线性回归建模显然不合理).这个也是G-CNN: an Iterative Grid Based Object Detector多次迭代实现目标准确定位的关键.
线性回归就是给定输入的特征向量X,学习一组参数W,使得经过线性回归后的值跟真实值Y(Ground Truth)非常接近.即.那么Bounding-box中我们的输入以及输出分别是什么呢?
输入:![]() 这个是什么?输入就是这四个数值吗?其实真正的输入是这个窗口对应的CNN特征,也就是R-CNN中的Pool5feature(特征向量)。(注:训练阶段输入还包括 Ground Truth,也就是下边提到的
这个是什么?输入就是这四个数值吗?其实真正的输入是这个窗口对应的CNN特征,也就是R-CNN中的Pool5feature(特征向量)。(注:训练阶段输入还包括 Ground Truth,也就是下边提到的![]() )
)
输出:需要进行的平移变换和尺度缩放![]() ,或者说是
,或者说是![]() 。我们的最终输出不应该是Ground Truth吗?是的,但是有了这四个变换我们就可以直接得到Ground Truth,这里还有个问题,根据上面4个公式我们可以知道,P经过
。我们的最终输出不应该是Ground Truth吗?是的,但是有了这四个变换我们就可以直接得到Ground Truth,这里还有个问题,根据上面4个公式我们可以知道,P经过![]() ,得到的并不是真实值G,而是预测值
,得到的并不是真实值G,而是预测值![]() 。
。
的确,这四个值应该是经过 Ground Truth 和Proposal计算得到的真正需要的平移量![]() 和尺度缩放
和尺度缩放![]() 。
。
这也就是R-CNN中的:
那么目标函数可以表示为![]() 是输入Proposal的特征向量,
是输入Proposal的特征向量,![]() 是要学习的参数(*表示
是要学习的参数(*表示![]() ,也就是每一个变换对应一个目标函数),
,也就是每一个变换对应一个目标函数),![]() 是得到的预测值。我们要让预测值跟真实值
是得到的预测值。我们要让预测值跟真实值![]() 差距最小,得到损失函数为:
差距最小,得到损失函数为:
函数优化目标为:
利用梯度下降法或者最小二乘法就可以得到![]() 。
。
1. bbox_transform 计算与anchor有最大IOU的GT的偏移量
计算与anchor有最大IOU的GT的偏移量,边框回归:
import numpy as np
"""计算与anchor有最大IOU的GT的偏移量"""
#ex_rois:表示内部anchor;gt_rois:表示与anchor最匹配的GT
#下面本来都不是H*W而是内部的anchors,方便书写,写成那样了。
def bbox_transform(ex_rois, gt_rois):
#得到anchor的(x,y,w,h)
ex_widths = ex_rois[:, 2] - ex_rois[:, 0] + 1.0#(H*W,)
ex_heights = ex_rois[:, 3] - ex_rois[:, 1] + 1.0
ex_ctr_x = ex_rois[:, 0] + 0.5 * ex_widths
ex_ctr_y = ex_rois[:, 1] + 0.5 * ex_heights
# 得到GT的(x,y,w,h)
#注意:当前的GT不是最一开始传进来的所有GT,而是与对应anchor最匹配的GT,可能有重复信息
gt_widths = gt_rois[:, 2] - gt_rois[:, 0] + 1.0
gt_heights = gt_rois[:, 3] - gt_rois[:, 1] + 1.0 #(H*W,)
gt_ctr_x = gt_rois[:, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths
gt_ctr_y = gt_rois[:, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights
#按照损失函数中的计算公式,计算,得到对应的偏移量
targets_dx = (gt_ctr_x - ex_ctr_x) / ex_widths
targets_dy = (gt_ctr_y - ex_ctr_y) / ex_heights
targets_dw = np.log(gt_widths / ex_widths)
targets_dh = np.log(gt_heights / ex_heights)
#看到vstack想到内存地址不连续,需要np.ascontiguousarray
targets = torch.stack(
(targets_dx, targets_dy, targets_dw, targets_dh),1)
return targets #targets (H*W,4)caffe版本引用:
#bbox_overlaps里有vastck
overlaps = bbox_overlaps( #返回大小连续的overlaps,等同于排序 、
np.ascontiguousarray(anchors, dtype=np.float),
np.ascontiguousarray(gt_boxes, dtype=np.float))
2. bbox_transform_batch
def bbox_transform_batch(ex_rois, gt_rois):
if ex_rois.dim() == 2:
ex_widths = ex_rois[:, 2] - ex_rois[:, 0] + 1.0 #ex_widths (H*W,)
ex_heights = ex_rois[:, 3] - ex_rois[:, 1] + 1.0
ex_ctr_x = ex_rois[:, 0] + 0.5 * ex_widths
ex_ctr_y = ex_rois[:, 1] + 0.5 * ex_heights
gt_widths = gt_rois[:, :, 2] - gt_rois[:, :, 0] + 1.0
gt_heights = gt_rois[:, :, 3] - gt_rois[:, :, 1] + 1.0
gt_ctr_x = gt_rois[:, :, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths#gt_ctr_x (B,H*W)
gt_ctr_y = gt_rois[:, :, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights
#ex_ctr_x.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_ctr_x) :(H*W,)_>(1,H*W)_>(B,H*W) / (H*W,)
targets_dx = (gt_ctr_x - ex_ctr_x.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_ctr_x)) / ex_widths
