安装
- yum安装
yum install ansible
- pip安装
pip install ansible
Hello Ansible
- 创建资产文件(inventory)
[servers]
192.168.137.3 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
192.168.137.4 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
servers是一个组名称,可以把具有相同用途的机器归为同一个组,例如:
[mysql_servers]
在安装MySQL时只需指定这个组安装:
ansible -i inventory mysql_servers -m shell -a 'yum install mysql'
- ansible常用参数
-a MODULE_ARGS, --args=MODULE_ARGS
eg: ansible -i inventory 192.168.137.4 -m shell -a 'echo haha'
模块shell 之后带的参数
-i INVENTORY, --inventory-file=INVENTORY
指定资产文件
-m MODULE_NAME, --module-name=MODULE_NAME
指定模块,如上面的shell模块
- 使用ansible
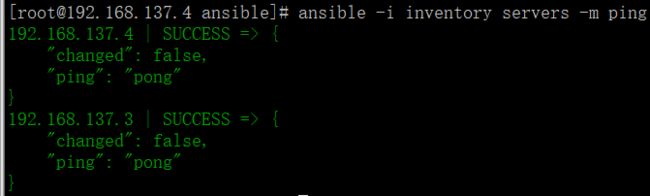
资产文件inventory中 servers 组内所用机器执行 ping 模块,测试机器状态。
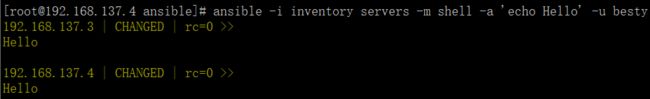
资产文件inventory中 servers 组内所用机器执行 shell 模块,并使用besty用户执行 echo 命令。
Configuring Ansible (配置ansible)
- ansible使用 INI 配置
INI配置格式(参考MySQL)
[section]
key = value
-
配置文件的选择 (按以下顺序加载配置文件)
- ANSIBLE_CONFIG (Firstly)
export ANSIBLE_CONFIG="/data/ansible/ansible.cfg"
配置文件就是:/data/ansible/ansible.cfg- ./ansible.cfg (Secondly)
若无 ANSIBLE_CONFIG 环境变量,配置文件优先选择当前目录的 ansible.cfg
- ~/.ansible.cfg (Thirdly)
家目录下的 .ansible.cfg,注意是隐藏文件
- /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg (Lastly)
用软件包管理工具(yum/apt/dnf/pip)安装时自动生成
-
Configuration using environment variables (使用环境变量配置)
export ANSIBLE_SUDO_USER=root
The ANSIBLE_SUDO_USER variable can then be used as part of the playbooks.
定义的 ANSIBLE_SUDO_USER 变量就能在 playbooks中使用了 -
Configuration using ansible.cfg
- hostfile
This parameter indicates the path to the inventory file
默认的inventory文件:
hostfile = /etc/ansible/hosts- library
The library parameter points to the path of the directory where Ansible modules are stored
自定义模块的存储路径,默认:
library = /usr/share/ansible- forks
This parameter is the default number of processes that you want Ansible to spawn
ansible执行时打开的最大进程数: forks = 5- remote_port
远程机器的的ssh端口: remote_port = 22
- timeout
This is the default value for the timeout of SSH connection attempts:
timeout = 60- log_path
日志存储路径
log_path = /var/log/ansible.log
Working with playbooks
playbooks 是一个to-do list,包含了远程需要执行的 任务列表,每个任务会调用一个模块,用 yaml 编写
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/07/yaml.html
- playbooks编写
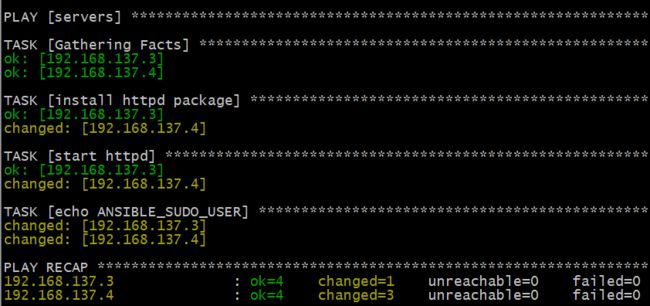
- playbooks/setup_apache.yml
- hosts: servers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name=httpd state=latest
sudo: yes
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
sudo: yes
- name: echo ANSIBLE_SUDO_USER
shell: echo "The sudo user is {{ lookup('env','ANSIBLE_SUDO_USER') }}" > /data/user
sudo: yes
ANSIBLE_SUDO_USER是之前定义的环境变量: export ANSIBLE_SUDO_USER=root
- 一个playbook包含如下三个部分:
- hosts:指定要执行任务的是那些机器,这里是 [server] 组
- remote_user: 被管理机器执行任务时使用的用户
- tasks: 任务列表(to-do list), 本例安装 httpd 服务并启动, name参数 可选, 推荐下面这种写法:
tasks:
- yum: name=httpd state=latest
sudo: yes
- service: name=httpd state=started
sudo: yes
- 执行ansible-playbook
# ansible-playbook -i hosts playbooks/setup_apache.yml
playbooks 具有 幂等性(Idempotency),即执行多次和执行一次达到的 状态(state)是一样的.
