算法与来源:
快速排序、广度优先搜索、狄克斯特拉算法、贪婪算法、动态规划、其它说明
来源:https://book.douban.com/subject/26979890/
快速排序
分而治之的思想
找到简单的基线条件(递归退出条件)
确定缩小问题规模的方法,最终符合基线条件
例如对多个数进行求和时,考虑两个数的求和方案,进而归纳三个数的求和时候,转化为一个数与另两个数(一个整体)的求和。最终确定多个数求和时候的方案。
再或者完成土地的方块划分问题:https://www.cnblogs.com/lshedward/p/10436874.html
快速排序的思路
分而治之的方法,首先考虑最小问题规模:1个数(排序完成,不需要排序)
2个数时:
首先寻找基准数,如第一个数字。然后以这个基准数字比较,确定另外一个数字的位置在基准左边还是右边。
3个数时:
首先寻找基准数,如第一个数字。然后以这个基准数字比较,确定另外两个数字的位置在基准左边还是右边。若剩下两个数字都在基准的左边(或右边),转化为2个数时的问题;若左右都为一个数,转化为1个数问题。
n个数时:
首先寻找基准数,如第一个数字。然后以这个基准数字比较,确定另外n-1个数字的位置在基准左边还是右边。然后递归缩小问题的规模。
代码
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) < 2:
return arr
else:
pivot = arr[0]
left=[i for i in arr[1:] if ipivot]
return quick_sort(left) + [mid] + quick_sort(right)
快速排序的复杂度与比较
参阅如:https://blog.csdn.net/iechenyb/article/details/81941022中表。
复杂度计算方法:
当n个元素排序时时候快速排序,则排序过程中,认为使用的排序层数为log(n),每层需要的时间为n,总体时间复杂度nlog(n)
当快速排序的基准数不恰当时候,取得时间复杂度n*n
广度优先搜索
广度优先搜索解决的问题类似于图结点中的最短路径条数问题或能转化为此类的问题。
问题提出
查找你人脉中的特定职业岗位的是否存在,并最短的问题。
参阅:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a537ffb9b1eb
如图:找到THOM
需要的数据结构
队列:用于判断数据的位次,按照顺序遍历数据
散列表:查询、插入速度快,能完成键值映射,以完成图中的关系显示。
问题思路
1:一度关系加入队列,通过自己认识的人获取他们的职业,对他们的职业进行判断,完成一度关系搜索。
2:不是需要查找的人,则将二度关系插入到队列,便于随后搜索。
3:以此类推。
代码
https://github.com/egonSchiele/grokking_algorithms/blob/master/06_breadth-first_search/python/01_breadth-first_search.py
因为是按照一度、二度关系依次检索,则检索过程中出现结果自然是最短路径。
代码首先构建了图表关系,通过while然后循环查找与添加数据到队列。
from collections import deque
def person_is_seller(name):
return name[-1] == 'm'
graph = {}
graph["you"] = ["alice", "bob", "claire"]
graph["bob"] = ["anuj", "peggy"]
graph["alice"] = ["peggy"]
graph["claire"] = ["thom", "jonny"]
graph["anuj"] = []
graph["peggy"] = []
graph["thom"] = []
graph["jonny"] = []
def search(name):
search_queue = deque()
search_queue += graph[name]
# This array is how you keep track of which people you've searched before.
searched = []
while search_queue:
person = search_queue.popleft()
# Only search this person if you haven't already searched them.
if person not in searched:
if person_is_seller(person):
print(person + " is a mango seller!")