targets_dy = (gt_ctr_y - ex_ctr_y.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_ctr_y)) / ex_heights
targets_dw = torch.log(gt_widths / ex_widths.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_widths))
targets_dh = torch.log(gt_heights / ex_heights.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_heights))
elif ex_rois.dim() == 3:
ex_widths = ex_rois[:, :, 2] - ex_rois[:, :, 0] + 1.0
ex_heights = ex_rois[:,:, 3] - ex_rois[:,:, 1] + 1.0
ex_ctr_x = ex_rois[:, :, 0] + 0.5 * ex_widths
ex_ctr_y = ex_rois[:, :, 1] + 0.5 * ex_heights
gt_widths = gt_rois[:, :, 2] - gt_rois[:, :, 0] + 1.0
gt_heights = gt_rois[:, :, 3] - gt_rois[:, :, 1] + 1.0
gt_ctr_x = gt_rois[:, :, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths
gt_ctr_y = gt_rois[:, :, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights
targets_dx = (gt_ctr_x - ex_ctr_x) / ex_widths
targets_dy = (gt_ctr_y - ex_ctr_y) / ex_heights
targets_dw = torch.log(gt_widths / ex_widths)
targets_dh = torch.log(gt_heights / ex_heights)
else:
raise ValueError('ex_roi input dimension is not correct.')
#targets (B,H*W,4)
targets = torch.stack(
(targets_dx, targets_dy, targets_dw, targets_dh),2)pytorch版本的引用
overlaps = bbox_overlaps_batch(anchors, gt_boxes)3. bbox_transform_inv 根据anchor和偏移量计算proposals
def bbox_transform_inv(boxes, deltas):
""" 根据anchor和偏移量计算proposals"""
if boxes.shape[0] == 0:
return np.zeros((0, deltas.shape[1]), dtype=deltas.dtype)
boxes = boxes.astype(deltas.dtype, copy=False)#转换数据类型,使得二者一致
#将anchor还原为(x,y,w,h)的格式
widths = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0] + 1.0
heights = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1] + 1.0
ctr_x = boxes[:, 0] + 0.5 * widths
ctr_y = boxes[:, 1] + 0.5 * heights
#得到(x,y,w,h)方向上的偏移量
dx = deltas[:, 0::4] #!4表示步长,每隔4个选一个。
dy = deltas[:, 1::4]
dw = deltas[:, 2::4]
dh = deltas[:, 3::4]
pred_ctr_x = dx * widths[:, np.newaxis] + ctr_x[:, np.newaxis]#np.newaxis,表示将widths增加一维,使得其能够相加
pred_ctr_y = dy * heights[:, np.newaxis] + ctr_y[:, np.newaxis]
pred_w = np.exp(dw) * widths[:, np.newaxis]
pred_h = np.exp(dh) * heights[:, np.newaxis]
pred_boxes = np.zeros(deltas.shape, dtype=deltas.dtype)
#最后返回的是左上和右下顶点的坐标[x1,y1,x2,y2]。
# x1
pred_boxes[:, 0::4] = pred_ctr_x - 0.5 * pred_w
# y1
pred_boxes[:, 1::4] = pred_ctr_y - 0.5 * pred_h
# x2
pred_boxes[:, 2::4] = pred_ctr_x + 0.5 * pred_w
# y2
pred_boxes[:, 3::4] = pred_ctr_y + 0.5 * pred_h
return pred_boxes4. clip_boxes 将proposals的边界限制在图片内
# 调用格式 proposals = clip_boxes(proposals, im_info[:2])
def clip_boxes(boxes, im_shape):
"""将proposals的边界限制在图片内"""
# x1 >= 0
boxes[:, 0::4] = np.maximum(np.minimum(boxes[:, 0::4], im_shape[1] - 1), 0)
# y1 >= 0
boxes[:, 1::4] = np.maximum(np.minimum(boxes[:, 1::4], im_shape[0] - 1), 0)
# x2 < im_shape[1]
boxes[:, 2::4] = np.maximum(np.minimum(boxes[:, 2::4], im_shape[1] - 1), 0)
# y2 < im_shape[0]
boxes[:, 3::4] = np.maximum(np.minimum(boxes[:, 3::4], im_shape[0] - 1), 0)
return boxes
5. clip_boxes_batch
def clip_boxes_batch(boxes, im_shape, batch_size):
"""
Clip boxes to image boundaries.
