如何使用Pytorch-Metric-Learning?
文章目录
- 如何使用Pytorch-Metric-Learning?
-
- 1.Pytorch-Metric-Learning库9个模块的功能
-
- 1.1 Sampler模块
- 1.2 Miner模块
- 1.3 Loss模块
- 1.4 Reducer模块
- 1.5 Distance模块
- 1.6 Regularizer模块
- 1.7 Trainer模块
- 1.8 Tester模块
- 1.9 Utils模块
- 2.如何使用PyTorch Metric Learning库中的Loss?
-
- 2.1 使用方法
- 2.2 调用原理
- 3.根据PyTorch Metric Learning库自定义Loss
-
- 3.1 通用Loss模板(简单版本)
- 3.2 通用Loss模板(使用distances和reducers版本)
- 3.3 使用`indices_tuple`注意项
- 参考
如何使用Pytorch-Metric-Learning?
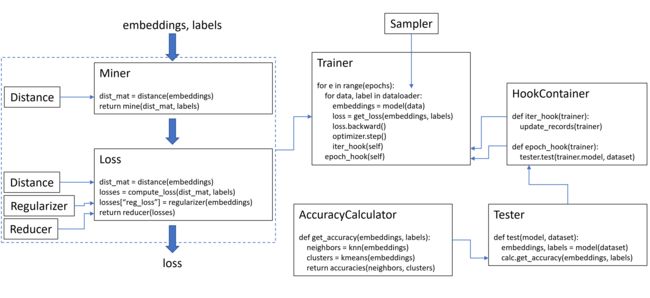
PyTorch-Metric-Learning 是一个基于 PyTorch 的开源库,专门用于度量学习(Metric Learning)的实现和研究。度量学习是一类机器学习任务,旨在学习一个距离函数,使得相似的样本在特征空间中靠得更近,而不相似的样本更远。该库包含9个模块(可用模块概览,点击查看),每个模块都可在现有的代码库中独立使用,或者组合起来完成完整的训练和测试工作流。
1.Pytorch-Metric-Learning库9个模块的功能
通常流程:Your Data --> Sampler --> Miner --> Loss --> Reducer --> Final loss value
1.1 Sampler模块
采样器只是torch.utils.data.Sampler类的扩展,即它们被传递给PyTorch数据加载器(特别是作为采样器参数,除非另有说明)。用于确定批次应如何形成。
1.2 Miner模块
挖掘函数(Mining functions)接收一个包含 n 个嵌入的批次,并返回 k pairs/triplets,用于计算损失:
- Pair miners输出一个大小为 4 的元组:(anchors, positives, anchors, negatives)。
- Triplet miners输出一个大小为 3 的元组:(anchors, positives, negatives)。
- 如果没有使用元组挖掘函数,损失函数将默认使用批次中的所有可能的对/三元组。
from pytorch_metric_learning import miners, losses
miner_func = miners.SomeMiner()
loss_func = losses.SomeLoss()
miner_output = miner_func(embeddings, labels)
losses = loss_func(embeddings, labels, miner_output)
1.3 Loss模块
Loss模块中,包含了许多的loss函数。loss函数的用法如下:
from pytorch_metric_learning import losses
loss_func = losses.SomeLoss() # 实例化想要的loss
loss = loss_func(embeddings, labels) # 根据loss的compute_loss传入相对应的参数来计算损失
loss与miner结合使用的用法如下:
from pytorch_metric_learning import miners
miner_func = miners.SomeMiner() # 实例化miner
loss_func = losses.SomeLoss() # 实例化loss
miner_output = miner_func(embeddings, labels) # 计算损失
loss = loss_func(embeddings, labels, miner_output) # 计算损失
对于某些损失,如果已经传入了pair/triplet索引,则不需要传入标签:
loss = loss_func(embeddings, indices_tuple=pairs)
# 也适用于ref_emb
loss = loss_func(embeddings, indices_tuple=pairs, ref_emb=ref_emb)
也可以使用reducer指定如何将loss减少到单个值:
from pytorch_metric_learning import reducers
reducer = reducers.SomeReducer()
loss_func = losses.SomeLoss(reducer=reducer)
loss = loss_func(embeddings, labels)
对于元组损失,可以将锚(anchors)的来源和正/负(positives/negatives)分开:
loss_func = losses.SomeLoss()
# anchors will come from embeddings
# positives/negatives will come from ref_emb
loss = loss_func(embeddings, labels, ref_emb=ref_emb, ref_labels=ref_labels)