可以理解为:1 n = 1
-v 选项输出更详细的信息, 可叠加3个 -v/-vv/-vvv
- 系统自带变量使用
- debug: msg={{ ansible_distribution }}
sudo: yes
- 列出playbook所有任务
ansible-playbook -i hosts playbooks/setup_apache.yml --list-tasks
- 执行任务前询问
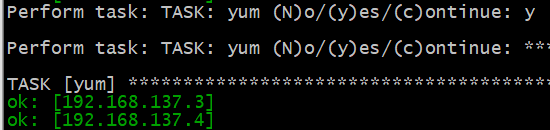
ansible-playbook -i hosts playbooks/setup_apache.yml --step
- playbooks variables
- 变量设置
Variables in an included task file
# cat playbooks/install_apache.yml
- set_fact: package_name=httpd
when: ansible_os_family == "RedHat"
- set_fact: package_name=apache2
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian"
# cat playbooks/setup_apache.yml
- hosts: servers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include: /data/ansible/playbooks/install_apache.yml
- yum: name={{ package_name }} state=latest
sudo: yes
- service: name={{ package_name }} state=started
sudo: yes
setup_apache.yml 真正用于执行任务,使用 include 模块导入playbooks/install_apache.yml文件
Variables in a playbook
# cat playbooks/setup_apache.yml
- hosts: servers
remote_user: root
vars:
- package_name: httpd
tasks:
- yum: name={{ package_name }} state=latest
sudo: yes
Variables in a global file
# cat playbooks/var1.yml
---
package_name: "apache2"
# cat playbooks/var2.yml
---
package_name: "httpd"
# cat playbooks/setup_apache.yml
- hosts: servers
remote_user: root
vars_files:
- var1.yml
- var2.yml
tasks:
- yum: name={{ package_name }} state=latest
sudo: yes
You tell Ansible which variable files need to be checked by using the vars_files key, vars_files 键值对,查找变量时顺序从下到上,先在 var2.yml 查找是否有 package_name 变量,若找到则使用 var2.yml定义的变量值,找不到则在 var1.yml 中查找
Facts as variables (可理解为常量)
ansible 192.168.137.4 -m setup
Command-line variables
执行命令时赋值
ansible-playbook -i hosts playbooks/apache.yml --extra-vars "package_name=apache2"
Working with inventory files
- Groups of groups
具有相同用途或者需要执行相同模块指令的机器可以归类为一个组
[db]
192.168.137.4
mysql_host
[application]
192.168.137.3
web.com
安装MySQL时执行以下命令
ansible db -i hosts -m shell "yum install mysql"
- Regular expressions with an inventory file
使用正则表达式
[db]
192.168.137.[2:4]
#表示 db 组有192.168.137.2-43 台机器
- Inventory Variables
在资产文件中定义变量
# 主机变量
[db]
192.168.137.4 dbname='game'
# 组变量,整个组都能使用
[db:vars]
dbport="3306"
dbname="game"
#以上变量在playbook能够使用
- Overriding configuration parameters with an inventory file
inventory 文件中定义变量 覆盖配置文件中的参数- ansible_ssh_user: 相当于 ssh {{ ansible_ssh_user }}@1.1.1.1
- ansible_ssh_port: 远程主机的 SSH 端口
- ansible_ssh_host: 连接远程主机时所用的实际地址,相当于 ssh {{ ansible_ssh_host }}
- ansible_connection: 连接类型 SSH/paramiko/local 3种选择,默认为SSH
- ansible_ssh_private_key_file: 指定远程认证的私钥,默认为 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- ansible_shell_type: shell类型 csh/zsh/ksh/bash
- ansible_python_interpreter: python解释器,默认为 /usr/bin/python
Working with modules
command modules
- command
- name: Backup a file
command: cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /data/httpd.conf
- raw
在没有安装python的环境远程执行任务时使用,可用于路由器/交换机
- name: Install vim
raw: yum -y install vim-common
sudo: yes
- script
- name: run a script
script: test.sh
# cat playbooks/test.sh
ls /etc/ | grep '^d' | wc -l
- shell
- name: List files in /tmp and redirect to a file
shell: /bin/ls -l /tmp > /tmp/list
File modules
- file
- name: Ensure httpd conf has right permissions and owner/group
file: path=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf owner=root group=root mode=0644
- name: Create a symlink in /tmp for httpd.conf
file: src=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf dest=/tmp/httpd.conf owner=root group=root state=link
- template
template 模块用于生成 jinja2 模板文件, 创建 jinja2 模板:
# cat playbooks/test.jinja2
The os_family is {{ ansible_os_family }}
- name: Create a test template
template: src=test dest=/tmp/testfile mode=644
# cat /tmp/testfile
The os_family is RedHat
jinja2学习文档
- copy
- name: Copy file remotely
copy: src=test2.conf dest=/etc/test2.conf owner=root group=root mode=0644