"""
num_rois = boxes.size(1)
boxes[boxes < 0] = 0
# batch_x = (im_shape[:,0]-1).view(batch_size, 1).expand(batch_size, num_rois)
# batch_y = (im_shape[:,1]-1).view(batch_size, 1).expand(batch_size, num_rois)
batch_x = im_shape[:, 1] - 1
batch_y = im_shape[:, 0] - 1
boxes[:,:,0][boxes[:,:,0] > batch_x] = batch_x
boxes[:,:,1][boxes[:,:,1] > batch_y] = batch_y
boxes[:,:,2][boxes[:,:,2] > batch_x] = batch_x
boxes[:,:,3][boxes[:,:,3] > batch_y] = batch_y
return boxes6. bbox_overlaps
def bbox_overlaps(anchors, gt_boxes):
"""
anchors: (N, 4) ndarray of float
gt_boxes: (K, 4) ndarray of float
overlaps: (N, K) ndarray of overlap between boxes and query_boxes
"""
N = anchors.size(0)
K = gt_boxes.size(0)
#gt_boxes_area (1, K)
gt_boxes_area = ((gt_boxes[:,2] - gt_boxes[:,0] + 1) *
(gt_boxes[:,3] - gt_boxes[:,1] + 1)).view(1, K)
#anchors_area (N, 1)
anchors_area = ((anchors[:,2] - anchors[:,0] + 1) *
(anchors[:,3] - anchors[:,1] + 1)).view(N, 1)
#anchors(N, 4) _>boxes(N, K, 4)
boxes = anchors.view(N, 1, 4).expand(N, K, 4)
#gt_boxes: (K, 4) _> query_boxes(N, K, 4)
query_boxes = gt_boxes.view(1, K, 4).expand(N, K, 4)
iw = (torch.min(boxes[:,:,2], query_boxes[:,:,2]) -
torch.max(boxes[:,:,0], query_boxes[:,:,0]) + 1)
iw[iw < 0] = 0
ih = (torch.min(boxes[:,:,3], query_boxes[:,:,3]) -
torch.max(boxes[:,:,1], query_boxes[:,:,1]) + 1)
ih[ih < 0] = 0
#broad (1, K)+(N, 1)= (N, K) - (N, K)
ua = anchors_area + gt_boxes_area - (iw * ih)
overlaps = iw * ih / ua
return overlaps7. bbox_overlaps_batch
# --------------------------------------------------------
# Fast R-CNN
# Copyright (c) 2015 Microsoft
# Licensed under The MIT License [see LICENSE for details]
# Written by Ross Girshick
# --------------------------------------------------------
# --------------------------------------------------------
# Reorganized and modified by Jianwei Yang and Jiasen Lu
# --------------------------------------------------------
import torch
import numpy as np
import pdb
#下面本来都不是H*W而是内部的anchors,方便书写,写成那样了。
def bbox_transform(ex_rois, gt_rois):
ex_widths = ex_rois[:, 2] - ex_rois[:, 0] + 1.0 #(H*W,)
ex_heights = ex_rois[:, 3] - ex_rois[:, 1] + 1.0
ex_ctr_x = ex_rois[:, 0] + 0.5 * ex_widths
ex_ctr_y = ex_rois[:, 1] + 0.5 * ex_heights
#注意:当前的GT不是最一开始传进来的所有GT,而是与对应anchor最匹配的GT,可能有重复信息
gt_widths = gt_rois[:, 2] - gt_rois[:, 0] + 1.0
gt_heights = gt_rois[:, 3] - gt_rois[:, 1] + 1.0
gt_ctr_x = gt_rois[:, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths #(H*W,)
gt_ctr_y = gt_rois[:, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights
targets_dx = (gt_ctr_x - ex_ctr_x) / ex_widths
targets_dy = (gt_ctr_y - ex_ctr_y) / ex_heights
targets_dw = torch.log(gt_widths / ex_widths)
targets_dh = torch.log(gt_heights / ex_heights)
#targets (H*W,4)
targets = torch.stack(
(targets_dx, targets_dy, targets_dw, targets_dh),1)