1.4 Reducer模块
reducer指定如何从多个loss值变为单个loss值。例如,ContrastiveLoss计算批次中每个正对和负对的损失。reducer将获取所有这些每对loss,并将它们减少到单个值。reducer的使用是将其传入到损失函数中,如下所示:
from pytorch_metric_learning import losses, reducers
reducer = reducers.SomeReducer()
loss_func = losses.SomeLoss(reducer=reducer)
loss = loss_func(embeddings, labels)
原理:在内部,loss函数创建一个包含loss和其他信息的字典。reducer接受这个字典,执行reducer,并返回一个可以调用.backward()的值。
1.5 Distance模块
Distance用于计算输入嵌入之间的成对距离/相似性。下面以TripletMarginLoss损失为例,解释其功能与用途:
from pytorch_metric_learning.losses import TripletMarginLoss
loss_func = TripletMarginLoss(margin=0.2)
该损失函数试图最小化 [ d a p − d a n + m a r g i n ] + [\mathrm{d_{ap}-d_{an}+margin}]_{+} [dap−dan+margin]+。通常, d a p d_{ap} dap和 d a n d_{an} dan表示欧几里得或L2距离。但是如果我们想使用平方L2距离,或者非归一化的L1距离,或者像信噪比这样完全不同的距离度量呢?使用Distance模块,可以轻松尝试这些想法:
### TripletMarginLoss with squared L2 distance ###
from pytorch_metric_learning.distances import LpDistance
loss_func = TripletMarginLoss(margin=0.2, distance=LpDistance(power=2))
### TripletMarginLoss with unnormalized L1 distance ###
loss_func = TripletMarginLoss(margin=0.2, distance=LpDistance(normalize_embeddings=False, p=1))
### TripletMarginLoss with signal-to-noise ratio###
from pytorch_metric_learning.distances import SNRDistance
loss_func = TripletMarginLoss(margin=0.2, distance=SNRDistance())
### TripletMarginLoss with cosine similarity##
from pytorch_metric_learning.distances import CosineSimilarity
loss_func = TripletMarginLoss(margin=0.2, distance=CosineSimilarity())
所有losses, miners, 和 regularizers都接受Distance参数。
1.6 Regularizer模块
Regularizer应用于权重和嵌入,而不需要标签或元组。 下面是一个将权重正则化器传递给损失函数的示例。
from pytorch_metric_learning import losses, regularizers
R = regularizers.RegularFaceRegularizer()
loss = losses.ArcFaceLoss(margin=30, num_classes=100, embedding_size=128, weight_regularizer=R)
1.7 Trainer模块
Trainer存在于这个库中,因为一些度量学习算法不仅仅是损失或挖掘函数。一些算法需要额外的网络、数据扩充、学习速率计划等。Trainer模块的目标是提供对这些类型的度量学习算法的访问。Trainer的使用如下:
from pytorch_metric_learning import trainers
t = trainers.SomeTrainingFunction(*args, **kwargs)
t.train(num_epochs=10)
1.8 Tester模块
Tester采用你的模型和数据集,并计算基于最近邻的准确性指标。请注意,Tester需要faiss包。Tester的使用如下:
from pytorch_metric_learning import testers
t = testers.SomeTestingFunction(*args, **kwargs)
dataset_dict = {"train": train_dataset, "val": val_dataset}
all_accuracies = tester.test(dataset_dict, epoch, model)
1.9 Utils模块
utils模块中包含了许多的工具包,具体请查阅此处。
2.如何使用PyTorch Metric Learning库中的Loss?
