libevent源码阅读笔记——通用时间队列
由于libevent支持 /dev/poll, kqueue(2), event ports, POSIX select(2), Windows select(), poll(2), and epoll(4).多平台网络IO,所以根据不同平台,也定义了不同eventop对象,它们被统一放入结构体指针数组eventops[]里。
libevent运用二进制形式,区分5种事件类型。event_add 函数用于添加超时、读、写、信号事件。超时事件由程序内部主动触发。老版本的超时事件的元素存在一个红黑树中,新版本引入了最小堆和队列共同来进行管理。下面介绍的都是libevent2.0.21版本内容。
先来介绍下对超时的管理,libevent用小根堆存储所有的超时时间,但是小根堆的时间复杂度为log(N),为了进一步提高效率,libevent采用了queue对相同超时间隔的Timer事件进行组织。Timer触发时间=当前绝对时间+超时间隔。所以具有相同超时间隔的Timer事件,它们的触发时间是不同的,可以按照升序排列在一起。
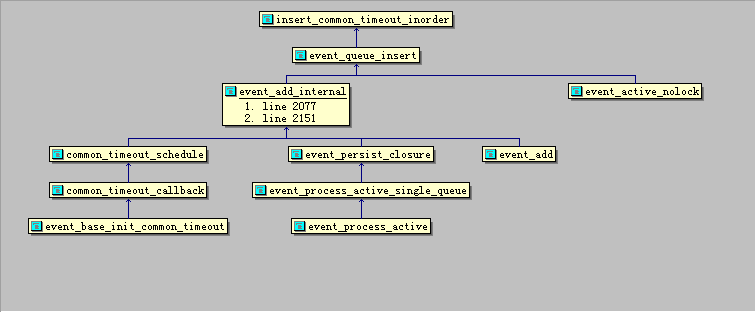
event_base_init_common_timeout函数用于初始化通用时间队列。
const struct timeval *
event_base_init_common_timeout(struct event_base *base,
const struct timeval *duration)
{
int i;
struct timeval tv;
const struct timeval *result=NULL;
struct common_timeout_list *new_ctl;
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
//有MICROSECONDS_MASK位的时间需要去除MICROSECONDS_MASK位才是真实的超时间隔
if (duration->tv_usec > 1000000) {
memcpy(&tv, duration, sizeof(struct timeval));
if (is_common_timeout(duration, base))
tv.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
tv.tv_sec += tv.tv_usec / 1000000;
tv.tv_usec %= 1000000;
duration = &tv;
}
//判断超时间隔tv是否已经存在于通用时间队列中
for (i = 0; i < base->n_common_timeouts; ++i) {
const struct common_timeout_list *ctl =
base->common_timeout_queues[i];
if (duration->tv_sec == ctl->duration.tv_sec &&
duration->tv_usec ==
(ctl->duration.tv_usec & MICROSECONDS_MASK)) {
EVUTIL_ASSERT(is_common_timeout(&ctl->duration, base));
result = &ctl->duration;
goto done;
}
}
//通用超时队列元素已达到上限
if (base->n_common_timeouts == MAX_COMMON_TIMEOUTS) {
event_warnx("%s: Too many common timeouts already in use; "
"we only support %d per event_base", __func__,
MAX_COMMON_TIMEOUTS);
goto done;
}
//分配的超时队列空间已被用完,realloc重新分配。16个或n_common_timeouts*2个元素
if (base->n_common_timeouts_allocated == base->n_common_timeouts) {
int n = base->n_common_timeouts < 16 ? 16 :
base->n_common_timeouts*2;
struct common_timeout_list **newqueues =
mm_realloc(base->common_timeout_queues,
n*sizeof(struct common_timeout_queue *));
if (!newqueues) {
event_warn("%s: realloc",__func__);
goto done;
}
base->n_common_timeouts_allocated = n;
base->common_timeout_queues = newqueues;
}
new_ctl = mm_calloc(1, sizeof(struct common_timeout_list));
if (!new_ctl) {
event_warn("%s: calloc",__func__);
goto done;
}
//libevent采用位运算,将通用Timer事件的tv_usec高位置MICROSECONDS_MASK位,表示该事件是个通用Timer事件
TAILQ_INIT(&new_ctl->events);
new_ctl->duration.tv_sec = duration->tv_sec;
new_ctl->duration.tv_usec =
duration->tv_usec | COMMON_TIMEOUT_MAGIC |
(base->n_common_timeouts << COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX_SHIFT);
//调用event_assign函数,将Timer事件进行赋值。common_timeout_queues每个元素都是common_timeout_list指针
//common_timeout_callback为事件的回调函数,将在下面介绍
evtimer_assign(&new_ctl->timeout_event, base,
common_timeout_callback, new_ctl);
new_ctl->timeout_event.ev_flags |= EVLIST_INTERNAL;
event_priority_set(&new_ctl->timeout_event, 0);
new_ctl->base = base;
base->common_timeout_queues[base->n_common_timeouts++] = new_ctl;
result = &new_ctl->duration;
done:
if (result)
EVUTIL_ASSERT(is_common_timeout(result, base));
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