return targets
def bbox_transform_batch(ex_rois, gt_rois):
if ex_rois.dim() == 2:
ex_widths = ex_rois[:, 2] - ex_rois[:, 0] + 1.0 #ex_widths (H*W,)
ex_heights = ex_rois[:, 3] - ex_rois[:, 1] + 1.0
ex_ctr_x = ex_rois[:, 0] + 0.5 * ex_widths
ex_ctr_y = ex_rois[:, 1] + 0.5 * ex_heights
gt_widths = gt_rois[:, :, 2] - gt_rois[:, :, 0] + 1.0
gt_heights = gt_rois[:, :, 3] - gt_rois[:, :, 1] + 1.0
gt_ctr_x = gt_rois[:, :, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths#gt_ctr_x (B,H*W)
gt_ctr_y = gt_rois[:, :, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights
#ex_ctr_x.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_ctr_x) :(H*W,)_>(1,H*W)_>(B,H*W) / (H*W,)
targets_dx = (gt_ctr_x - ex_ctr_x.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_ctr_x)) / ex_widths
targets_dy = (gt_ctr_y - ex_ctr_y.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_ctr_y)) / ex_heights
targets_dw = torch.log(gt_widths / ex_widths.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_widths))
targets_dh = torch.log(gt_heights / ex_heights.view(1,-1).expand_as(gt_heights))
elif ex_rois.dim() == 3:
ex_widths = ex_rois[:, :, 2] - ex_rois[:, :, 0] + 1.0
ex_heights = ex_rois[:,:, 3] - ex_rois[:,:, 1] + 1.0
ex_ctr_x = ex_rois[:, :, 0] + 0.5 * ex_widths
ex_ctr_y = ex_rois[:, :, 1] + 0.5 * ex_heights
gt_widths = gt_rois[:, :, 2] - gt_rois[:, :, 0] + 1.0
gt_heights = gt_rois[:, :, 3] - gt_rois[:, :, 1] + 1.0
gt_ctr_x = gt_rois[:, :, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths
gt_ctr_y = gt_rois[:, :, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights
targets_dx = (gt_ctr_x - ex_ctr_x) / ex_widths
targets_dy = (gt_ctr_y - ex_ctr_y) / ex_heights
targets_dw = torch.log(gt_widths / ex_widths)
targets_dh = torch.log(gt_heights / ex_heights)
else:
raise ValueError('ex_roi input dimension is not correct.')
#targets (B,H*W,4)
targets = torch.stack(
(targets_dx, targets_dy, targets_dw, targets_dh),2)
return targets
def bbox_transform_inv(boxes, deltas, batch_size):
widths = boxes[:, :, 2] - boxes[:, :, 0] + 1.0
heights = boxes[:, :, 3] - boxes[:, :, 1] + 1.0
ctr_x = boxes[:, :, 0] + 0.5 * widths
ctr_y = boxes[:, :, 1] + 0.5 * heights
dx = deltas[:, :, 0::4]
dy = deltas[:, :, 1::4]
dw = deltas[:, :, 2::4]
dh = deltas[:, :, 3::4]
pred_ctr_x = dx * widths.unsqueeze(2) + ctr_x.unsqueeze(2)
pred_ctr_y = dy * heights.unsqueeze(2) + ctr_y.unsqueeze(2)
pred_w = torch.exp(dw) * widths.unsqueeze(2)
pred_h = torch.exp(dh) * heights.unsqueeze(2)
pred_boxes = deltas.clone()
# x1
pred_boxes[:, :, 0::4] = pred_ctr_x - 0.5 * pred_w
# y1
pred_boxes[:, :, 1::4] = pred_ctr_y - 0.5 * pred_h
# x2
pred_boxes[:, :, 2::4] = pred_ctr_x + 0.5 * pred_w
# y2
pred_boxes[:, :, 3::4] = pred_ctr_y + 0.5 * pred_h
return pred_boxes
def clip_boxes_batch(boxes, im_shape, batch_size):
"""
Clip boxes to image boundaries.
