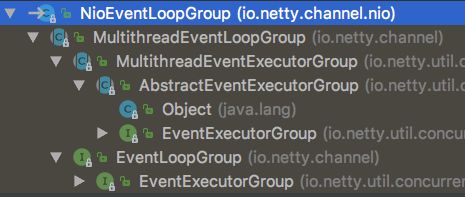
本文以常见的NioEventLoopGroup为切入点分析Netty的EventLoopGroup,NioEventLoopGroup的类层次结构如下图所示,下面将按照类层次结构自底向上依次分析。
EventExecutorGroup接口
EventExecutorGroup接口继承了Java并发包的ScheduledExecutorService接口,覆盖了原接口的方法,主要区别在于返回值换成了Netty自身的Future实现,另外新添加了几个方法。
public interface EventExecutorGroup extends ScheduledExecutorService, Iterable {
boolean isShuttingDown();
Future shutdownGracefully();
Future shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
Future terminationFuture();
@Override
@Deprecated
void shutdown();
@Override
@Deprecated
List shutdownNow();
/**
* Returns one of the {@link EventExecutor}s managed by this {@link EventExecutorGroup}.
*/
EventExecutor next();
@Override
Iterator iterator();
@Override
Future submit(Runnable task);
@Override
Future submit(Runnable task, T result);
@Override
Future submit(Callable task);
@Override
ScheduledFuture schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
@Override
ScheduledFuture schedule(Callable callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
@Override
ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit);
@Override
ScheduledFuture scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
}
AbstractEventExecutorGroup类
查看AbstractEventExecutorGroup类,可以发现该类提供EventExecutorGroup接口的默认实现,都是委托给next方法,该方法定义在EventExecutorGroup接口中,用于取得EventExecutorGroup管理的一个EventExecutor。
public abstract class AbstractEventExecutorGroup implements EventExecutorGroup {
@Override
public Future submit(Runnable task) {
return next().submit(task);
}
@Override
public Future submit(Runnable task, T result) {
return next().submit(task, result);
}
@Override
public Future submit(Callable task) {
return next().submit(task);
}
// 省略一些代码
}
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup类
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup类的部分代码如下,构造函数中有一些值得注意的地方:
- 该EventExecutorGroup会有nThreads个EventExecutor;
- EventExecutorChooserFactory接口是用来选取下一个EventExecutor的,next方法中有体现;
- Executor参数是给newChild方法创建EventExecutor用的,若没有提供Executor,则会使用默认的ThreadPerTaskExecutor;
- children = new EventExecutor[nThreads]; 这句代码构造了数组去引用本EventExecutorGroup所管理的EventExecutor;
- for循环中的children[i] = newChild(executor, args); 利用抽象方法newChild初始化了数组的每个EventExecutor。在后文会看到newChild方法的用处是给各个子类如NioEventLoopGroup、EpollEventLoopGroup和KQueueEventLoopGroup等创建自己特色的EventLoop。
public abstract class MultithreadEventExecutorGroup extends AbstractEventExecutorGroup {
private final EventExecutor[] children;
private final Set readonlyChildren;
private final AtomicInteger terminatedChildren = new AtomicInteger();
private final Promise terminationFuture = new DefaultPromise(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
private final EventExecutorChooserFactory.EventExecutorChooser chooser;
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory, Object... args) {
this(nThreads, threadFactory == null ? null : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(threadFactory), args);
}
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
this(nThreads, executor, DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory.INSTANCE, args);
}
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,
EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {
if (nThreads <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));
}
if (executor == null) {
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
}
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
if (!success) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
// Let the caller handle the interruption.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
// 省略一些代码
}
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
return chooser.next();
}
/**
* Create a new EventExecutor which will later then accessible via the {@link #next()} method. This method will be
* called for each thread that will serve this {@link MultithreadEventExecutorGroup}.
*
*/
protected abstract EventExecutor newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception;
// 省略一些代码
}
MultithreadEventLoopGroup类
MultithreadEventLoopGroup类继承了MultithreadEventExecutorGroup类同时实现了EventLoopGroup接口,这个接口继承了EventExecutorGroup接口,允许通道注册和后续处理。
- DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS用于表示默认EventLoop线程数,若配置了io.netty.eventLoopThreads属性,则取该值,否则取默认值为可用处理器数的2倍;
- 构造函数均是在内部仅调用了父类对应的构造函数。
public abstract class MultithreadEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventExecutorGroup implements EventLoopGroup {
private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS;
static {
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt(
"io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: {}", DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS);
}
}
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);
}
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory, Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, threadFactory, args);
}
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory,
Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, chooserFactory, args);
}
@Override
public EventLoop next() {
return (EventLoop) super.next();
}
@Override
protected abstract EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception;
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return next().register(channel);
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(ChannelPromise promise) {
return next().register(promise);
}
// 省略一些代码
}
NioEventLoopGroup类
NioEventLoopGroup类的构造函数依然如其父类一样清晰易懂,在此不再赘述。比较重要的是实现了抽象方法newChild,用于新建NioEventLoop实例:
- executor可以在构造函数中传入,或者使用MultithreadEventExecutorGroup类默认创建的ThreadPerTaskExecutor;
- 可变参数args依次是SelectorProvider、SelectStrategyFactory和RejectedExecutionHandler,默认值分别为SelectorProvider.provider(),、DefaultSelectStrategyFactory.INSTANCE和RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject(),这些顺着NioEventLoopGroup类的构造函数找到父类MultithreadEventExecutorGroup的构造函数即可理解,在此不再赘述。
public class NioEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventLoopGroup {
// 省略构造函数代码
public void setIoRatio(int ioRatio) {
for (EventExecutor e: this) {
((NioEventLoop) e).setIoRatio(ioRatio);
}
}
public void rebuildSelectors() {
for (EventExecutor e: this) {
((NioEventLoop) e).rebuildSelector();
}
}
@Override
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0],
((SelectStrategyFactory) args[1]).newSelectStrategy(), (RejectedExecutionHandler) args[2]);
}
}
从MultithreadEventExecutorGroup构造函数和newChild方法不难理解《Netty实战》3.1.2所述:
一个EventLoopGroup包含一个或者多个EventLoop;
以前的文章中提到过AbstractBootstrap类的initAndRegister方法,该方法中的config().group().register(channel) 这一句便是将新建的通道注册到EventLoop上。NioEventLoopGroup的register方法在MultithreadEventLoopGroup类中定义,如上节代码所示先调用next方法得到下一个EventLoop(即NioEventLoop),然后将通道注册到该NioEventLoop上。