最近项目开发中,我负责给数据库加索引。Mysql提供了丰富的索引类型,主要是B树索引(前缀索引、复合索引),Hash索引,空间数据索引(R-Tree),全文索引。各种索引的应用条件考虑的因素会很多,所以提供一种方式验证sql语句执行效率对于索引选择决策就至关重要。
show profile VS performance schema
Mysql 提供了两种方式,一种是show profile syntax,一种是Performance schema。前者在5.7版本中已经摒弃,并且没办法获取其他线程的执行时间。
NOTE: These statements are deprecated as of MySQL 5.6.7 and will be removed in a future MySQL release. Use the Performance Schema instead; see Section 22.17.1, “Query Profiling Using Performance Schema” .
实际上前者能做的,后者都能做,并且后者还可以获取到每一个sql语句执行阶段(stage)消耗的时间。接下来就介绍performance schema的使用
开启Docker
在Docker 官网下载安装即可
docker ps
运行Mysql数据库
从官网拉去github镜像 & 运行
docker pull mysql:latest
本地运行两个数据库,用于对比有索引和没索引的执行时间消耗
docker run -d -p 13306:3306 --name mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=**password** mysql
docker run -d -p 13306:3306 --name mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=**password** mysql
导入测试数据
因为有足够的权限,我是从线上的数据库导出了一份完整的数据,然后导入到本地的,如果你没有线上环境的数据,可以使用Mysql官方提供的测试数据,放在了 Github上。
导出数据
mysql -u sunkuo -p -B databaseName > ~/Desktop/db.sql
导入数据
mysql -u root -h 127.0.0.1 -P 13306 -p < ~/Desktop/db.sql
mysql -u root -h 127.0.0.1 -P 13307 -p < ~/Desktop/db.sql
注意,如果线上的数据库已经有索引了,那么请修复db.sql,将里面建表的语句去掉索引部分。
Performance schema table
简单介绍下performanche_schema 数据库和里面相关的表。Performanc_schema数据库是Mysql提供的用来在较低层面监控服务器执行的特性,它有这样几个特征。
- 底层监控服务器执行能力,使用Performance_schema存储引擎和Performance_schema数据库,聚焦于性能数据。
The Performance Schema provides a way to inspect internal execution of the server at runtime. It is implemented using the PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA storage engine and the performance_schema database. The Performance Schema focuses primarily on performance data.
- 监控服务器事件,“事件”是任何花时间并且被检测的事情。
The Performance Schema monitors server events. An “event” is anything the server does that takes time and has been instrumented so that timing information can be collected.
- 此事件不同于日志事件和循环事件。
Performance Schema events are distinct from events written to the server's binary log (which describe data modifications) and Event Scheduler events (which are a type of stored program).
- 针对特定Mysql实例。
Performance Schema events are specific to a given instance of the MySQL Server. Performance Schema tables are considered local to the server, and changes to them are not replicated or written to the binary log.
- 可以监控当前时间、历史事件、和汇总。
Current events are available, as well as event histories and summaries. This enables you to determine how many times instrumented activities were performed and how much time they took.
- 监控配置可以通过修改Performance_data数据库里面的表进行,立即生效。
Performance Schema configuration can be modified dynamically by updating tables in the performance_schema database through SQL statements. Configuration changes affect data collection immediately.
- 数据存在内存中,不占据硬盘。
Tables in the Performance Schema are in-memory tables that use no persistent on-disk storage. The contents are repopulated beginning at server startup and discarded at server shutdown
Performance_schema数据库中主要有这样几类数据表。
- Setup tables; 存储配置选项。
- Current events tables; 包含每个线程最近的事件。
- History tables; 和Current events tables表结构一样,但是每个线程的行更多。
- Summary tables; 包含聚合信息。
- Instance tables; Document what types of objects are instrumented.
- Miscellaneous tables; These do not fall into any of the other table groups.(我也没看懂这个表是干什么用的)
获取sql执行时间
开启Performance_schema选项
show variables like 'performance_schema'
一般情况下,Performance_shema都是默认开启的,如果你想关闭它,需要在配置文件里添加如下语句
performance_schema=off
然后重启Mysql实例
配置需要监控的表
Mysql Performance_schema里面的监控也是基于生产、消费者模式。代码里面的事件产生事件和记录消耗事件,Performance_schema里面的数据表记录这些事件(消费这些事件),所以我们要确保两件事情
- 生产sql执行时间的生产者需要打开(通过配置setup_instruments表)
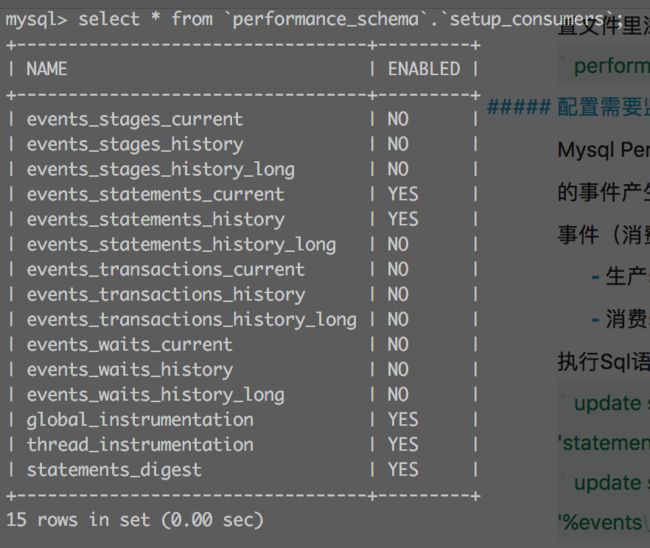
- 消费sql执行时间的消费者需要打开(通过配置setup_consumers表)
执行Sql语句来做到这两件事情
update setup_instruments set ENABLED='YES', TIMED='YES' where name like 'statement%'
update setup\_consumers set ENABLED='YES' where name like '%events\_statements\_%’;
可以通过下面的语句确认下
select * from setup_instruments where name like 'statement%'
select * from setup_consumers
执行语句
查看执行时间
在这里,我们通过events_statements_history 查看执行时间。该表显示当前线程最近的N条记录执行时间。
select event_id, TRUNCATE(TIMER_WAIT/1000000000000,6), sql_text from events\_statements\_history order by event_id asc limit 1;
可以看到
从而我们知道刚才的sql语句执行时间是0.0136秒
获取sql执行阶段消耗时间
开启Performance_schema选项
在上一步我们已经开启了Performance_schema,此处不再复述。
配置需要监控的表
- 生产sql执行时间的生产者需要打开(通过配置setup_instruments表)
update setup_instruments set ENABLED='YES', TIMED='YES' where name like 'stage%' - 消费sql执行时间的消费者需要打开(通过配置setup_consumers表)
update setup_consumers set ENABLED='YES' where name like '%events_stages_%'
执行语句
获取EventId
select event_id, TRUNCATE(TIMER_WAIT/1000000000000,6), sql_text from events_statements_history order by event_id asc limit 1;
在输出结果中,记录event_id,下一步查询会用到
查看执行阶段消耗时间
SELECT event_name AS Stage, TRUNCATE(TIMER_WAIT/1000000000000,6) AS Duration FROM performance_schema.events_stages_history WHERE NESTING_EVENT_ID=eventId;
总结
本文对Performance_schema做了一个简单的介绍,帮助大家更好的衡量mysql 索引效率,而不是凭空想象。