"""
num_rois = boxes.size(1)
boxes[boxes < 0] = 0
# batch_x = (im_shape[:,0]-1).view(batch_size, 1).expand(batch_size, num_rois)
# batch_y = (im_shape[:,1]-1).view(batch_size, 1).expand(batch_size, num_rois)
batch_x = im_shape[:, 1] - 1
batch_y = im_shape[:, 0] - 1
boxes[:,:,0][boxes[:,:,0] > batch_x] = batch_x
boxes[:,:,1][boxes[:,:,1] > batch_y] = batch_y
boxes[:,:,2][boxes[:,:,2] > batch_x] = batch_x
boxes[:,:,3][boxes[:,:,3] > batch_y] = batch_y
return boxes
def clip_boxes(boxes, im_shape, batch_size):
for i in range(batch_size):
boxes[i,:,0::4].clamp_(0, im_shape[i, 1]-1)
boxes[i,:,1::4].clamp_(0, im_shape[i, 0]-1)
boxes[i,:,2::4].clamp_(0, im_shape[i, 1]-1)
boxes[i,:,3::4].clamp_(0, im_shape[i, 0]-1)
return boxes
def bbox_overlaps(anchors, gt_boxes):
"""
anchors: (N, 4) ndarray of float
gt_boxes: (K, 4) ndarray of float
overlaps: (N, K) ndarray of overlap between boxes and query_boxes
"""
N = anchors.size(0)
K = gt_boxes.size(0)
#gt_boxes_area (1, K)
gt_boxes_area = ((gt_boxes[:,2] - gt_boxes[:,0] + 1) *
(gt_boxes[:,3] - gt_boxes[:,1] + 1)).view(1, K)
#anchors_area (N, 1)
anchors_area = ((anchors[:,2] - anchors[:,0] + 1) *
(anchors[:,3] - anchors[:,1] + 1)).view(N, 1)
#anchors(N, 4) _>boxes(N, K, 4)
boxes = anchors.view(N, 1, 4).expand(N, K, 4)
#gt_boxes: (K, 4) _> query_boxes(N, K, 4)
query_boxes = gt_boxes.view(1, K, 4).expand(N, K, 4)
iw = (torch.min(boxes[:,:,2], query_boxes[:,:,2]) -
torch.max(boxes[:,:,0], query_boxes[:,:,0]) + 1)
iw[iw < 0] = 0
ih = (torch.min(boxes[:,:,3], query_boxes[:,:,3]) -
torch.max(boxes[:,:,1], query_boxes[:,:,1]) + 1)
ih[ih < 0] = 0
#broad (1, K)+(N, 1)= (N, K) - (N, K)
ua = anchors_area + gt_boxes_area - (iw * ih)
overlaps = iw * ih / ua
return overlaps
def bbox_overlaps_batch(anchors, gt_boxes):
"""
anchors: (N, 4) ndarray of float
gt_boxes: (b, K, 5) ndarray of float
选一个比较大的k如果一张图片中gt达不到k,其余的用0填充
overlaps: (N, K) ndarray of overlap between boxes and query_boxes
"""
batch_size = gt_boxes.size(0)
# (N, 4)
if anchors.dim() == 2:
N = anchors.size(0)
K = gt_boxes.size(1)
#torch中直接利用reshape可替代先view然后contiguous()
#anchors (N, 4) _> (b, N, 4)
anchors = anchors.view(1, N, 4).expand(batch_size, N, 4).contiguous()
#gt_boxes (b, K, 5) _> (b, K, 4)
gt_boxes = gt_boxes[:,:,:4].contiguous()
#(b, n, 1)
gt_boxes_x = (gt_boxes[:,:,2] - gt_boxes[:,:,0] + 1)
gt_boxes_y = (gt_boxes[:,:,3] - gt_boxes[:,:,1] + 1)
gt_boxes_area = (gt_boxes_x * gt_boxes_y).view(batch_size, 1, K)
#(b ,1 ,k)
anchors_boxes_x = (anchors[:,:,2] - anchors[:,:,0] + 1)