2.1 使用方法
以TripletMarginLoss为例进行讲解,以下是TripletMarginLoss的源代码:
import torch
from ..reducers import AvgNonZeroReducer
from ..utils import loss_and_miner_utils as lmu
from .base_metric_loss_function import BaseMetricLossFunction
class TripletMarginLoss(BaseMetricLossFunction):
"""
Args:
margin: The desired difference between the anchor-positive distance and the
anchor-negative distance.
swap: Use the positive-negative distance instead of anchor-negative distance,
if it violates the margin more.
smooth_loss: Use the log-exp version of the triplet loss
"""
def __init__(
self,
margin=0.05,
swap=False,
smooth_loss=False,
triplets_per_anchor="all",
**kwargs
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.margin = margin
self.swap = swap
self.smooth_loss = smooth_loss
self.triplets_per_anchor = triplets_per_anchor
self.add_to_recordable_attributes(list_of_names=["margin"], is_stat=False)
def compute_loss(self, embeddings, labels, indices_tuple):
indices_tuple = lmu.convert_to_triplets(
indices_tuple, labels, t_per_anchor=self.triplets_per_anchor
)
anchor_idx, positive_idx, negative_idx = indices_tuple
if len(anchor_idx) == 0:
return self.zero_losses()
mat = self.distance(embeddings)
ap_dists = mat[anchor_idx, positive_idx]
an_dists = mat[anchor_idx, negative_idx]
if self.swap:
pn_dists = mat[positive_idx, negative_idx]
an_dists = self.distance.smallest_dist(an_dists, pn_dists)
current_margins = self.distance.margin(ap_dists, an_dists)
violation = current_margins + self.margin
if self.smooth_loss:
loss = torch.nn.functional.softplus(violation)
else:
loss = torch.nn.functional.relu(violation)
return {
"loss": {
"losses": loss,
"indices": indices_tuple,
"reduction_type": "triplet",
}
}
def get_default_reducer(self):
return AvgNonZeroReducer()
当我们想要使用TripletMarginLoss损失时,首先要初始化TripletMarginLoss。
from pytorch_metric_learning import losses
loss_func = losses.TripletMarginLoss()
要计算训练循环中的损失,请传入模型计算的嵌入(embeddings)、相应的标签(labels)与索引元组(indices_tuple)。嵌入应该具有大小(N,embedding_size),标签应该具有大小(N),其中N是批量大小。索引元组为3元组(anchors, positives, negatives)或4元组(anchors, positives, anchors, negatives),该案例传入的是3元组,因为源码中的compute_loss函数。具体使用如下:
"""
自己构建三元组的示例:
"""
for i, (data, labels) in enumerate(dataloader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
embeddings = model(data)
indices_tuple = (anchor_idx, positive_idx, negative_idx) # 自己构建
loss = loss_func(embeddings, labels, indices_tuple) # indices_tuple可以是自己构建的,也可以是通过Miner得到的,根据具体情况对待
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
"""
通过Miner得到三元组的示例:
"""
from pytorch_metric_learning import miners, losses
miner = miners.MultiSimilarityMiner()
loss_func = losses.TripletMarginLoss()
for i, (data, labels) in enumerate(dataloader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
embeddings = model(data)
hard_pairs = miner(embeddings, labels) # 得到三元组
loss = loss_func(embeddings, labels, hard_pairs)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
在上面的代码中,Miner找到了它认为特别困难的正负对。请注意,即使TripletMarginLoss对三元组(triplets)进行操作,仍然可以成对(pairs)传递。这是因为在必要时,库会自动将对转换为三元组,并将三元组转换为对。
2.2 调用原理
在使用库中的TripletMarginLoss函数时,我们首先需要初始化TripletMarginLoss,然后在计算TripletMarginLoss的时候,我们传入的参数与源码中的compute_loss函数一致。感觉有点像PyTorch模型的forward函数。一般这种方法的调用是通过python的特殊方法__call__函数实现的,比如:
def __call__(self, embeddings, labels, indices_tuple=None):
return self.compute_loss(embeddings, labels, indices_tuple)
但是源码中并未定义__call__方法。如果该TripletMarginLoss继承自torch.nn.Module,并且定义了forward方法,如下。那么尽管没有显式定义 __call__ 方法,但是我们依旧可以这样使用。
class TripletMarginLoss(BaseMetricLossFunction):
# ... 其他代码 ...
def forward(self, embeddings, labels, indices_tuple=None):
return self.compute_loss(embeddings, labels, indices_tuple)
但是即没有定义 __call__ 方法,也没有定义 forward 方法,那么为什么还可以loss = loss_func(embeddings, labels, hard_pairs)直接使用呢?