return result;
}通用Timer事件的回调函数
static void
common_timeout_callback(evutil_socket_t fd, short what, void *arg)
{
struct timeval now;
struct common_timeout_list *ctl = arg;
struct event_base *base = ctl->base;
struct event *ev = NULL;
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
gettime(base, &now);
while (1) {
//从队列的时间数组中取第一个元素,如果时间未到跳出循环,否则从事件队列中删除
//并且激活超时事件
ev = TAILQ_FIRST(&ctl->events);
if (!ev || ev->ev_timeout.tv_sec > now.tv_sec ||
(ev->ev_timeout.tv_sec == now.tv_sec &&
(ev->ev_timeout.tv_usec&MICROSECONDS_MASK) > now.tv_usec))
break;
event_del_internal(ev);
event_active_nolock(ev, EV_TIMEOUT, 1);
}
//如果通用队列还未空,则说明还有Timer时间需要触发
if (ev)
common_timeout_schedule(ctl, &now, ev);
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
}common_timeout_schedule将通用Timer队列中第一个event插入到event_base的minheap中
static void
common_timeout_schedule(struct common_timeout_list *ctl,
const struct timeval *now, struct event *head)
{
struct timeval timeout = head->ev_timeout;
//去除通用Timer标志位,插入到event_base的最小堆中
timeout.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
event_add_internal(&ctl->timeout_event, &timeout, 1);
}insert_common_timeout_inorder 函数将按照从小到大的顺序将通用Timer时间添加到通用Timer事件队列中。
在初始化完成common_timeout_queues后,可以通过event_add/event_process_active,往common_timeout_queues里添加元素。
永久Timer事件会被不断地激活、触发
static inline void
event_persist_closure(struct event_base *base, struct event *ev)
{
/* reschedule the persistent event if we have a timeout. */
if (ev->ev_io_timeout.tv_sec || ev->ev_io_timeout.tv_usec) {
/* If there was a timeout, we want it to run at an interval of
* ev_io_timeout after the last time it was _scheduled_ for,
* not ev_io_timeout after _now_. If it fired for another
* reason, though, the timeout ought to start ticking _now_. */
struct timeval run_at, relative_to, delay, now;
ev_uint32_t usec_mask = 0;
EVUTIL_ASSERT(is_same_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout,
&ev->ev_io_timeout));
gettime(base, &now);
if (is_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout, base)) {
delay = ev->ev_io_timeout;
usec_mask = delay.tv_usec & ~MICROSECONDS_MASK;
delay.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
if (ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT) {
relative_to = ev->ev_timeout;
relative_to.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
} else {
relative_to = now;
}
} else {
delay = ev->ev_io_timeout;
if (ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT) {
relative_to = ev->ev_timeout;
} else {
relative_to = now;
}
}
evutil_timeradd(&relative_to, &delay, &run_at);
if (evutil_timercmp(&run_at, &now, <)) {
/* Looks like we missed at least one invocation due to
* a clock jump, not running the event loop for a
* while, really slow callbacks, or
* something. Reschedule relative to now.
*/
evutil_timeradd(&now, &delay, &run_at);
}
//如果该PERSIST事件是通用Timer事件,则依然以通用Timer事件的方式
//添加到通用Timer事件列表中,该Timer事件将不会被放到
//event_base的minheap中
run_at.tv_usec |= usec_mask;
event_add_internal(ev, &run_at, 1);
}
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
//执行PERSIST Timer事件的回调函数
(*ev->ev_callback)(ev->ev_fd, ev->ev_res, ev->ev_arg);
}