anchors_boxes_y = (anchors[:,:,3] - anchors[:,:,1] + 1)
anchors_area = (anchors_boxes_x * anchors_boxes_y).view(batch_size, N, 1)
gt_area_zero = (gt_boxes_x == 1) & (gt_boxes_y == 1)
anchors_area_zero = (anchors_boxes_x == 1) & (anchors_boxes_y == 1)
#(b, N, 4) _> (b, N, 1, 4) _> (b, N, k, 4),先N就k所以(b, N, 1, 4)不是(b, 1, N, 4)
boxes = anchors.view(batch_size, N, 1, 4).expand(batch_size, N, K, 4)
#(b, K, 4) _> (b, 1, K, 4) _> (b, N, k, 4)
query_boxes = gt_boxes.view(batch_size, 1, K, 4).expand(batch_size, N, K, 4)
iw = (torch.min(boxes[:,:,:,2], query_boxes[:,:,:,2]) -
torch.max(boxes[:,:,:,0], query_boxes[:,:,:,0]) + 1)
iw[iw < 0] = 0
ih = (torch.min(boxes[:,:,:,3], query_boxes[:,:,:,3]) -
torch.max(boxes[:,:,:,1], query_boxes[:,:,:,1]) + 1)
ih[ih < 0] = 0
# (b, n, 1)+(b ,1 ,k) - (b, n, k)
ua = anchors_area + gt_boxes_area - (iw * ih)
overlaps = iw * ih / ua
# mask the overlap here.
overlaps.masked_fill_(gt_area_zero.view(batch_size, 1, K).expand(batch_size, N, K), 0)
overlaps.masked_fill_(anchors_area_zero.view(batch_size, N, 1).expand(batch_size, N, K), -1)
# (b, N, 4 or 5)
elif anchors.dim() == 3:
N = anchors.size(1)
K = gt_boxes.size(1)
if anchors.size(2) == 4:
anchors = anchors[:,:,:4].contiguous()
else:
anchors = anchors[:,:,1:5].contiguous()
gt_boxes = gt_boxes[:,:,:4].contiguous()
gt_boxes_x = (gt_boxes[:,:,2] - gt_boxes[:,:,0] + 1)
gt_boxes_y = (gt_boxes[:,:,3] - gt_boxes[:,:,1] + 1)
gt_boxes_area = (gt_boxes_x * gt_boxes_y).view(batch_size, 1, K)
anchors_boxes_x = (anchors[:,:,2] - anchors[:,:,0] + 1)
anchors_boxes_y = (anchors[:,:,3] - anchors[:,:,1] + 1)
anchors_area = (anchors_boxes_x * anchors_boxes_y).view(batch_size, N, 1)
gt_area_zero = (gt_boxes_x == 1) & (gt_boxes_y == 1)
anchors_area_zero = (anchors_boxes_x == 1) & (anchors_boxes_y == 1)
boxes = anchors.view(batch_size, N, 1, 4).expand(batch_size, N, K, 4)
query_boxes = gt_boxes.view(batch_size, 1, K, 4).expand(batch_size, N, K, 4)
iw = (torch.min(boxes[:,:,:,2], query_boxes[:,:,:,2]) -
torch.max(boxes[:,:,:,0], query_boxes[:,:,:,0]) + 1)
iw[iw < 0] = 0
ih = (torch.min(boxes[:,:,:,3], query_boxes[:,:,:,3]) -
torch.max(boxes[:,:,:,1], query_boxes[:,:,:,1]) + 1)
ih[ih < 0] = 0
ua = anchors_area + gt_boxes_area - (iw * ih)
overlaps = iw * ih / ua
# mask the overlap here.
overlaps.masked_fill_(gt_area_zero.view(batch_size, 1, K).expand(batch_size, N, K), 0)
overlaps.masked_fill_(anchors_area_zero.view(batch_size, N, 1).expand(batch_size, N, K), -1)
else:
raise ValueError('anchors input dimension is not correct.')
return overlaps