return True
else:
search_queue += graph[person]
# Marks this person as searched
searched.append(person)
return False
search("you")
狄克斯特拉算法
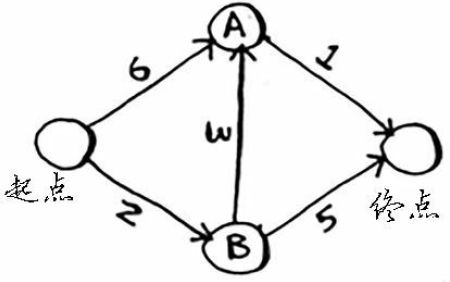
狄克斯特拉算法解决在加权图中前往目的地的最优路径(单向非负权)
问题提出
获取从起点到终点的最优路径
解决思路
1:从起点判断到A、B的权值(更新后到A点6,到B点2)
2:以最小的权值B点判断到A、终点的权值,并比较原先到A、终点的值,更小则做出更新(更新后到A点为5,到终点为7)
3:以A点出发,得到到终点的权值(5+1),比较原来到终点的权值(7),并更新,得到最优路径和权值为6。
数据结构
通过散列嵌套散列,完成图表的graph建设:
graph = {}
graph["start"] = {}
graph["start"]["a"] = 6
graph["start"]["b"] = 2
graph["a"] = {}
graph["a"]["fin"] = 1
graph["b"] = {}
graph["b"]["a"] = 3
graph["b"]["fin"] = 5
graph["fin"] = {}
最优权值表示,初始化costs并添值:
# the costs table
infinity = float("inf")
costs = {}
costs["a"] = 6
costs["b"] = 2
costs["fin"] = infinity
初始化parents表,用于建立图最优路径记录
parents = {}
parents["a"] = "start"
parents["b"] = "start"
parents["fin"] = None
代码
https://github.com/egonSchiele/grokking_algorithms/blob/master/07_dijkstras_algorithm/python/01_dijkstras_algorithm.py
processed表示已经处理的节点,将不再处理
find_lowest_cost_node函数遍历找到此结点下对应的结点中最小的路径权值结点
processed = []
def find_lowest_cost_node(costs):
lowest_cost = float("inf")
lowest_cost_node = None
for node in costs:
cost = costs[node]
if cost < lowest_cost and node not in processed:
lowest_cost = cost
lowest_cost_node = node
return lowest_cost_node
node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs)
# If you've processed all the nodes, this while loop is done.
while node is not None:
cost = costs[node]
# Go through all the neighbors of this node.
neighbors = graph[node]
for n in neighbors.keys():
new_cost = cost + neighbors[n]
# If it's cheaper to get to this neighbor by going through this node...
if costs[n] > new_cost:
costs[n] = new_cost
# This node becomes the new parent for this neighbor.
parents[n] = node
# Mark the node as processed.
processed.append(node)
# Find the next node to process, and loop.
node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs)
print("Cost from the start to each node:")
print(costs)
贪婪算法
贪婪算法通过局部最优解企图获得全局最优解,面临NP完全问题,速度快,获得近似最优解。
问题提出
旅行商问题
https://www.jianshu.com/p/478f6b1fe60f
思路
针对复杂很慢才能全局最优解的问题,采用每次找局部最可能,直到结束。
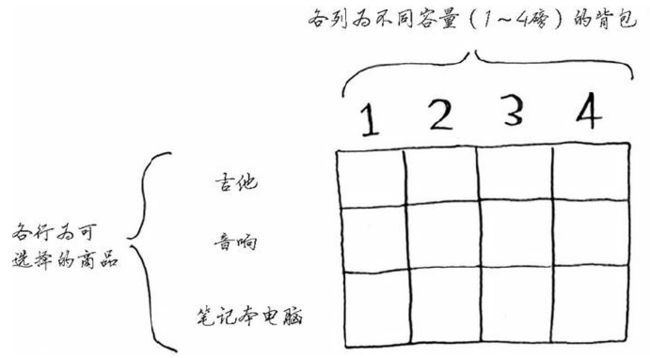
背包问题:当数个价值不同的大小不同的商品放入一定容量的背包,直接考虑其价值而不考虑大小,按步填充。获取可能的最大价值。
等,都是贪婪算法。
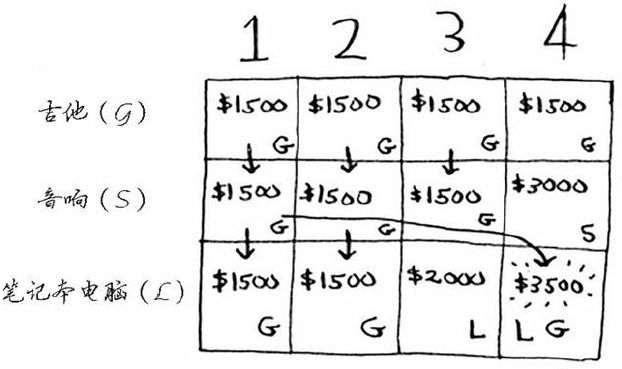
动态规划
使用网格来进行的算法解决问题,首先计算缩小的问题规模,进而确定最终问题规模。
问题提出
总4磅的容量装入更高价值的物品
思路
绘制表格,找到最小的单元容量,然后一步步确定在不同容量下的最大价值,最终获得总价值。
参阅:算法图解书
其它
狄克斯特拉算法不能计算包含负边权的图,如果需要计算则需要贝尔曼--福德算法。
KNN算法的K一般取sqrt(N),N为总数量
MapReduce作为一个分布式算法,在数据映射和归并有良好效果。
布隆过滤器和HyperLogLog用于海量数据检索过程中,使用概率型方法,得到极可能正确的检索结果。