这是因为TripletMarginLoss继承自 BaseMetricLossFunction, TripletMarginLoss 会继承 BaseMetricLossFunction 中的所有方法和属性。而在BaseMetricLossFunction中实现了 forward 方法。所以即使 TripletMarginLoss 自己没有显式定义这些方法,作为子类,它会自动继承父类的行为,并使用父类的方法来实现损失计算逻辑。
3.根据PyTorch Metric Learning库自定义Loss
3.1 通用Loss模板(简单版本)
from pytorch_metric_learning.losses import BaseMetricLossFunction
import torch
class BarebonesLoss(BaseMetricLossFunction):
def compute_loss(self, embeddings, labels, indices_tuple, ref_emb, ref_labels):
# perform some calculation #
some_loss = torch.mean(embeddings)
# put into dictionary #
return {
"loss": {
"losses": some_loss,
"indices": None,
"reduction_type": "already_reduced",
}
}
3.2 通用Loss模板(使用distances和reducers版本)
通过添加distances和reducers来增强损失函数的功能。
from pytorch_metric_learning.losses import BaseMetricLossFunction
from pytorch_metric_learning.reducers import AvgNonZeroReducer
from pytorch_metric_learning.distances import CosineSimilarity
from pytorch_metric_learning.utils import loss_and_miner_utils as lmu
import torch
class FullFeaturedLoss(BaseMetricLossFunction):
def compute_loss(self, embeddings, labels, indices_tuple, ref_emb, ref_labels):
indices_tuple = lmu.convert_to_triplets(indices_tuple, labels)
anchors, positives, negatives = indices_tuple
if len(anchors) == 0:
return self.zero_losses()
mat = self.distance(embeddings)
ap_dists = mat[anchors, positives]
an_dists = mat[anchors, negatives]
# perform some calculations #
losses1 = ap_dists - an_dists
losses2 = ap_dists * 5
losses3 = torch.mean(embeddings)
# put into dictionary #
return {
"loss1": {
"losses": losses1,
"indices": indices_tuple,
"reduction_type": "triplet",
},
"loss2": {
"losses": losses2,
"indices": (anchors, positives),
"reduction_type": "pos_pair",
},
"loss3": {
"losses": losses3,
"indices": None,
"reduction_type": "already_reduced",
},
}
def get_default_reducer(self):
return AvgNonZeroReducer()
def get_default_distance(self):
return CosineSimilarity()
def _sub_loss_names(self):
return ["loss1", "loss2", "loss3"]
- 该损失函数对三元组进行操作,因此
convert_to_triplets用于将indices_tuple转换为三元组形式。 self.distance返回成对的距离矩阵。- 损失函数的输出是一个包含多个子损失的字典。这就是重写
_sub_loss_names函数的原因。 - 默认情况下,
get_default_reducer被覆盖以使用AvgNonZeroReducer,而不是MeanReducer。 - 默认情况下,
get_default_distance被覆盖以使用CosineSimilarity,而不是LpDistances(p=2)。
3.3 使用indices_tuple注意项
使用indices_tuple,需要使用适当的转换函数,这样我们不需要知道将传入什么类型的indices_tuple,因为转换函数会自动处理。indices_tuple三种可能的形式:
- None
- 大小为4的元组,表示miner pairs 的索引(anchors, positives, anchors, negatives)
- 大小为3的元组,表示miner triplets 的索引(anchors, positives, negatives)
from pytorch_metric_learning.utils import loss_and_miner_utils as lmu
# For a pair based loss
# After conversion, indices_tuple will be a tuple of size 4
indices_tuple = lmu.convert_to_pairs(indices_tuple, labels)
# For a triplet based loss
# After conversion, indices_tuple will be a tuple of size 3
indices_tuple = lmu.convert_to_triplets(indices_tuple, labels)
# For a classification based loss
# miner_weights.shape == labels.shape
# You can use these to weight your loss
miner_weights = lmu.convert_to_weights(indices_tuple, labels, dtype=torch.float32)
参考
- PyTorch Metric Learning官方库
- PyTorch Metric Learning中文库
- PyTorch Metric Learning官方文档
- pytorch-metric-learning度量学习工具